Question: PART A. Match Column A with Column B MISD Choose... Shared memory Choose... SMP Choose... CISC Choose... registers Choose... SIMD Choose... multiple streams Choose... MIMD
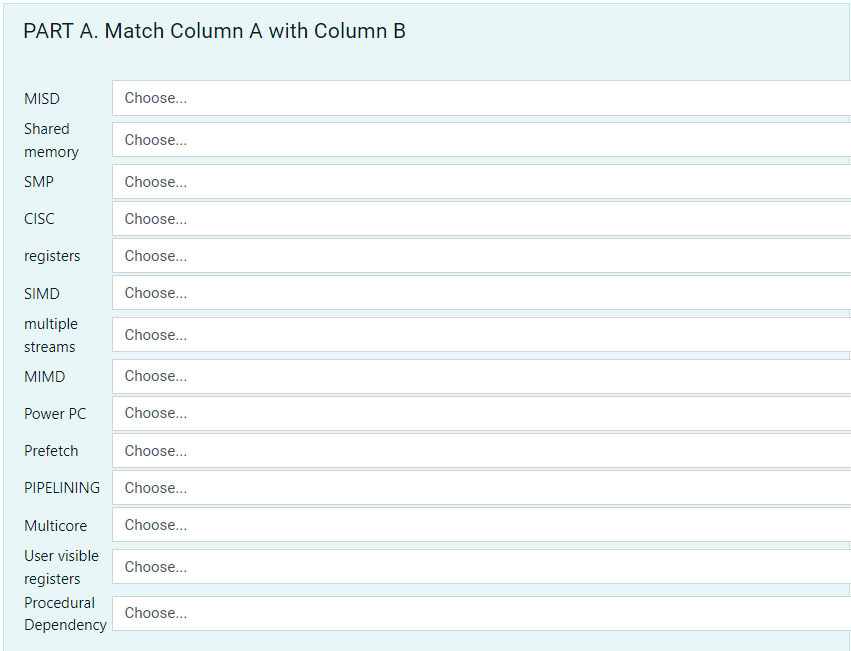
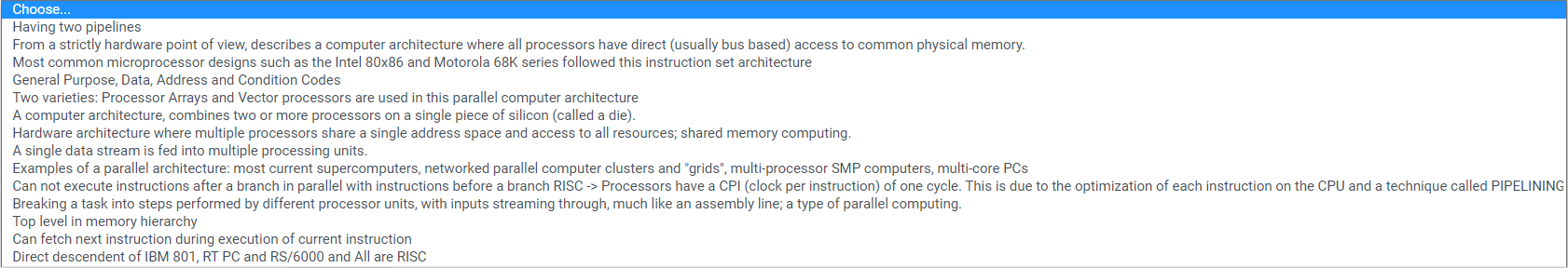
PART A. Match Column A with Column B MISD Choose... Shared memory Choose... SMP Choose... CISC Choose... registers Choose... SIMD Choose... multiple streams Choose... MIMD Choose... Power PC Choose... Prefetch Choose... PIPELINING Choose... Choose... Choose... Multicore User visible registers Procedural Dependency Choose... Choose... Having two pipelines From a strictly hardware point of view, describes a computer architecture where all processors have direct (usually bus based) access to common physical memory. Most common microprocessor designs such as the Intel 80x86 and Motorola 68K series followed this instruction set architecture General Purpose, Data, Address and Condition Codes Two varieties: Processor Arrays and Vector processors are used in this parallel computer architecture A computer architecture, combines two or more processors on a single piece of silicon (called a die). Hardware architecture where multiple processors share a single address space and access to all resources; shared memory computing. A single data stream is fed into multiple processing units. Examples of a parallel architecture: most current supercomputers, networked parallel computer clusters and "grids", multi-processor SMP computers, multi-core PCs Can not execute instructions after a branch in parallel with instructions before a branch RISC -> Processors have a CPI (clock per instruction) of one cycle. This is due to the optimization of each instruction on the CPU and a technique called PIPELINING Breaking a task into steps performed by different processor units, with inputs streaming through, much like an assembly line; a type of parallel computing. Top level in memory hierarchy Can fetch next instruction during execution of current instruction Direct descendent of IBM 801, RT PC and RS/6000 and All are RISC
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


