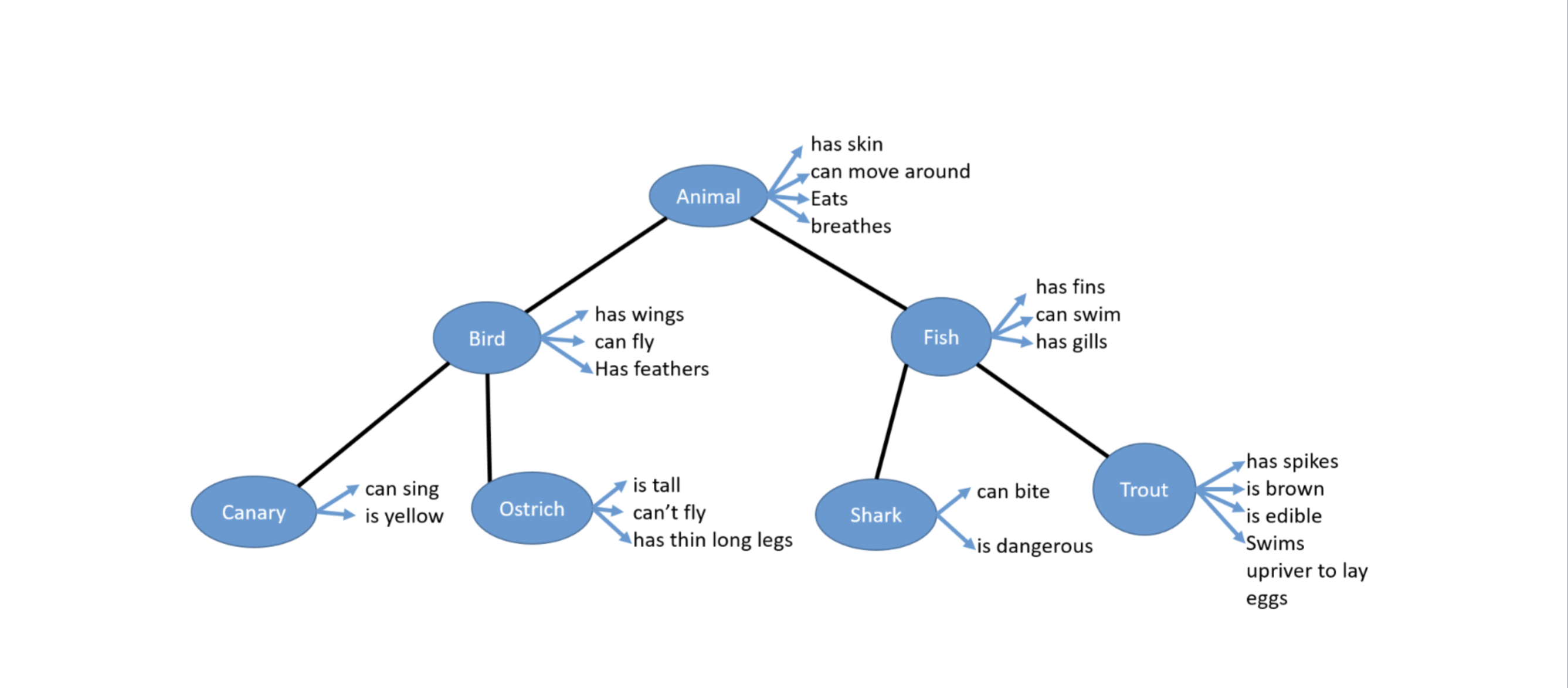
Question: Part 1 : Implement the full animal class hierarchy a ) You are required to complete a Java implementation of the full inheritance hierarchy above
Part : Implement the full animal class hierarchy
a You are required to complete a Java implementation of the full inheritance hierarchy
above making full use of what you know so far about inheritance. Each of the circles in
the figure above represents a class. As in the example code I provided, some of the
attributes of a class above are encoded in Java as fields and some as methods eg I
have chosen hasSkin to be a field and 'can move around' to be a method, move You
should make similar decisions with the remaining classes. Avoid unnecessary repetition
of fields and methods. Inheritance is about inheriting fields and methods from the
superclass and overriding them only when necessary. The example code provided
illustrates how fields and method are inherited from superclasses and you should try to
follow its example.
b For every leaf class Canary Ostrich, Shark, Trout I want you to implement an equals
and toString method that correctly overrides the method inherited from the superclass.
Every toString method returns a String value describing the state of the object. Each
of the toString methods that you implement should include values of fields inherited
from the object's superclass. The example code contains a partially completed toString
method for the Canary class. Remember to annotate all overriden methods with
@Overriden, as demonstrated in the example code
c For an Ostrich object, your code should implement the simplest way to get it to output
"I am a bird but cannot fly" when it is called upon to move.
Hint: This does not involve creating or overriding a new method. See lecture slides.
Part : Test the classes in your hierarchy
The second part of the assignment involves creating a class to demonstrate that the classes you
have defined in Part actually work. This is similar to the idea used in Assignment where a
class was used to test different transaction scenarios.
Create a class called AnimalTest with a main method and two test methods, which you will call
from the main method. The first test method will demonstrate the output of the toString
method. The second test method will demonstrate that your equals methods work as expected.
Choose a suitable name for each method.
a test method: this method will demonstrate that your toString method works
correctly. It should do this by populating an array with animal objects and then looping
over the elements of the array and printing out the output of the toString method of
each element. If you are unsure how to use an Array, consult the tutorial notes on Arrays
in the week folder.
First of all create an Array of Animal references with size
Animal animals new Animal; This declares and allocates memory for an array
of Animal references with spaces
In each element of the Array I want you to put a reference to an object of the four leaf
animals in your hierarchy Canary Ostrich, Shark, Trout There are spaces in the
array, one for each type of animal.
As demonstrated in the lecture and in the Arrays tutorial PDF each animal object
Canary Ostrich, Shark, Trout will be referenced by an element of the Animals array.
Eg
animals new CanaryBluey; Assigning a reference to a Canary object to the
first position in the array. Remember the first position in any array is always at index
Now add a reference for each animal object to the remaining spaces in the Array. When
finished you will have an array of four Animal references. Each reference points to an
object belonging to an Animal subclass eg Ostrich, Canary, Shark, Trout
Then, write a loop and iterate over the array calling System.println to print out the
contents of each element in the array see the arrays tutorial, if you have difficulties
Eg
System.out.printlnanimalsi; Where i is the value of the loop variable
If you have written your toString method correctly, the String value of the object at
each position in the array will be output
Note: Do not call toString directly as in this example:
System.out.printlnanimalsitoString;
When you try to print an object out, Java will automatically look for its toString
method. So marks will be lost if you directly call the toString method. This is never
done.
b test method: this method demonstrates that your equals methods work correctly. Use
an array, like the one used in test and demonstrate the output of the different elements.
Note: An array is not necessary to demonstrate that equals works or toString
however, I want you to get some practice in using Arrays.
I am leaving the specific implementation of this method for you to demonstrate.
Use comments to explain your code.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


