Question: part A - prepare a multi-step and a single-step income statements under each of the 2 inventory systems part A - Prepare multi-step income statements
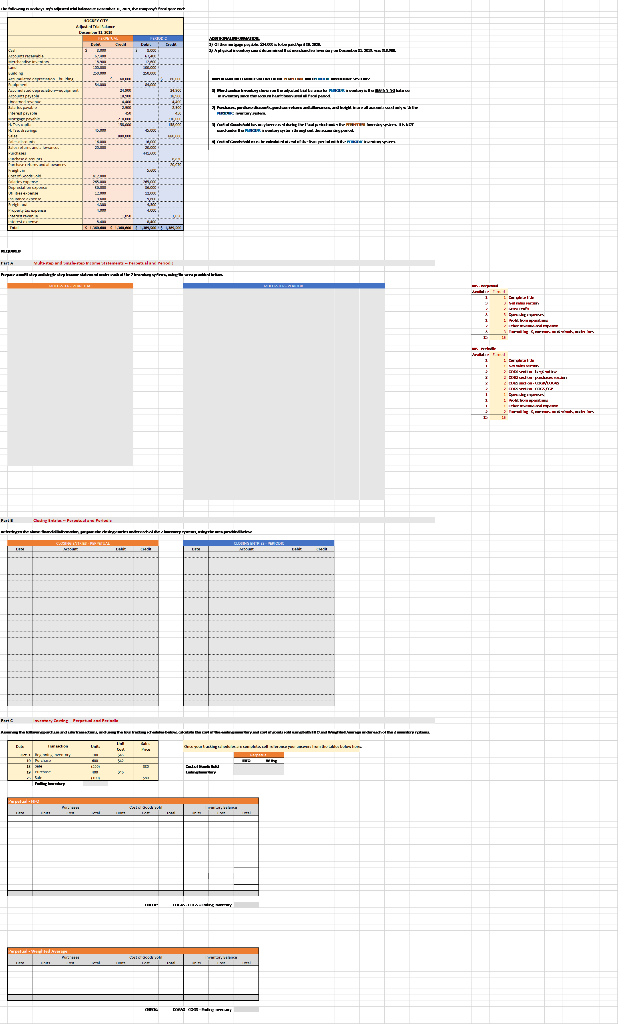
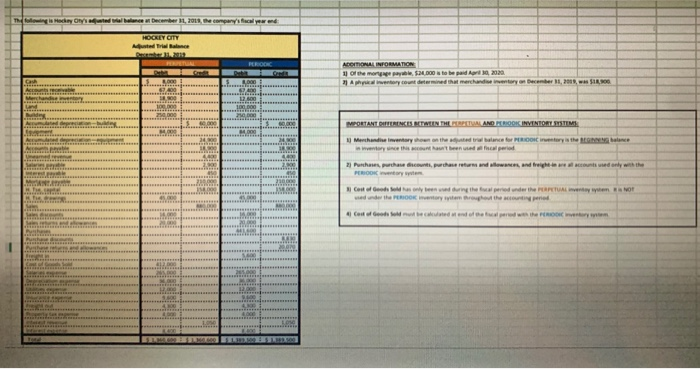

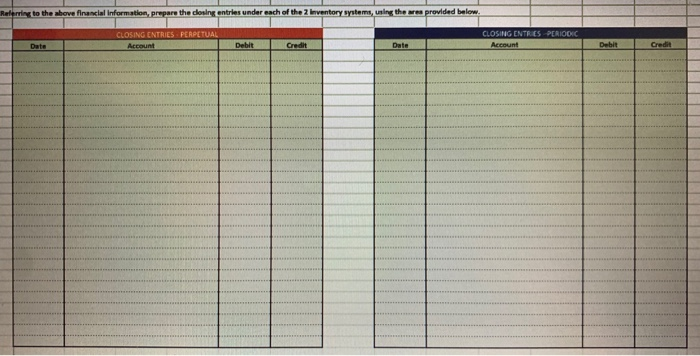
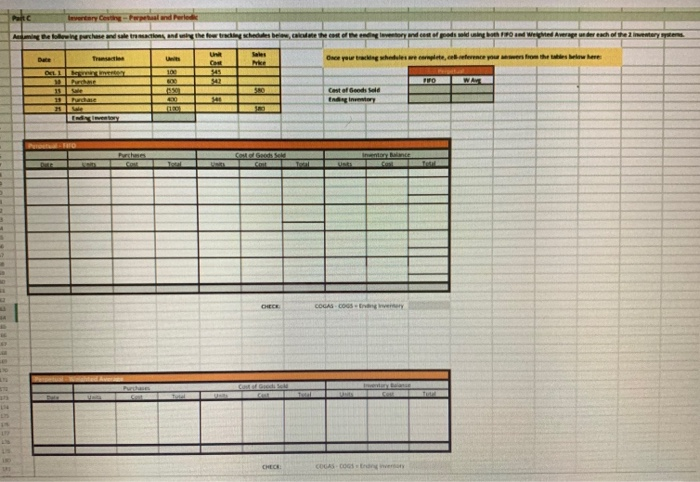
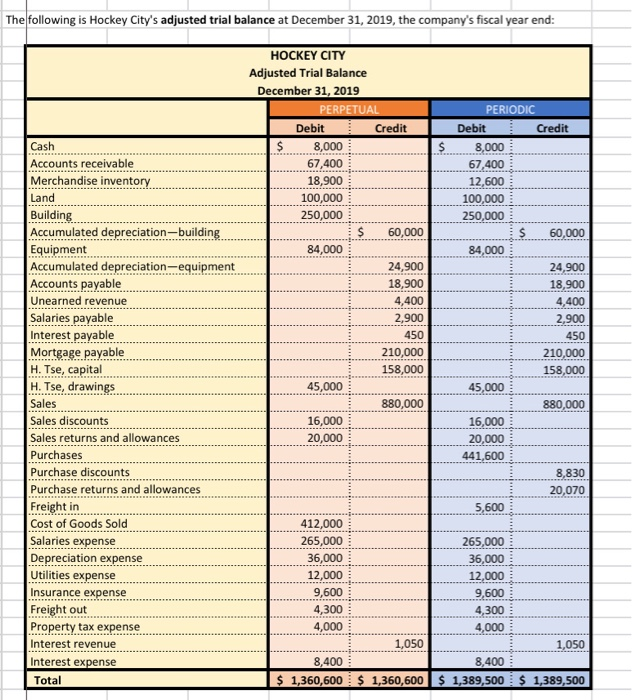
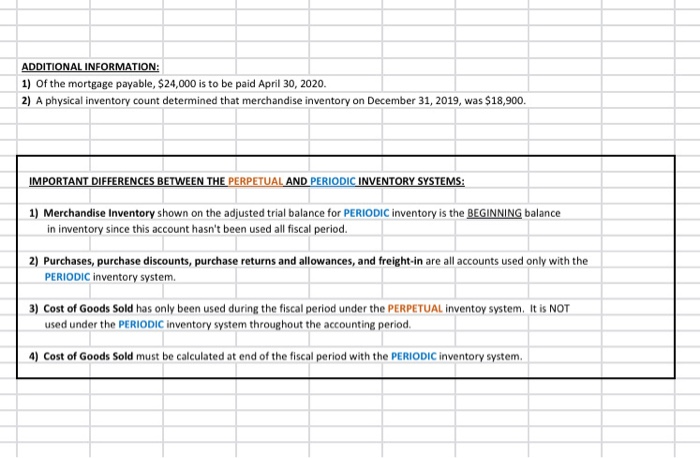
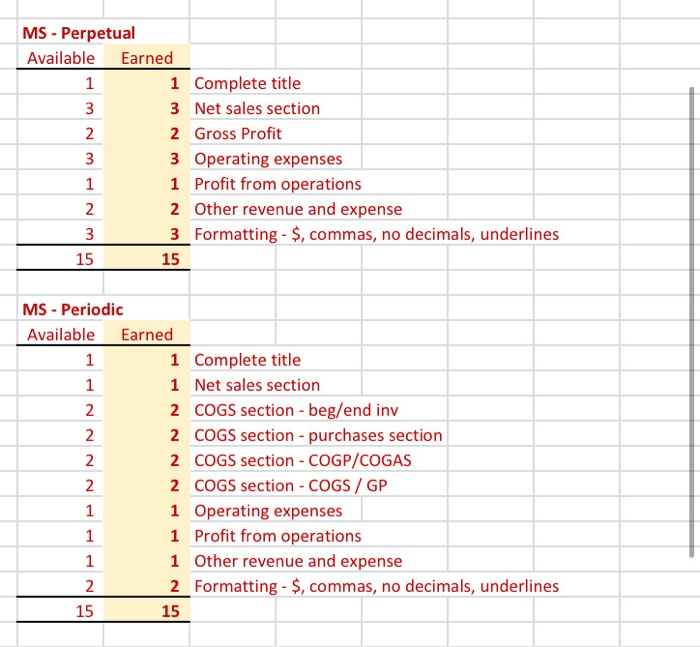
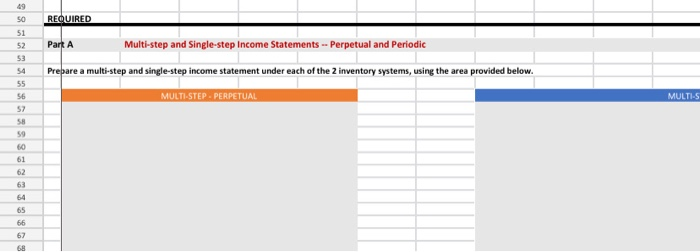
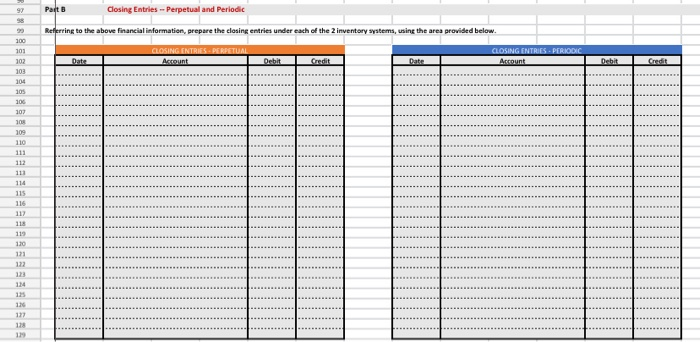
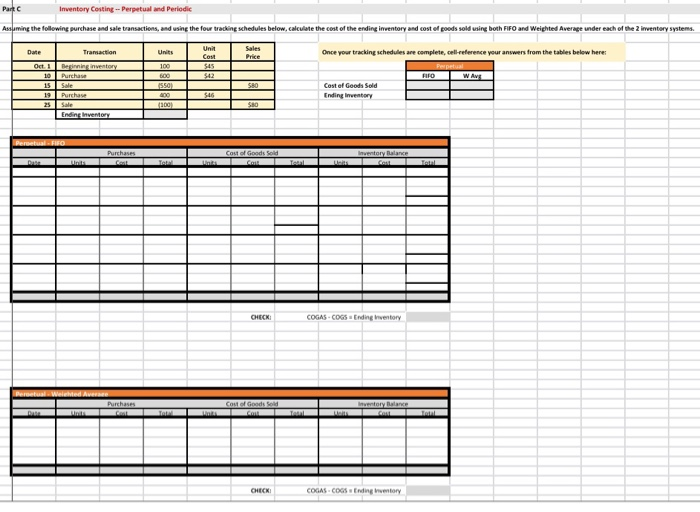
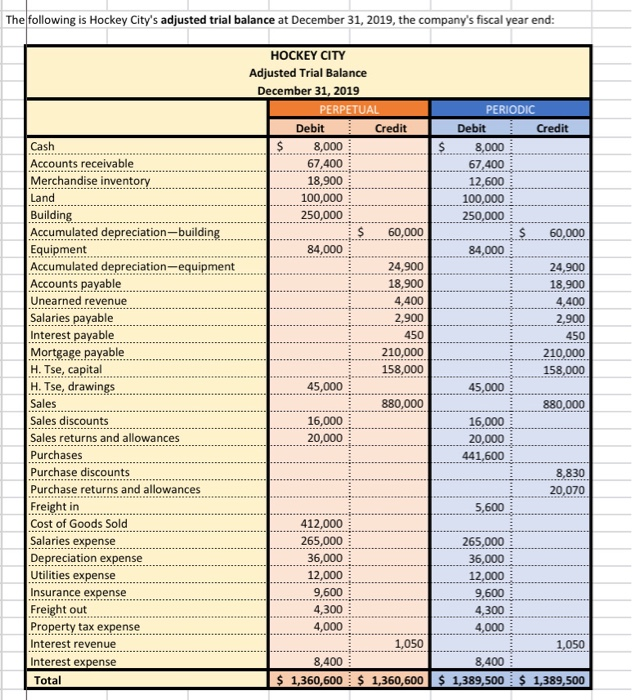
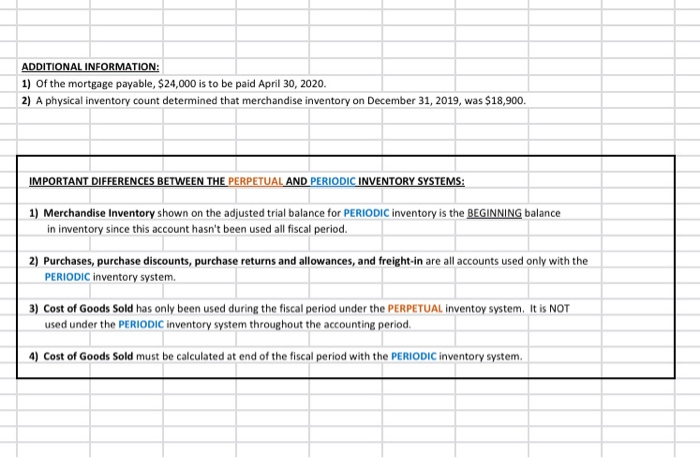
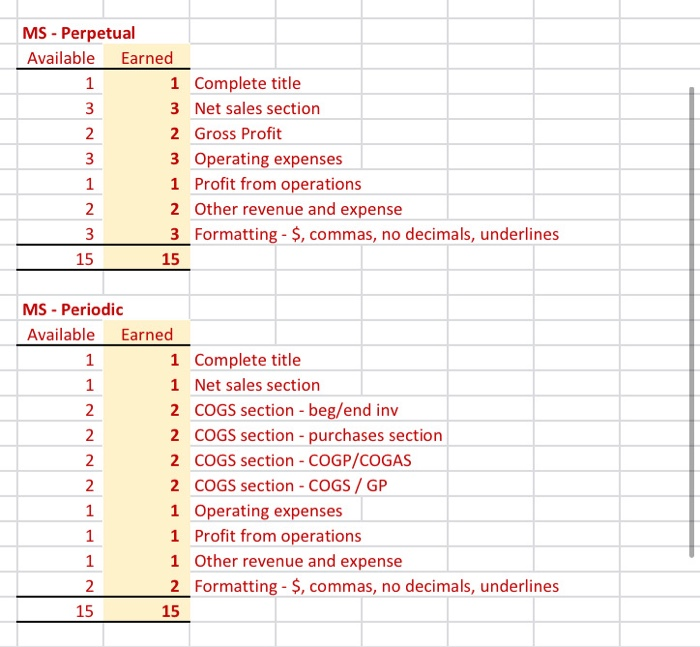
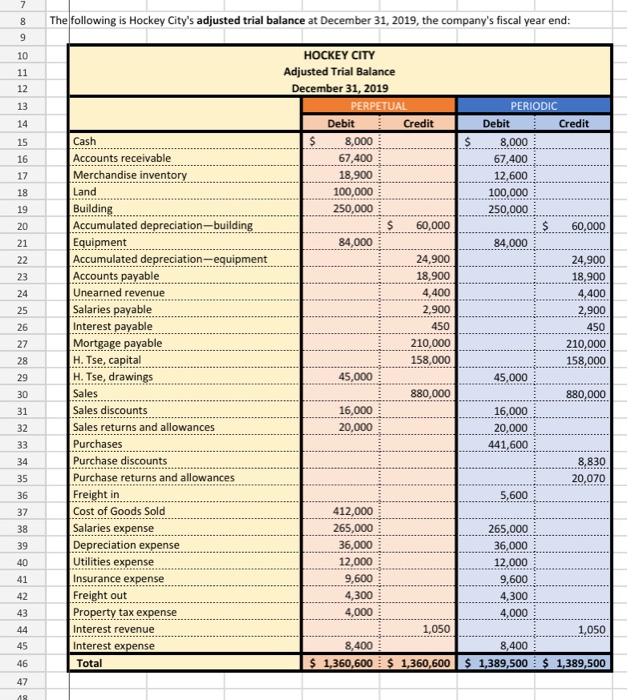
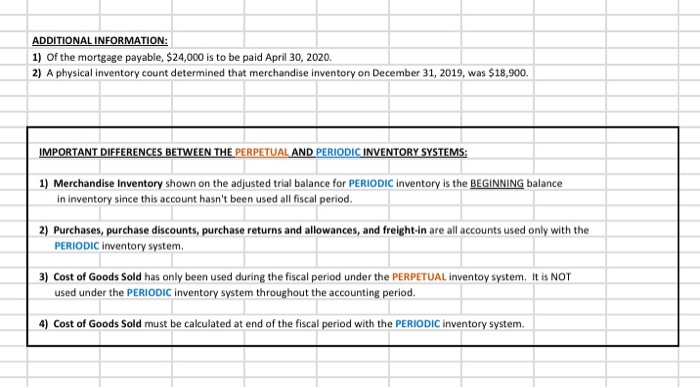
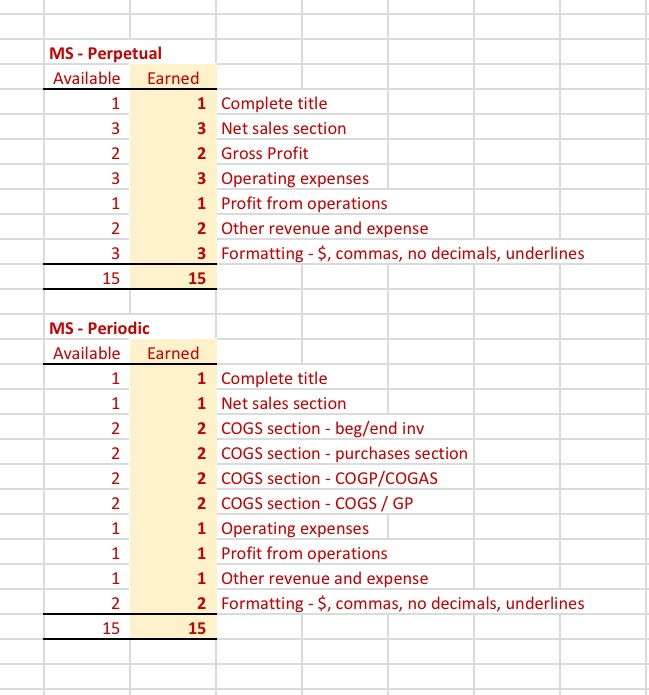


Referring to the above financial Information, prepare the closing entries under each of the 2nventory system, uning the we provided below. CLOSINGENTE ESPEROCKC CLOSING ENTRIES PERPETUAL Account Date Debit Credit Debit Credit The following is Hockey City's adjusted trial balance at December 31, 2019, the company's fiscal year end: HOCKEY CITY Adjusted Trial Balance December 31, 2019 PERPETUAL Debit Credit Cash .... 8,000 $ 67,400 18,900 100,000 250,000 60,000 84,000 24,900 18,900 4,400 2,900 450 210,000 158,000 PERIODIC Debit Credit 8,000 67,400 12,600 100,000 250,000 60,000 84,000 24,900 18,900 4,400 2,900 450 210,000 158,000 45,000 880,000 16,000 20,000 441,600 8.830 45,000 Accounts receivable Merchandise inventory Land Building Accumulated depreciation-building Equipment Accumulated depreciation-equipment Accounts payable Unearned revenue Salaries payable Interest payable Mortgage payable H. Tse, capital H. Tse, drawings Sales Sales discounts Sales returns and allowances Purchases Purchase discounts Purchase returns and allowances Freight in Cost of Goods Sold Salaries expense Depreciation expense Utilities expense Insurance expense Freight out Property tax expense Interest revenue Interest expense Total 880,000 16,000 20,000 20,070 5,600 412,000 265,000 36,000 12,000 9,600 4,300 4,000 265,000 36,000 12,000 9,600 4,300 4,000 1.050 1,050 8.400 8,400 $ 1,360,600 $ 1,360,600 $ 1,389,500 $ 1,389,500 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: 1) Of the mortgage payable, $24,000 is to be paid April 30, 2020. 2) A physical inventory count determined that merchandise inventory on December 31, 2019, was $18,900. IMPORTANT DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE PERPETUAL AND PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEMS: 1) Merchandise Inventory shown on the adjusted trial balance for PERIODIC inventory is the BEGINNING balance in inventory since this account hasn't been used all fiscal period. 2) Purchases, purchase discounts, purchase returns and allowances, and freight-in are all accounts used only with the PERIODIC inventory system. 3) Cost of Goods Sold has only been used during the fiscal period under the PERPETUAL inventoy system. It is NOT used under the PERIODIC Inventory system throughout the accounting period. 4) Cost of Goods Sold must be calculated at end of the fiscal period with the PERIODIC inventory system. MS - Perpetual Available Earned 1 Complete title 3 Net sales section 2 Gross Profit 3 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 2 Other revenue and expense 3 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 MS - Periodic Available Earned 1 Complete title 1 Net sales section 2 COGS section - beg/end inv 2 COGS section - purchases section 2 COGS section - COGP/COGAS 2 COGS section - COGS / GP 1 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 1 Other revenue and expense 2 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 REQUIRED Part A Multi-step and Single-step Income Statements -- Perpetual and Periodic Prepare a multi-step and single-step income statement under each of the 2 inventory systems, using the area provided below. MULTI-STEP. PERPETUAL MULTI-S MS - Perpetual Available Earned 1 Complete title 3 Net sales section 2 Gross Profit 3 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 2 Other revenue and expense 3 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 MS - Periodic Available Earned 1 Complete title 1 Net sales section 2 COGS section - beg/end inv 2 COGS section - purchases section 2 COGS section - COGP/COGAS 2 COGS section - COGS / GP 1 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 1 Other revenue and expense 2 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: 1) of the mortgage payable, $24,000 is to be paid April 30, 2020. 2) A physical inventory count determined that merchandise inventory on December 31, 2019, was $18,900. IMPORTANT DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE PERPETUAL AND PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEMS: 1) Merchandise Inventory shown on the adjusted trial balance for PERIODIC Inventory is the BEGINNING balance in inventory since this account hasn't been used all fiscal period. 2) Purchases, purchase discounts, purchase returns and allowances, and freight-in are all accounts used only with the PERIODIC inventory system. 3) Cost of Goods Sold has only been used during the fiscal period under the PERPETUAL inventoy system. It is NOT used under the PERIODIC inventory system throughout the accounting period. 4) Cost of Goods Sold must be calculated at end of the fiscal period with the PERIODIC inventory system. MS - Perpetual Available Earned 1 Complete title 3 Net sales section 2 Gross Profit 3 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 2 Other revenue and expense 3 3 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 NWNW MS - Periodic Available Earned 1 Complete title 1 Net sales section 2 COGS section - beg/end inv 2 COGS section - purchases section 2 COGS section - COGP/COGAS 2 COGS section - COGS / GP 1 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 1 Other revenue and expense 2 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines GNPANNNN Pharoah Company had beginning inventory of $70,000; net sales of $385,000; and cost of goods purchased of $295,000. In the previous year, the company had a gross profit margin of 45%. Calculate the estimated cost of the ending inventory using the gross profit method. Estimated cost of ending inventory & Current Attempt in Progress On July 31, Crane Company had the following data related to the retail inventory method: goods available for sale at cost $23,328; at retail $36,000; and sales of $26,000. Calculate the estimated cost of the ending inventory using the retail inventory method. (Round percentage to 2 decimal places, e.g 52.75% and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) Estimated cost of ending inventory $ Referring to the above financial Information, prepare the closing entries under each of the 2nventory system, uning the we provided below. CLOSINGENTE ESPEROCKC CLOSING ENTRIES PERPETUAL Account Date Debit Credit Debit Credit The following is Hockey City's adjusted trial balance at December 31, 2019, the company's fiscal year end: HOCKEY CITY Adjusted Trial Balance December 31, 2019 PERPETUAL Debit Credit Cash .... 8,000 $ 67,400 18,900 100,000 250,000 60,000 84,000 24,900 18,900 4,400 2,900 450 210,000 158,000 PERIODIC Debit Credit 8,000 67,400 12,600 100,000 250,000 60,000 84,000 24,900 18,900 4,400 2,900 450 210,000 158,000 45,000 880,000 16,000 20,000 441,600 8.830 45,000 Accounts receivable Merchandise inventory Land Building Accumulated depreciation-building Equipment Accumulated depreciation-equipment Accounts payable Unearned revenue Salaries payable Interest payable Mortgage payable H. Tse, capital H. Tse, drawings Sales Sales discounts Sales returns and allowances Purchases Purchase discounts Purchase returns and allowances Freight in Cost of Goods Sold Salaries expense Depreciation expense Utilities expense Insurance expense Freight out Property tax expense Interest revenue Interest expense Total 880,000 16,000 20,000 20,070 5,600 412,000 265,000 36,000 12,000 9,600 4,300 4,000 265,000 36,000 12,000 9,600 4,300 4,000 1.050 1,050 8.400 8,400 $ 1,360,600 $ 1,360,600 $ 1,389,500 $ 1,389,500 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: 1) Of the mortgage payable, $24,000 is to be paid April 30, 2020. 2) A physical inventory count determined that merchandise inventory on December 31, 2019, was $18,900. IMPORTANT DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE PERPETUAL AND PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEMS: 1) Merchandise Inventory shown on the adjusted trial balance for PERIODIC inventory is the BEGINNING balance in inventory since this account hasn't been used all fiscal period. 2) Purchases, purchase discounts, purchase returns and allowances, and freight-in are all accounts used only with the PERIODIC inventory system. 3) Cost of Goods Sold has only been used during the fiscal period under the PERPETUAL inventoy system. It is NOT used under the PERIODIC Inventory system throughout the accounting period. 4) Cost of Goods Sold must be calculated at end of the fiscal period with the PERIODIC inventory system. MS - Perpetual Available Earned 1 Complete title 3 Net sales section 2 Gross Profit 3 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 2 Other revenue and expense 3 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 MS - Periodic Available Earned 1 Complete title 1 Net sales section 2 COGS section - beg/end inv 2 COGS section - purchases section 2 COGS section - COGP/COGAS 2 COGS section - COGS / GP 1 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 1 Other revenue and expense 2 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 REQUIRED Part A Multi-step and Single-step Income Statements -- Perpetual and Periodic Prepare a multi-step and single-step income statement under each of the 2 inventory systems, using the area provided below. MULTI-STEP. PERPETUAL MULTI-S MS - Perpetual Available Earned 1 Complete title 3 Net sales section 2 Gross Profit 3 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 2 Other revenue and expense 3 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 MS - Periodic Available Earned 1 Complete title 1 Net sales section 2 COGS section - beg/end inv 2 COGS section - purchases section 2 COGS section - COGP/COGAS 2 COGS section - COGS / GP 1 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 1 Other revenue and expense 2 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 15 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: 1) of the mortgage payable, $24,000 is to be paid April 30, 2020. 2) A physical inventory count determined that merchandise inventory on December 31, 2019, was $18,900. IMPORTANT DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE PERPETUAL AND PERIODIC INVENTORY SYSTEMS: 1) Merchandise Inventory shown on the adjusted trial balance for PERIODIC Inventory is the BEGINNING balance in inventory since this account hasn't been used all fiscal period. 2) Purchases, purchase discounts, purchase returns and allowances, and freight-in are all accounts used only with the PERIODIC inventory system. 3) Cost of Goods Sold has only been used during the fiscal period under the PERPETUAL inventoy system. It is NOT used under the PERIODIC inventory system throughout the accounting period. 4) Cost of Goods Sold must be calculated at end of the fiscal period with the PERIODIC inventory system. MS - Perpetual Available Earned 1 Complete title 3 Net sales section 2 Gross Profit 3 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 2 Other revenue and expense 3 3 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines 15 NWNW MS - Periodic Available Earned 1 Complete title 1 Net sales section 2 COGS section - beg/end inv 2 COGS section - purchases section 2 COGS section - COGP/COGAS 2 COGS section - COGS / GP 1 Operating expenses 1 Profit from operations 1 Other revenue and expense 2 Formatting - $, commas, no decimals, underlines GNPANNNN Pharoah Company had beginning inventory of $70,000; net sales of $385,000; and cost of goods purchased of $295,000. In the previous year, the company had a gross profit margin of 45%. Calculate the estimated cost of the ending inventory using the gross profit method. Estimated cost of ending inventory & Current Attempt in Progress On July 31, Crane Company had the following data related to the retail inventory method: goods available for sale at cost $23,328; at retail $36,000; and sales of $26,000. Calculate the estimated cost of the ending inventory using the retail inventory method. (Round percentage to 2 decimal places, e.g 52.75% and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275.) Estimated cost of ending inventory $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


