Question: Part 2: Print grades 0/50 points (graded) Write a function called print_grades that accepts the name of a file (string) as input argument. Assuming the
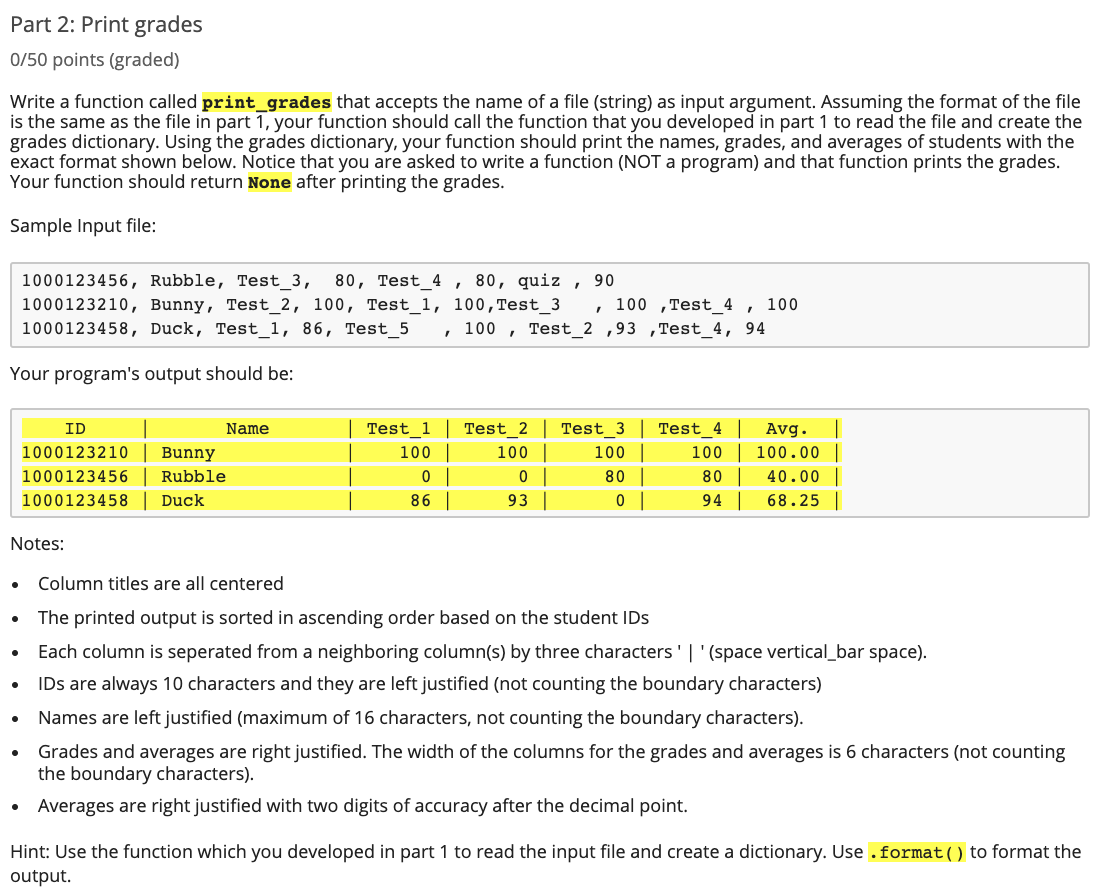
Part 2: Print grades 0/50 points (graded) Write a function called print_grades that accepts the name of a file (string) as input argument. Assuming the format of the file is the same as the file in part 1, your function should call the function that you developed in part 1 to read the file and create the grades dictionary. Using the grades dictionary, your function should print the names, grades, and averages of students with the exact format shown below. Notice that you are asked to write a function (NOT a program) and that function prints the grades. Your function should return None after printing the grades. Sample Input file: 1000123456, Rubble, Test_3, 80, Test_4, 80, quiz, 90 1000123210, Bunny, Test_2, 100, Test_1, 100, Test_3 , 100 ,Test_4, 100 1000123458, Duck, Test_1, 86, Test_ 5 1 00, Test_2 ,93 ,Test_4, 94 Your program's output should be: ID Name 1000123210 | Bunny 1000123456 | Rubble 1000123458 | Duck Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 100 100 100 0 0 80 86 93 0 Test 4 | Avg. 100 100.00 80 40.00 9 4 | 68.25 | | Notes: Column titles are all centered The printed output is sorted in ascending order based on the student IDs Each column is seperated from a neighboring column(s) by three characters'|'(space vertical_bar space). IDs are always 10 characters and they are left justified (not counting the boundary characters) Names are left justified (maximum of 16 characters, not counting the boundary characters). Grades and averages are right justified. The width of the columns for the grades and averages is 6 characters (not counting the boundary characters). Averages are right justified with two digits of accuracy after the decimal point. Hint: Use the function which you developed in part 1 to read the input file and create a dictionary. Use .format() to format the output. Part 2: Print grades 0/50 points (graded) Write a function called print_grades that accepts the name of a file (string) as input argument. Assuming the format of the file is the same as the file in part 1, your function should call the function that you developed in part 1 to read the file and create the grades dictionary. Using the grades dictionary, your function should print the names, grades, and averages of students with the exact format shown below. Notice that you are asked to write a function (NOT a program) and that function prints the grades. Your function should return None after printing the grades. Sample Input file: 1000123456, Rubble, Test_3, 80, Test_4, 80, quiz, 90 1000123210, Bunny, Test_2, 100, Test_1, 100, Test_3 , 100 ,Test_4, 100 1000123458, Duck, Test_1, 86, Test_ 5 1 00, Test_2 ,93 ,Test_4, 94 Your program's output should be: ID Name 1000123210 | Bunny 1000123456 | Rubble 1000123458 | Duck Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 100 100 100 0 0 80 86 93 0 Test 4 | Avg. 100 100.00 80 40.00 9 4 | 68.25 | | Notes: Column titles are all centered The printed output is sorted in ascending order based on the student IDs Each column is seperated from a neighboring column(s) by three characters'|'(space vertical_bar space). IDs are always 10 characters and they are left justified (not counting the boundary characters) Names are left justified (maximum of 16 characters, not counting the boundary characters). Grades and averages are right justified. The width of the columns for the grades and averages is 6 characters (not counting the boundary characters). Averages are right justified with two digits of accuracy after the decimal point. Hint: Use the function which you developed in part 1 to read the input file and create a dictionary. Use .format() to format the output
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


