Question: Part A Object A, which has been charged to + 16 nC is at the origin. Object B, which has been charged to - 30
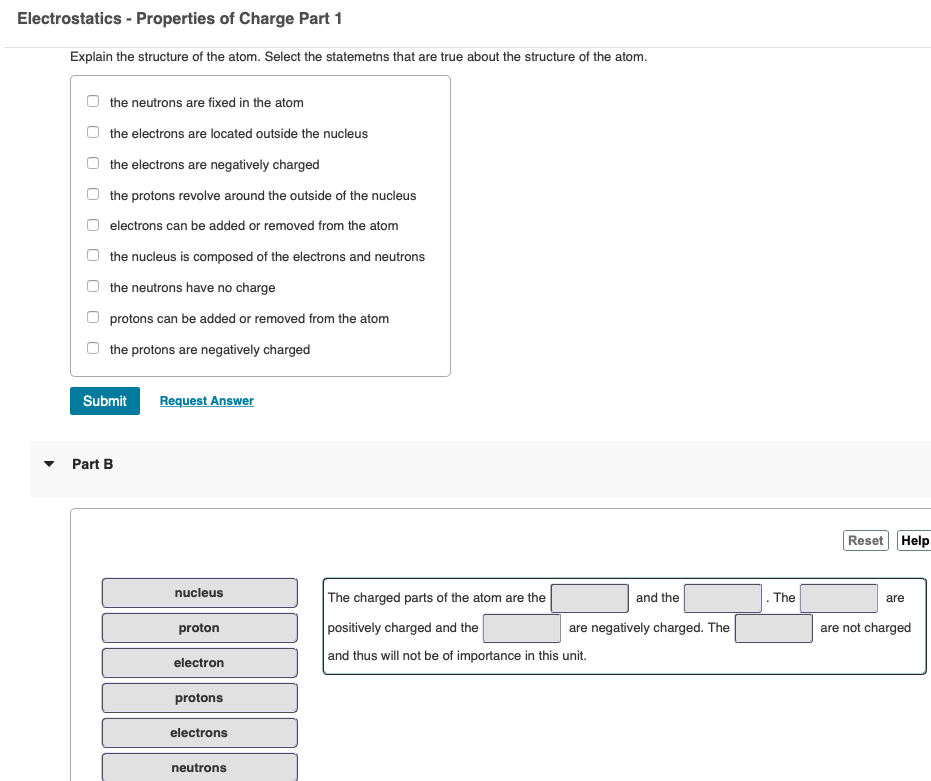
Part A Object A, which has been charged to + 16 nC is at the origin. Object B, which has been charged to - 30 nC , is at (r, y) = (0.0 cm , 2.0 cm). What is the magnitude of the electric force on object A? Express your answer in newtons. AEd ? F = N Submit Request Answer Part B What is the magnitude of the electric force on object B? Express your answer in newtons. IVO AEd ? F = N Submit Request Answer Part CPart A When sugar is poured from the box into the sugar bowl, the rubbing of sugar grains creates a static electric charge that repels the grains, and causes sugar to go flying out in all directions. If each of two sugar grains acquires a charge of 5.24 x 1011 C at a separation of 4.33 x 105 m, with what force will they repel each other? ? Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Boppo the clown carries two mylar balloons that rub against a circus elephant, causing the balloons to separate. Each balloon acquires 27.14 X 107 C of charge. How large is the electric force between them when they are separated by a distance of 0.50 m? ? Value Units Submit Request AnswerAglass rod is charged to + 3.!) DC by rubbing. v Par\". Have electrons been removed from the rod or protons added? Explain. Essay answers are limited to about 500 words (3800 characters maximum. Including apnoea}. 3301'.) Characteris} remaining _Request Answer V Par'lB How many electrons have been removed or protons added? [Bx/E AE H F' C) mi m mm\" An object becomes charged due to an excess or deficiency (shortage) of electrons. Knowing the exact number of excess or deficient electrons in an object allows one to determine the object's charge. The charge of one electron is 1.6x10-19 C. Use this to determine the charge of the following objects. Part A 4.89 x 10 excess electrons HA Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B 3 x 10 deficient electrons ? Value Units Submit Request Answer Part C A gold atom with 79 protons and 88 electrons. PearsonElectrostatics - Properties of Charge Part 1 Explain the structure at the atom. Select the statemetns that are tme about the structure of the atom. the neutrons are fixed in the atom the electrons are located outside the nucleus the electrons are negatively charged the protons revolve around the outside of the nucleus electrons can be added or removed from the atom the nucleus is composed of the electrons and neutrons the neutrons have no charge protons can be added or removed from the atom the protons are negatively charged m Ft_equest Answer 7 Part5 nuoleul The charged parts of the atom are the :l and the .The are proton positively charged and the are negatively charged. The I: are not charged and thus will not be of importance in this unit; neutrons illlli Part A There is 8.87 x 10-1 C of charge on a rod. How many electrons are present on the rod? VO AEd electrons Submit Request Answer Part B How many electrons are transferred in a lightning bolt of 27 C? AEd ? electrons Submit Request
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


