Question: PART #3 C programming to implement a simple shell. Warning: you should not use any system call (e.g., system(ls);) throughout this assignment (and thereafter). Task1.



PART#3
C programming to implement a simple shell.
Warning: you should not use any "system" call (e.g., system("ls");) throughout this assignment (and thereafter).
Task1. One to Three Commands in Pipe
You may use the sample code provided to handle two commands in pipe, to make a simple shell.
Your shell handles one command, or two or three commands in pipe ("ls | wc -l" or "ls | grep ".c" | sot").
For example, if there are two commands in pipe, the parent gets the command (for example, "ls | wc -l") to recognize that there are two commands piped together. Thus it will have a pipe to be shared, and then fork a child process (to do "ls") which will fork its child process (to do "wc -l") with the pipe shared (so that the output of one process doing "ls" will be input to the input of the other process doing "wc -l"). Meanwhile the parent waits till all the child processes are terminated, and then back to the loop for the next command from the user. Extending the shell for two commands in pipe, your shell should handle up to "three commands in pipe" (for example, "ls | grep ".c" | sort").
Task2. A Command with File Redirection ( output, >> append).
Continuing Task 1, your shell program should handle one command ("ls > out1.txt") or two commands in pipe (for example, "ls | sort > out2.txt").
Hint. You may use dup or dup2 to redirect the file input or output for the given command ("ls") which a child process will execute (with exec).
if file redirection is specified for input "
then for child process to do:
fid = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
close(STD_INPUT);
dup(fid);
close(fid);
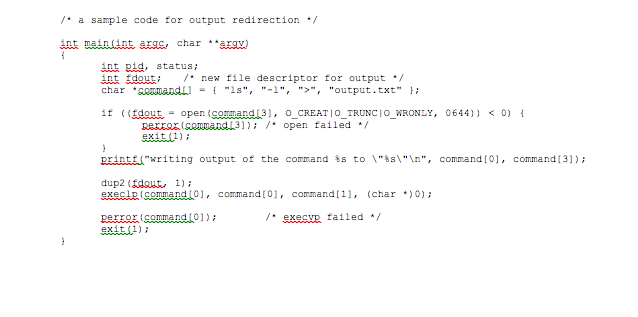
/* a sample code for output redirection */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int pid, status;
int fdout; /* new file descriptor for output */
char *command[] = { "ls", "-l", ">", "output.txt" };
if ((fdout = open(command[3], O_CREAT|O_TRUNC|O_WRONLY, 0644))
perror(command[3]); /* open failed */
exit(1);
}
printf("writing output of the command %s to \"%s\" ", command[0], command[3]);
dup2(fdout, 1);
execlp(command[0], command[0], command[1], (char *)0);
perror(command[0]); /* execvp failed */
exit(1);
}
/* sample shell to handle two commands with pipe: ls | wc -l */
#include
#include
char *cmd1[] = { "/bin/ls", 0 };
char *cmd2[] = { "/bin/wc", "-l", 0 };
void run2com();
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int pid, status;
int fd[2];
pipe(fd);
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
run2com(fd);
exit(0);
} else if (pid > 0) {
while ((pid = wait(&status)) != -1)
fprintf(stderr, "process %d exits with %d ", pid, WEXITSTATUS(status));
} else {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
exit(0);
}
void run2com(int pfd[])
{
int pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid ==0) {
dup2(pfd[0], 0);
close(pfd[1]);
execvp(cmd2[0], cmd2);
perror(cmd2[0]);
} else if (pid > 0) {
dup2(pfd[1], 1);
close(pfd[0]);
execvp(cmd1[0], cmd1);
perror(cmd1[0]);
} else {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
}
PART3.
Your program list and run (copy and paste here), and submit (1) this document with your answers and runs, and (2) all your codes in a .zip file.
PART#3 C programming to implement a simple shell. Warning: you should not use any "system call (e.g., system throughout this assignment (and thereafter). Taski. One to Three Commands in Pipe You may use the sample code provided to handle two commands in pipe, to make a simple shell. Your shell handles one command, or two or three commands in pipe ("ls I wc -l" or "ls l grep ".c" Sot") For example, if there are two commands in pipe, the parent gets the command (for example, "ls I wc -l") o recognize that there are two commands piped together. Thus it will have a pipe to be shared, and then fork a child process (to do "is") which will fork its child process (to do "we -l") with the pipe shared (so that the output of one process doing "ls" will be input to the input of the other process doing "we -1"). Meanwhile the parent waits till all the child processes are terminated, and then back to the loop for the next command from the user. Extending the shell for two commands in pipe, your shell should handle up to "three commands in pipe" (for example "is I grep sort"). Task2. A Command with File Redirection input output, append). Continuing Task 1, your shell program should handle one command ("is outl txt") or two commands in pipe (for example, "ls I sort out2.txt"). Hint. You may use dup or dup2 to redirect the file input or output for the given command ("ls") which a child process will execute (with exec) file redirection is specified for input filename f then for child process to do fid en (filename o RDONLY); close (STD INPUT); dup (fid) close (fid)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


