Question: Part 3 : Regularization In this section we will study the effect of regularization on our predictors. To do this you will need to implement
Part : Regularization
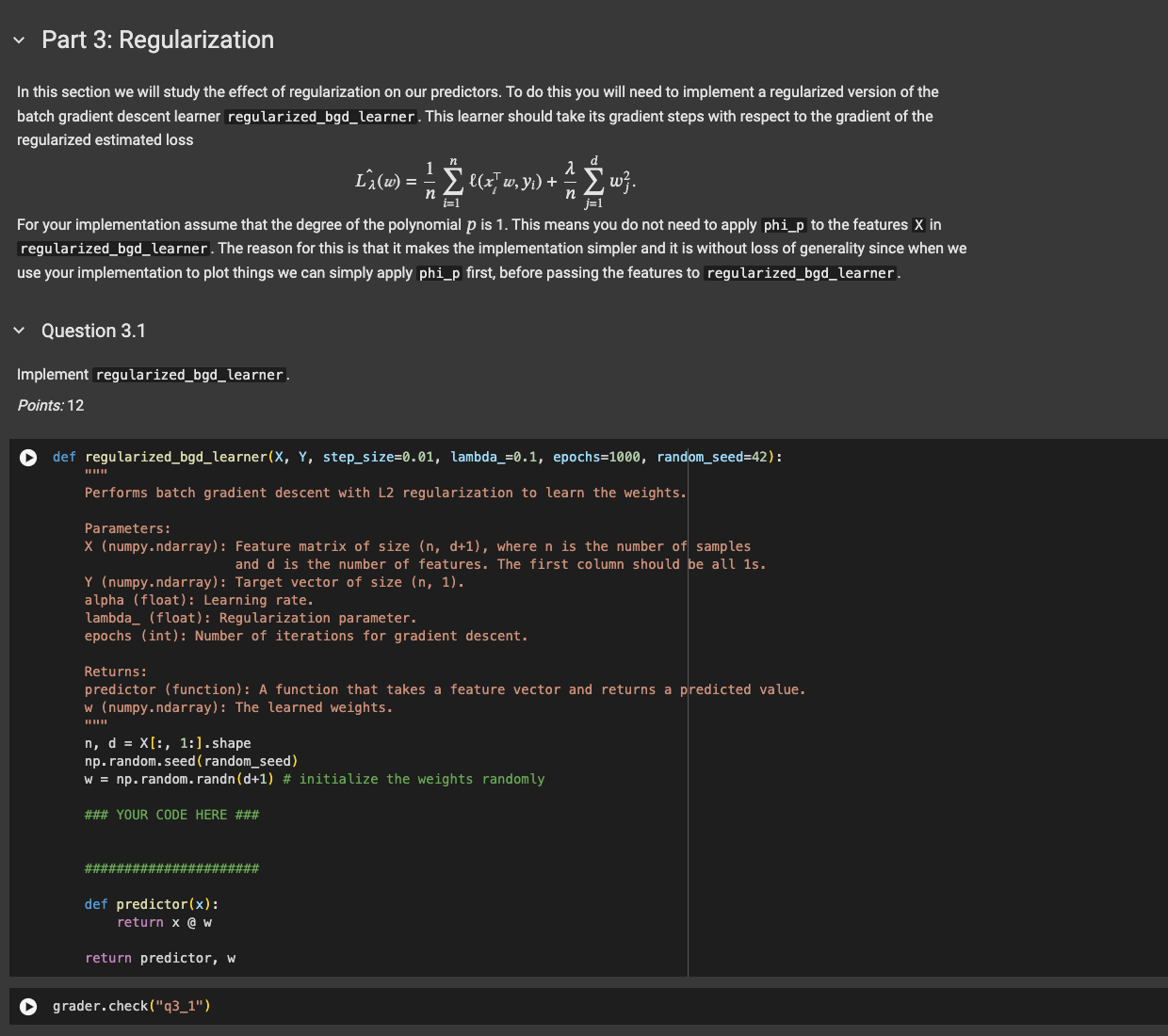
In this section we will study the effect of regularization on our predictors. To do this you will need to implement a regularized version of the batch gradient descent learner regularizedbgdlearner. This learner should take its gradient steps with respect to the gradient of the regularized estimated loss
hatLlambdawfracnsuminellleftxitop w yirightfraclambdansumjd wj
For your implementation assume that the degree of the polynomial p is This means you do not need to apply phip to the features mathbfX in regularizedbgdlearner. The reason for this is that it makes the implementation simpler and it is without loss of generality since when we use your implementation to plot things we can simply apply phip first, before passing the features to regularizedbgdlearner.
Question
Implement regularizedbgdlearner.
Points:
def regularizedbgdlearnerX Y stepsize lambda epochs randomseed:
Performs batch gradient descent with L regularization to learn the weights.
Parameters:
X numpyndarray: Feature matrix of size n d where n is the number of samples
and d is the number of features. The first column should be all s
Y numpyndarray: Target vector of size n
alpha float: Learning rate.
lambdafloat: Regularization parameter.
epochs int: Number of iterations for gradient descent.
Returns:
predictor function: A function that takes a feature vector and returns a predicted value.
w numpyndarray: The learned weights.
n d X::shape
nprandom.seedrandomseed
w nprandom.randnd # initialize the weights randomly
### YOUR CODE HERE ###
######################
def predictorx:
return x @ w
return predictor, w
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


