Question: Part 5 rectangle _ area Define a function named rectangle _ area with one parameter of type Rectangle ( defined in the provided data.py file
Part
rectanglearea
Define a function named rectanglearea with one parameter of type Rectangle defined in
the provided data.py file This function must compute and return the area of the provided
rectangle with the assumption that the rectangle is properly axisaligned ie the topleft corner
is above and to the left of the bottomright corner, the vertical sides of the rectangle are parallel
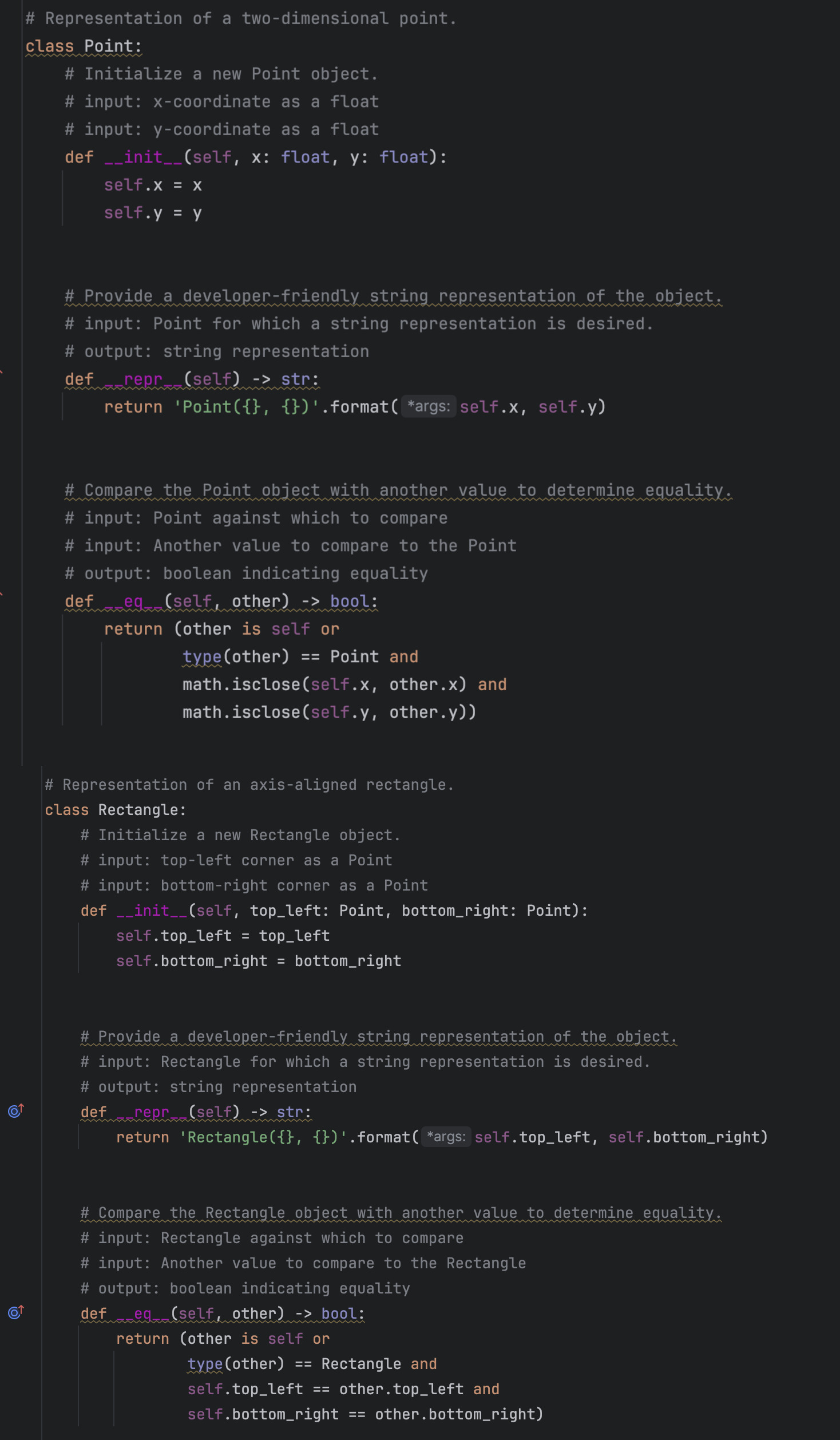
to the yaxis, and the horizontal sides of the rectangle are parallel to the xaxis# Representation of a twodimensional point.
class Point:
# Initialize a new Point object.
# input: coordinate as a float
# input: coordinate as a float
def self : float, : float:
self.
self.y
# Provide a developerfriendly string representation of the object.
# input: Point for which a string representation is desired.
# output: string representation
def repr self str:
return 'Pointformatargs: self.x self.y
# Compare the Point object with another value to determine equality
# input: Point against which to compare
# input: Another value to compare to the Point
# output: boolean indicating equality
def eg self other bool:
return other is self or
typeother Point and
math.iscloseselfx other.x and
math.iscloseselfy other.y# Representation of an axisaligned rectangle.
class Rectangle:
# Initialize a new Rectangle object.
# input: topleft corner as a Point
# input: bottomright corner as a Point
def self topleft: Point, bottomright: Point:
self.topleft topleft
self.bottomright bottomright
# Provide a developerfriendly string representation of the object.
# input: Rectangle for which a string representation is desired.
# output: string representation
def repr self str:
return 'Rectangleformatargs: self.topleft, self.bottomright
# Compare the Rectangle object with another value to determine equality
# input: Rectangle against which to compare
# input: Another value to compare to the Rectangle
# output: boolean indicating equality
def eq self other bool:
return other is self or
typeother Rectangle and
self.topleft other.topleft and
self.bottomright other.bottomright# Representation of a twodimensional point.
class Point:
# Initialize a new Point object.
# input: coordinate as a float
# input: coordinate as a float
def self : float, : float:
self.
self.y
# Provide a developerfriendly string representation of the object.
# input: Point for which a string representation is desired.
# output: string representation
def repr self str:
return 'Pointformatargs: self.x self.y
# Compare the Point object with another value to determine equality
# input: Point against which to compare
# input: Another value to compare to the Point
# output: boolean indicating equality
def eg self other bool:
return other is self or
typeother Point and
math.iscloseselfx other.x and
math.iscloseselfy other.y
# Representation of an axisaligned rectangle.
class Rectangle:
# Initialize a new Rectangle object.
# input: topleft corner as a Point
# input: bottomright corner as a Point
def self topleft: Point, bottomright: Point:
self.topleft topleft
self.bottomright bottomright
# Provide a developerfriendly string representation of the object.
# input: Rectangle for which a string representation is desired.
# output: string representation
def repr self str:
return 'Rectangleformatargs: self.topleft, self.bottomright
# Compare the Rectangle object with another value to determine equality:
# input: Rectangle against which to compare
# input: Another value to compare to the Rectangle
# output: boolean indicating equality
def eg self other bool:
return other is self or
typeother Rectangle and
self.topleft other.topleft and
self.bottomright other.bottomright
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


