Question: Options in order: will, might is obligated, would like equal, exceed, be less than at a premium, at a discount, at par chart: Variable Name:
Options in order:
will, might
is obligated, would like
equal, exceed, be less than
at a premium, at a discount, at par
chart: Variable Name: Bond's Annual Coupon Payment, Bond's Market Price, Bond's Semiannual Coupon Payment
Variable Value: $45.00, $72.00, $144.00, $180.00
reasonable, unreasonable
$1,055, $844, $1,266, $739
equal to, greater than, less than
a premium, par, a discount

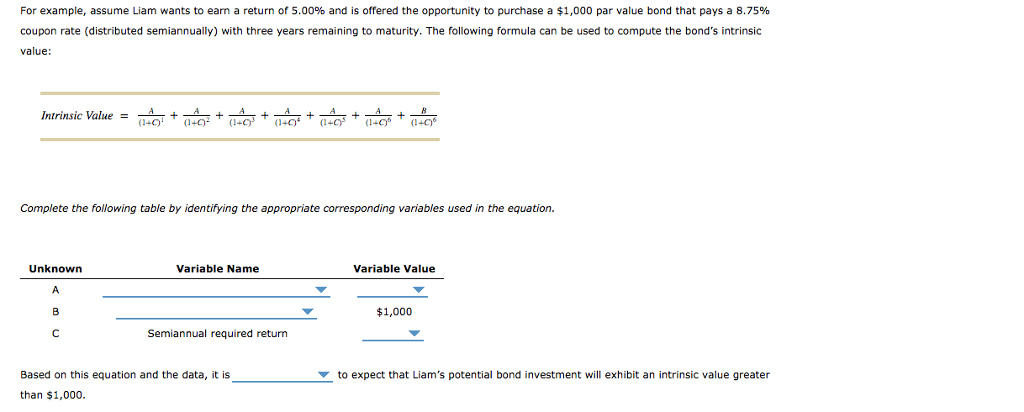

8. Bond valuation The process of bond valuation is based on the fundamental concept that the current price of a security can be determined by calculating the present value of the cash flows that the security will generate in the future. There is a consistent and predictable relationship between a bond's coupon rate, its par value, a bondholder's required return, and the bond's resulting intrinsic value. Trading at a discount, trading at a premium, and trading at par refer to particular relationships between a bond's intrinsic value and its par value. These result from the relationship between a bond's coupon rate and a bondholder's required rate of return. Remember, a bond's coupon rate partially determines the interest-based return that a bond pay, and a bondholder's required return reflects the return that a bondholder to receive from a given investment The mathematics of bond valuation imply a predictable relationship between the bond's coupon rate, the bondholder's required return, the bond's par value, and its intrinsic value. Tese elationships can be summarized as follows: When the bond's coupon rate is equal to the bondholder's required return, the bond's intrinsic value will equal its par value, and the bond will trade at par. When the bond's coupon rate is greater to the bondholder's required return, the bond's intrinsic value will bond will trade at a premium. When the bond's coupon rate is less than the bondholder's required return, the bond's intrinsic value will be less than its par value, and the bond its par value, and the
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


