Question: Part A 1. Set the two masses to equal values (ex. m1 = my = 3kg) and run the simulation five times for different initial

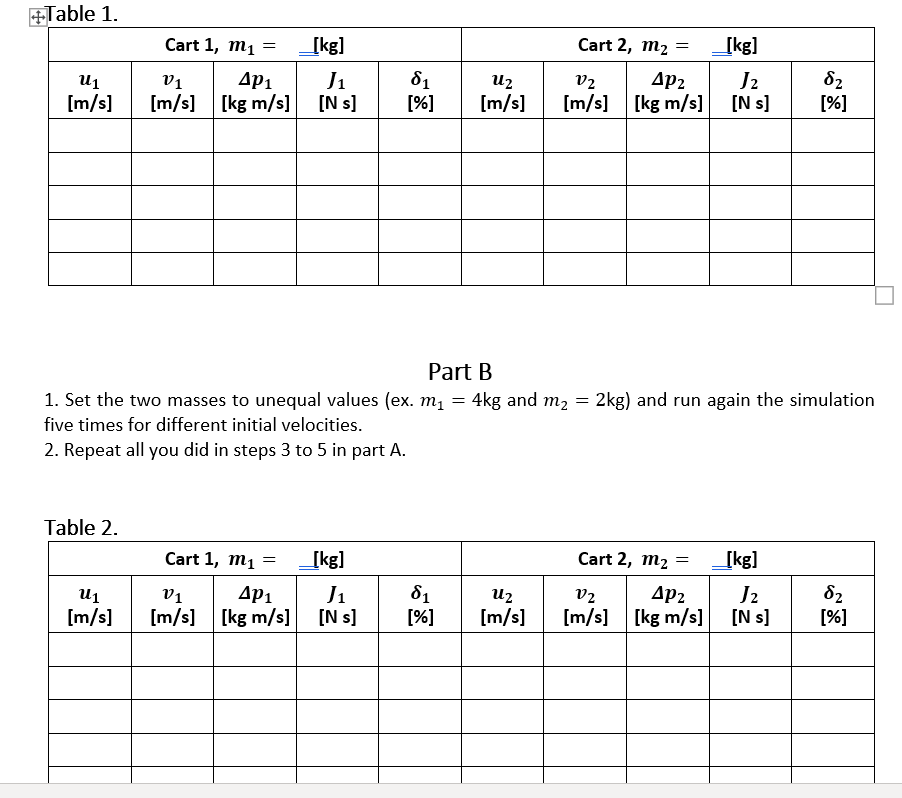


Part A 1. Set the two masses to equal values (ex. m1 = my = 3kg) and run the simulation five times for different initial velocities. 2. Record the values of m, and my in the data table below. 3. For each step, record the initial velocities uj and u2 you chose, the final velocities v, and v2 calculated by the JavaScript simulation, and estimate from the graph the areas between the curves and the horizontal axis, and then report them as J, and J2 in the data table (1 = J F1 (t)dt and J2 = J F2 (t) dt). To facilitate a better view of the features of the graph, you can zoom in/out with the mouse wheel when the mouse pointer is in the graph area. 4. Calculate the changes in momentum Apj = miv] - mju, and Ap2 = M2v2 - mzu2 and write their values in the table. 5. Calculate the percentage differences 6, = 1 1 1 x 2 x 100% and 62 = _ 14p2 2 x 2 x 100% 14p1+/l 14p2+/21 1 | Page report them in the data table.+Table 1. Part B 1. Set the two masses to unequal values (ex. ml 2 4kg and mg 2 2kg] and run again the simulation five times for different initial velocities. 2. Repeat all you did in steps 3 to Sin part A. Questions 1. Show mathematically that a force applied on an object is related to the change in momentum like .r = 13mm: = Ar: = per) pm). (you might want to use the general form of the Newton's second Law F(t)dt 2 Lip = dp (tdtl 2. Based on the data collected while using the JavaScript simulation, what can you conclude if you compare the changes in momentum .413 and the values of impulsejfor the two carts? 3. Looking at the values of initial and final velocities of both carts in Part A [equal masses), can you observe any systematic behavior of these quantities? Is there a similar trend in the values of initial and final velocities of both carts in Part B (unequal masses)? 4. Consider two masses in a closed system [constant total mass, no mass exchange with the surroundings]. Show that Newton's third Law results in conservation of total momentum. 5. Why is the value of /1 negative, while /2 is positive, in all cases in Part A and Part B? 6. Consider a ball of 0.22 kg, initially at rest, is dropped from an initial height of 1.80 m. It rebounds back after colliding with the floor to a final height of 1.50 m. Determine the impulse on the ball delivered by the floor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


