Question: page 146 exercises 3 can you solve it on excel file please DryIce build its factories and how large should they be? 3. Sunchem, a
page 146 exercises 3
can you solve it on excel file please

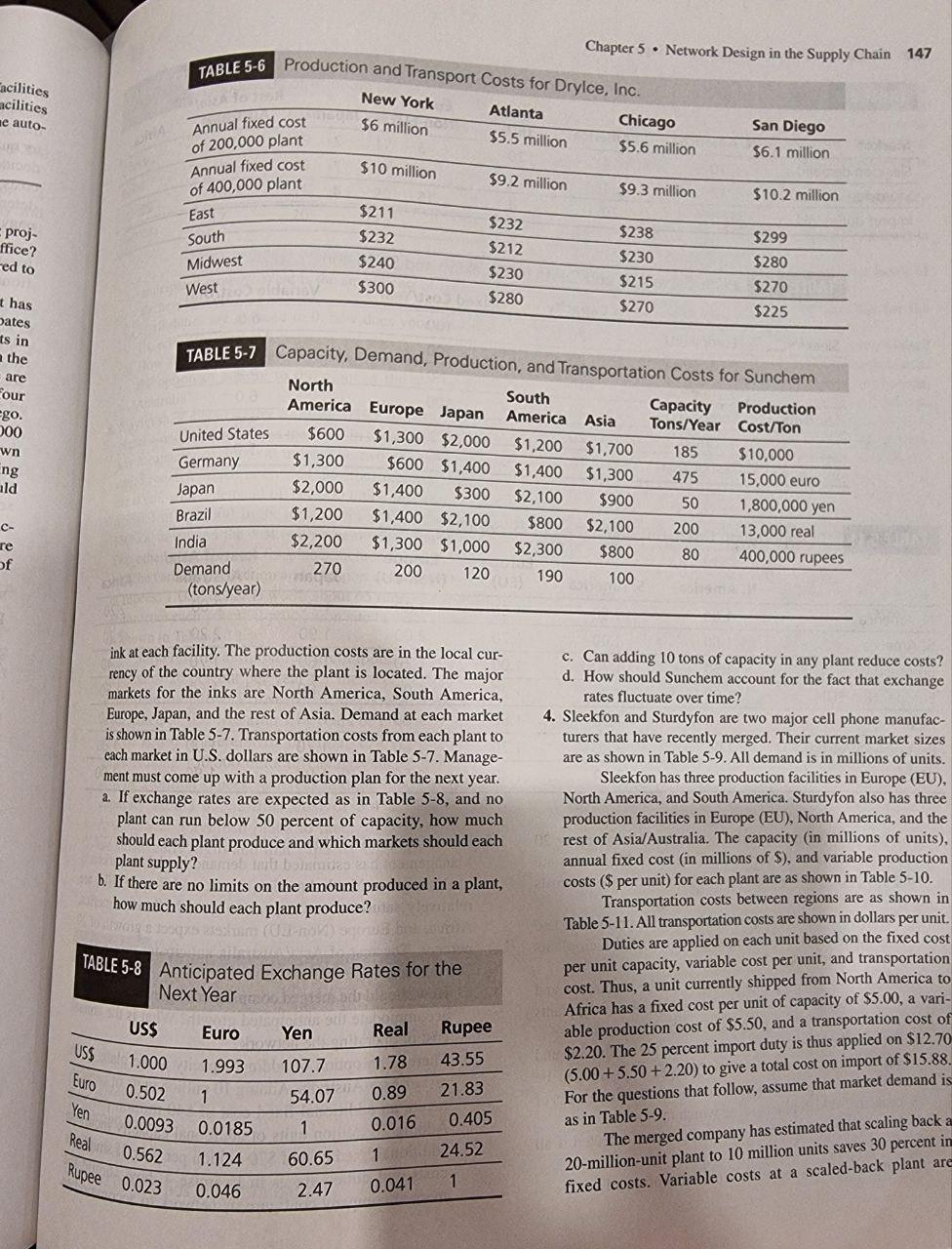
DryIce build its factories and how large should they be? 3. Sunchem, a manufacturer of printing inks, has five manufacturing plants worldwide. Their locations and capacities are shown in Table 5-7 along with the cost of producing 1 ton of Chapter 5 - Network Design in the Supply Chain 147 ink at each facility. The production costs are in the local cur- c. Can adding 10 tons of capacity in any plant reduce costs? rency of the country where the plant is located. The major d. How should Sunchem account for the fact that exchange markets for the inks are North America, South America, rates fluctuate over time? Europe, Japan, and the rest of Asia. Demand at each market is shown in Table 5-7. Transportation costs from each plant to 4. Sleekfon and Sturdyfon are two major cell phone manufacturers that have recently merged. Their current market sizes each market in U.S. dollars are shown in Table 5-7. Manage- are as shown in Table 5-9. All demand is in millions of units. ment must come up with a production plan for the next year. Sleekfon has three production facilities in Europe (EU), a. If exchange rates are expected as in Table 5-8, and no North America, and South America. Sturdyfon also has three plant can run below 50 percent of capacity, how much production facilities in Europe (EU), North America, and the should each plant produce and which markets should each rest of Asia/Australia. The capacity (in millions of units), plant supply? annual fixed cost (in millions of $ ), and variable production b. If there are no limits on the amount produced in a plant, costs (\$ per unit) for each plant are as shown in Table 5-10. how much should each plant produce? Transportation costs between regions are as shown in Table 5-11. All transportation costs are shown in dollars per unit. Duties are applied on each unit based on the fixed cost per unit capacity, variable cost per unit, and transportation cost. Thus, a unit currently shipped from North America to Africa has a fixed cost per unit of capacity of $5.00, a variable production cost of $5.50, and a transportation cost of $2.20. The 25 percent import duty is thus applied on $12.70 (5.00+5.50+2.20) to give a total cost on import of $15.88 For the questions that follow, assume that market demand is as in Table 5-9. The merged company has estimated that scaling back a 20-million-unit plant to 10 million units saves 30 percent in fixed costs. Variable costs at a scaled-back plant are






