Question: Overdispersion definition In some cases, a count random variable can have a higher variance than the predicted by the binomial or the Poisson distribution. For
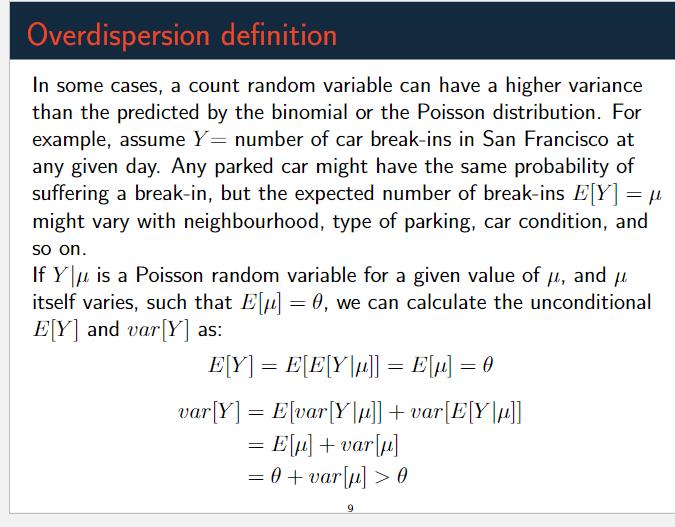
Overdispersion definition In some cases, a count random variable can have a higher variance than the predicted by the binomial or the Poisson distribution. For example, assume Y = number of car break-ins in San Francisco at any given day. Any parked car might have the same probability of suffering a break-in, but the expected number of break-ins E[Y ] = / might vary with neighbourhood, type of parking, car condition, and so on. If YA is a Poisson random variable for a given value of /, and itself varies, such that E = 0, we can calculate the unconditional E[Y] and var [Y ] as: E[Y] = E[ELY|/]] = El] = 0 var [Y] = E[var[Yla]] + var [E[Ylx]] = Elp] + varlu] = 0 + var > 0 9
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


