Question: Part A Part B Part C Part D Part E Problem 3: f(n)=4nlogn+n,g(n)=(n2n)/2 Show that f(n)=O(g(n)). That is, provide positive constants c and n0 that
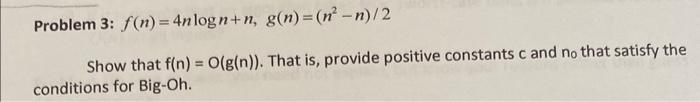




Problem 3: f(n)=4nlogn+n,g(n)=(n2n)/2 Show that f(n)=O(g(n)). That is, provide positive constants c and n0 that satisfy the conditions for Big-Oh. Problem 5: True or False? n=O(lgn) State and explain briefly. (No need to provide constants c and no.) Problem 1: f(n)=(n2n)/2,g(n)=6n Show that f(n)=(g(n). That is, provide positive constants c and n0 that satisfy the conditions for Big-Omega. Problem 8: f(n)=n2+3n+4,g(n)=6n2+7 Determine whether f(n) is O,, or of g(n). Show formally, by providing constants according to definitions. If , show both O and . If not, but O, show/argue why not . If not , show/argue why not O. Problem 9: For each of the following, indicate whether True or False (you need not explain, but know your reasons rather than guess when answering). a) If it is proven that an algorithm takes O(n2) worst-case time, is it possible that it takes O(n) on some inputs? b) If it is proven that an algorithm takes O(n2) worst-case time, is it possible that it takes O(n) on all inputs? c) If it is proven that an algorithm takes (n2) worst-case time, is it possible that it takes O(n) on some inputs? d) If it is proven that an algorithm takes (n2) worst-case time, is it possible that it takes O(n) on all inputs
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


