Question: Part 2: Holmes Manufacturing is considering a new machine that costs $270,000 and would reduce pretax manufacturing costs by $90,000 annually. The new machine will
Part 2:
Holmes Manufacturing is considering a new machine that costs $270,000 and would reduce pretax manufacturing costs by $90,000 annually. The new machine will be fully depreciated at the time of purchase. Management thinks the machine would have a value of $21,000 at the end of its 5-year operating life. Net operating working capital would increase by $26,000 initially, but it would be recovered at the end of the project's 5-year life. Holmes's marginal tax rate is 25%, and an 11% WACC is appropriate for the project.
- Calculate the project's NPV. Negative value, if any, should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ Calculate the project's IRR. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. % Calculate the project's MIRR. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. % Calculate the project's payback. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. years
- Assume management is unsure about the $90,000 cost savings-this figure could deviate by as much as plus or minus 20%. What would the NPV be under each of these situations? Negative values, if any, should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. 20% savings increase: $ 20% savings decrease: $
- Suppose the CFO wants you to do a scenario analysis with different values for the cost savings, the machine's salvage value, and the net operating working capital (NOWC) requirement. She asks you to use the following probabilities and values in the scenario analysis:
Calculate the project's expected NPV, its standard deviation, and its coefficient of variation. Negative values, if any, should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer for expected NPV and for standard deviation to the nearest cent and for coefficient of variation to two decimal places.Scenario Probability Cost Savings Salvage Value NOWC Worst case 0.35 $72,000 $16,000 $31,000 Base case 0.35 $90,000 $21,000 $26,000 Best case 0.30 $108,000 $26,000 $21,000 E(NPV): $ NPV: $ CV:
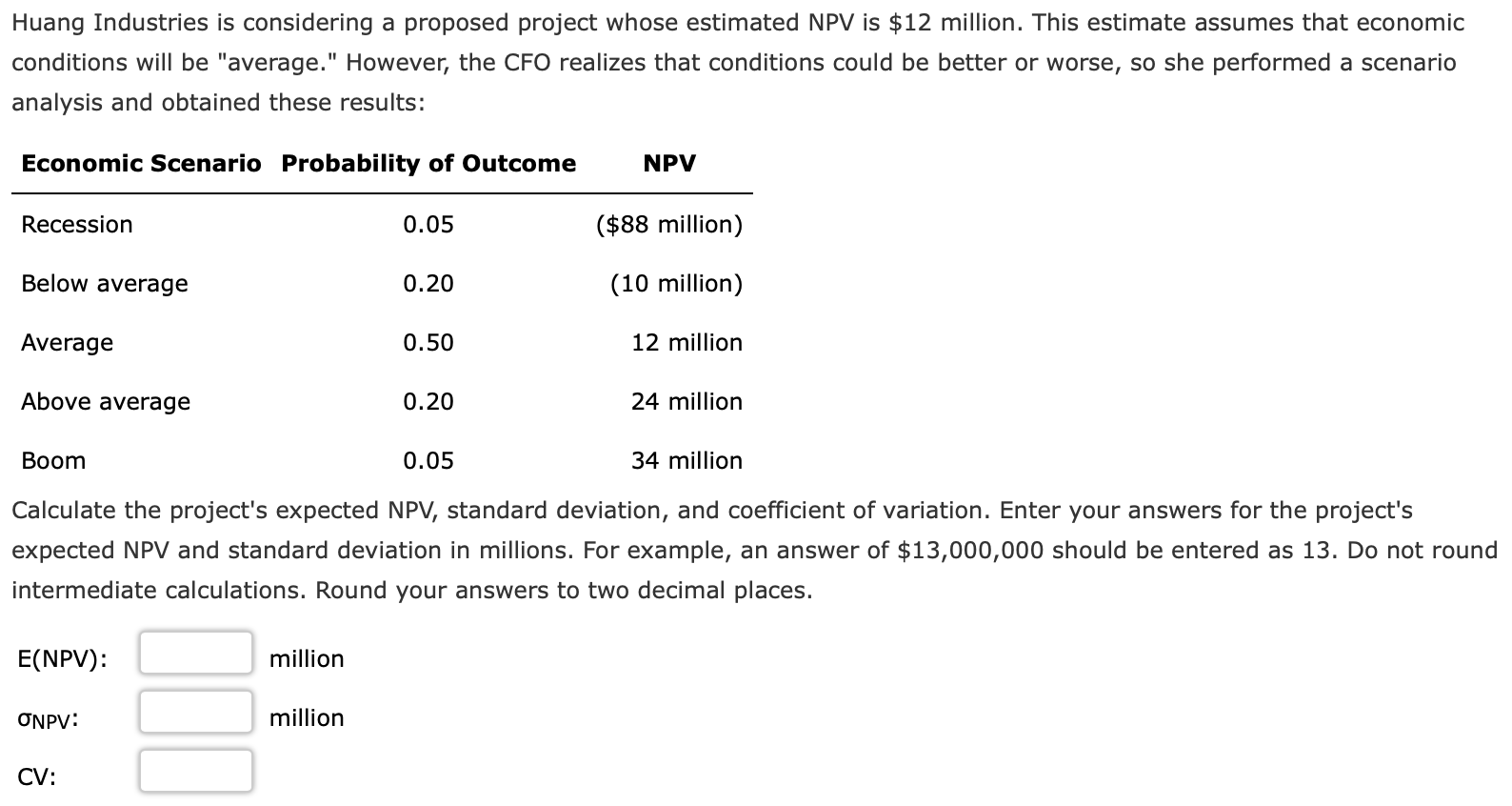
Huang Industries is considering a proposed project whose estimated NPV is $12 million. This estimate assumes that economic conditions will be "average." However, the CFO realizes that conditions could be better or worse, so she performed a scenario analysis and obtained these results: Economic Scenario Probability of Outcome NPV Recession 0.05 ($88 million) Below average 0.20 (10 million) Average 0.50 12 million Above average 0.20 24 million Boom 0.05 34 million Calculate the project's expected NPV, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation. Enter your answers for the project's expected NPV and standard deviation in millions. For example, an answer of $13,000,000 should be entered as 13. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. E(NPV): million ONPV: million CV
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


