Question: our product was exo please help solve question Diels-Alder Cycloaddition . furan maleic anhydride ende product Go product 149 Post-lab questions: 1. Determine the percent





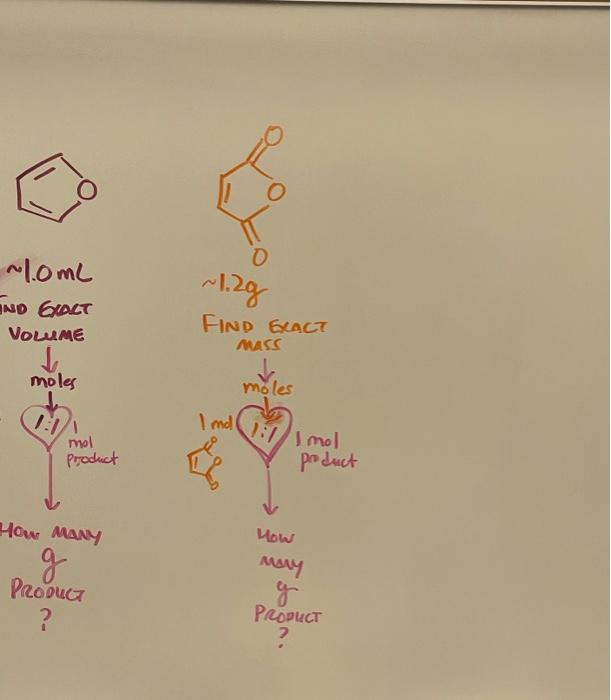
Diels-Alder Cycloaddition . furan maleic anhydride ende product Go product 149 Post-lab questions: 1. Determine the percent yield of your reaction. Here we will be applying the stoichiometry calculation material that you learned in CHEM 111. Follow the steps below to reach your answer. a. What is theoretical yield"? In stoichiometric calculations, what does it represent? The quantity of a product obtained hom the campaese conversion of me limining racrant in a numral puction b. List the steps that you need to follow to calculate the theoretical yield for the Diels-Alder reaction carried in this experiment Baiante me chimical Wacho - idnriny mi limning muagint Fina mous of nmining raqah - Appy me trueerid yield romula gylela - actwa wield 7100 - mucrericol utca c. Calculate the theoretical yield in grams for your Diels-Alder product Write out all your calculations. Density of furan is 0.936g/mL. maleis annyande = 1,2198 din product weight wax lub . Om = 2.029 . What was the actual yield of the Diels-Alder product produced in your reaction? (Look at the measurements from Week 2. Step 2d.) e. Calculate the percent yield. actual yield %yield = theoretical yield x 100 dol-009 2. Explain your percent yield results. What sources of error affected your results ? 3. Determine if your product is endo or exo using the data collected. Describe the experimental evidence (data) that led you to this conclusion. Draw the structure of the product. 4. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a Diels-Alder reaction showing both endo and exo products. There will be two curves. Draw one curve for the endo and another curve for the exo product. a) Identify the curve for the kinetically-controlled product and the curve for the thermodynamically-controlled product. b) Which product is usually favored in Diels-Alder reactions? Explain your answer c) If you increased the temperature of the reaction, how would you expect the ratio of endo to exo product to change? If so, would there be more exo or endo? Give your reasoning. 5. Proposed an explanation for your results. 6. What are some applications of the Diels-Alder reaction? What is it used for? Diels-Alder Cycloaddition In this experiment furan and maleic anhydride react to form a bicyclic Diels-Alder adduct. The bicyclic product can have and endo or exo stereochemistry. In Diels-Alder reactions the endo product forms faster - it has a lower energy transition state due to favorable pl orbital overlap. If the endo product forms the reaction is said to be under kinetic control Exo products are generally more stable than endo products because they are less sterically hindered if the exo product forms the reaction is said to be under thermodynamic control . furan maleic anhydride endo product exo product Figure 1: Die Aider reaction studied in this experiment After forming and purifying the Diels-Alder product, you will take the melting point and determine if the kinetic or the thermodynamic product was formed. The melting point of the endo product is 81C and the melting point of the exo product is 114C. Chemicals: furan, maleic anhydride, diethyl ether, hexanes, acetone Experimental Procedure A. Week 1: Reaction Set-up 1. Weigh 1.20g of maleic anhydride and transfer them to a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask 2. Add 10.00 mL of ether to the same 50ml Erlenmeyer flask. 3. Heat the mixture in a warm (not boiling water bath until all the anhydride has dissolved under a fure hood. Stir with a glass stirring rod if needed. Add more ether to replace any that evaporates. (Caution: Ether has a low boiling point and a tendency to quickly boil over when heated to excess. As soon as bubbles form, remove the flask from the water bath) 4. When the solution has cooled to room temperature, add 1.00 mL of furan to the 50ml Erlenmeyer flask 5. Stopper the flask and cover the seal with paraffilm to prevent evaporation. (Caution- Ether has a low boiling point - stoppering a warm flask will generate pressure and could lead to an explosion) e. Take out the sample and the thermometer. Turn off the melting apparatus and allow it to cool down. Ideally you want it to cool up to 15 degrees below your melting point 1. Retake the melting point measurement at a slower rate, inserting a second sample AA 0 ~1.0mL AND EXACT wling VOLME FIND GLACT MASS moles moles 1:11 Imd 111 mol mol Product poduct How many g Product ? How may g Product
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


