Question: Part 2 Module Files is complete, but this information is needed to solve the last part! I need help with Python Scripts and how to
Part 2 Module Files is complete, but this information is needed to solve the last part! I need help with "Python Scripts" and how to import a .py file. 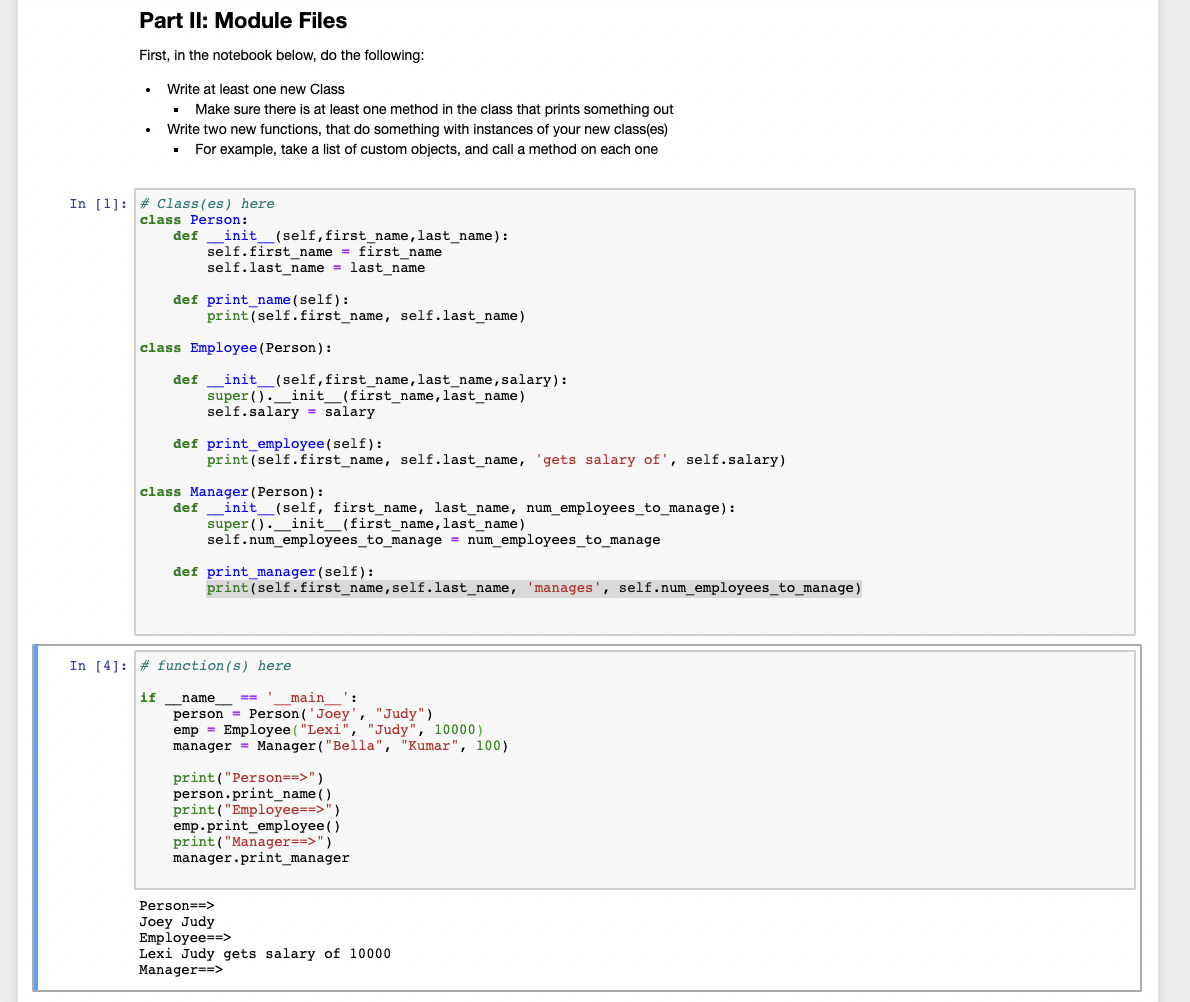
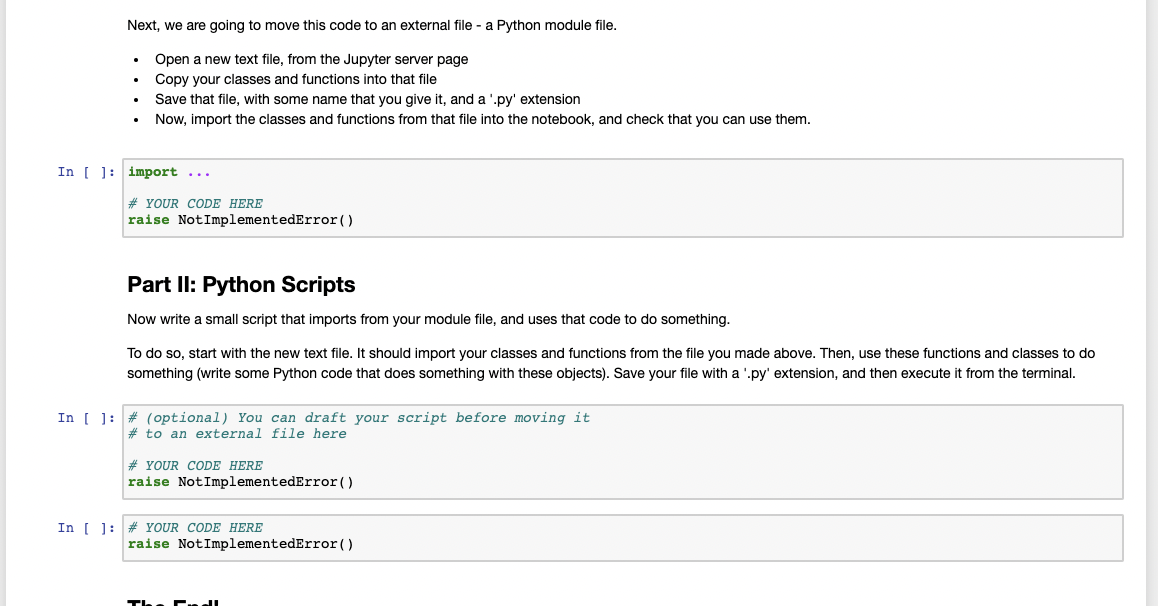
Part II: Module Files First, in the notebook below, do the following: . Write at least one new Class Make sure there is at least one method in the class that prints something out Write two new functions, that do something with instances of your new class(es) For example, take a list of custom objects, and call a method on each one In [1]: * Class(es) here class Person: def _init__(self, first_name, last_name): self.first_name = first_name self.last_name = last_name def print_name (self): print (self.first_name, self.last_name) class Employee (Person): def init__(self, first_name, last_name, salary): super() . _init__(first_name, last_name) self.salary = salary def print_employee (self): print(self.first_name, self.last_name, 'gets salary of', self.salary) def class Manager (Person): _init__(self, first_name, last_name, num_employees_to_manage): super() . __init_(first_name,last_name) self.num_employees_to_manage = num_employees_to_manage def print_manager (self): print(self.first_name, self.last_name, 'manages', self.num_employees_to_manage) In [4]: # function(s) here if name main person = Person('Joey', "Judy") emp = Employee ("Lexi", "Judy", 10000) manager - Manager ("Bella", "Kumar", 100) print("Person==>") person.print_name() print("Employee==>") emp.print_employee() print("Manager==>") manager.print_manager Person==> Joey Judy Employee==> Lexi Judy gets salary of 10000 Manager==> Next, we are going to move this code to an external file - a Python module file. Open a new text file, from the Jupyter server page Copy your classes and functions into that file Save that file, with some name that you give it, and a '.py' extension Now, import the classes and functions from that file into the notebook, and check that you can use them. In [ ]: import ... # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() Part II: Python Scripts Now write a small script that imports from your module file, and uses that code to do something. To do so, start with the new text file. It should import your classes and functions from the file you made above. Then, use these functions and classes to do something (write some Python code that does something with these objects). Save your file with a '.py' extension, and then execute it from the terminal. In [ ]: # (optional) You can draft your script before moving it # to an external file here # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() In (): *YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


