Question: P 2 . This problem explores the structural analysis of a truss. In the design of highway bridge structures and crane structures, engineers are often
P This problem explores the structural analysis of a truss. In the design of highway bridge structures and crane
structures, engineers are often required to compute the member forces and support reactions in planar truss structures.
The analysis of cantilever truss structures is governed by the following principles:
At each joint, the sum of internal and external forces in the horizontal and vertical directions must equal zero.
The sum of external forces and support reactions in the horizontal and vertical directions must equal zero.
For the entire structure and all possible substructures, the sum of moments must equal zero.
The truss elements can only carry axial forces, with tensile axial forces being positive and compressive axial
forces being negative.
All the joints are pinned the joints cannot transfer moments; only axial forces from the truss elements
The truss is statically determinate axial forces can be computed without knowledge of material properties
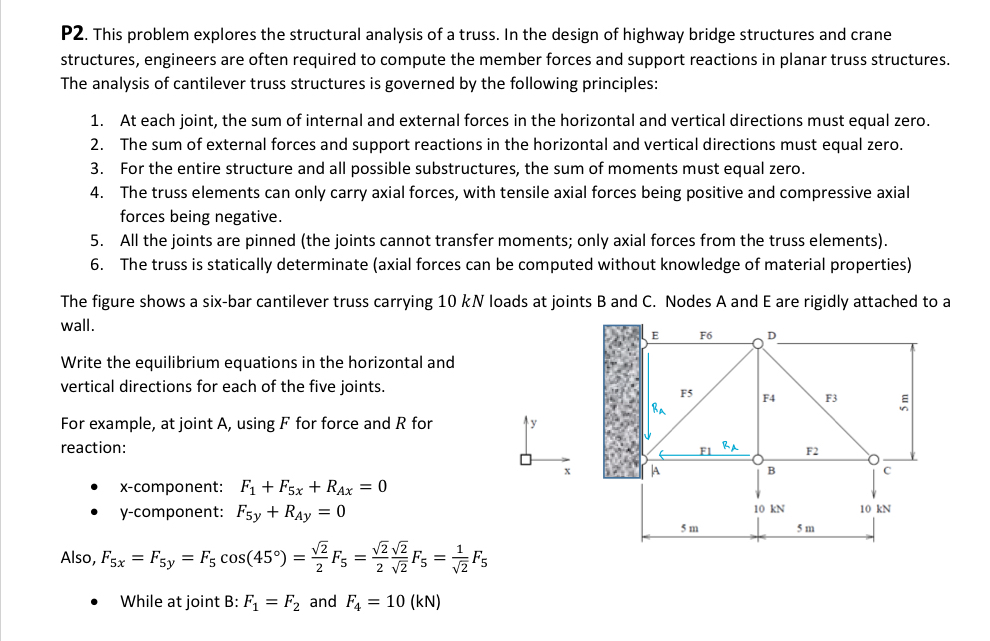
The figure shows a sixbar cantilever truss carrying kN loads at joints B and C Nodes A and E are rigidly attached to a
wall.
Write the equilibrium equations in the horizontal and
vertical directions for each of the five joints.
For example, at joint using for force and for
reaction:
xcomponent:
ycomponent:
Also,
While at joint B: and
P This problem explores the structural analysis of a truss. In the design of highway bridge structures and crane
structures, engineers are often required to compute the member forces and support reactions in planar truss structures.
The analysis of cantilever truss structures is governed by the following principles:
At each joint, the sum of internal and external forces in the horizontal and vertical directions must equal zero.
The sum of external forces and support reactions in the horizontal and vertical directions must equal zero.
For the entire structure and all possible substructures, the sum of moments must equal zero.
The truss elements can only carry axial forces, with tensile axial forces being positive and compressive axial
forces being negative.
All the joints are pinned the joints cannot transfer moments; only axial forces from the truss elements
The truss is statically determinate axial forces can be computed without knowledge of material properties
The figure shows a sixbar cantilever truss carrying kN loads at joints B and C Nodes A and E are rigidly attached to a
wall.
Write the equilibrium equations in the horizontal and
vertical directions for each of the five joints.
For example, at joint using for force and for
reaction:
xcomponent:
ycomponent:
Also,
While at joint B: and
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


