Question: PART A The Gambler's Fallacy is the idea that past events can affect future behavior. The fallacy often generates real financial consequences for those who
PART A
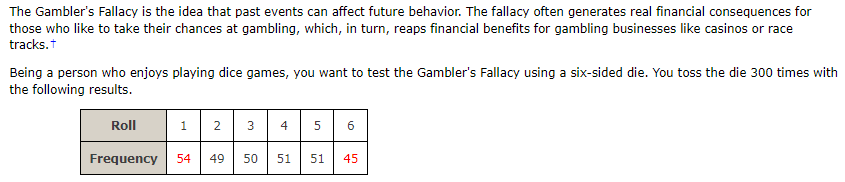

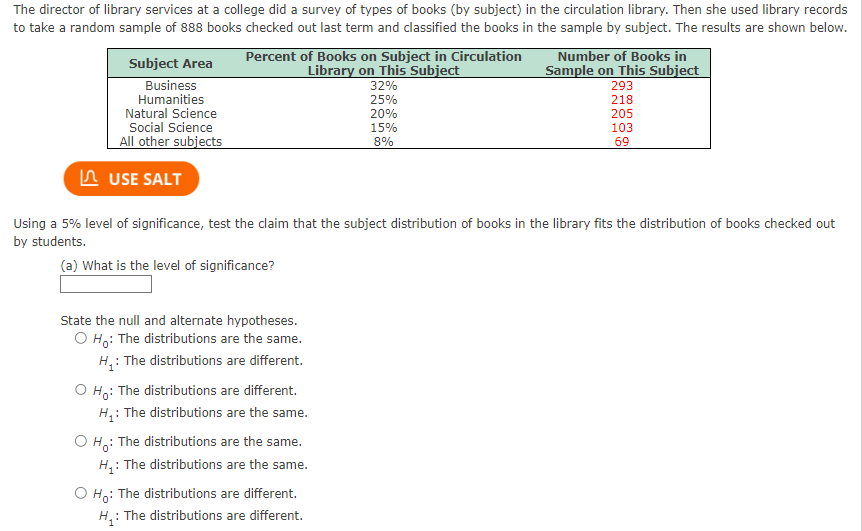

The Gambler's Fallacy is the idea that past events can affect future behavior. The fallacy often generates real financial consequences for those who like to take their chances at gambling, which, in turn, reaps financial benefits for gambling businesses like casinos or race tracks. t Being a person who enjoys playing dice games, you want to test the Gambler's Fallacy using a six-sided die. You toss the die 300 times with the following results. Roll 1 2 3 4 5 6 Frequency 54 49 50 51 51 45\fThe director of library services at a college did a survey of types of books (by subject) in the circulation library. Then she used library records to take a random sample of 888 books checked out last term and classified the books in the sample by subject. The results are shown below. Subject Area Percent of Books on Subject in Circulation Number of Books in Library on This Subject Sample on This Subject Business 32% 293 Humanities 25% 218 Natural Science 20% 205 Social Science 15% 103 All other subjects 8% 69 LA USE SALT Using a 5% level of significance, test the claim that the subject distribution of books in the library fits the distribution of books checked out by students. (a) What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. O H: The distributions are the same. H. : The distributions are different. O H: The distributions are different. H. : The distributions are the same. O H : The distributions are the same. H. : The distributions are the same. O Ho: The distributions are different. H. : The distributions are different.(b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to three decimal places. Round the test statistic to three decimal places.) Are all the expected frequencies greater than 5? O Yes O No What sampling distribution will you use? O normal O uniform O binomial O Student's t O chi-square What are the degrees of freedom? (c) Estimate the P-value of the sample test statistic. O P-value > 0.100 O 0.050 a, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. O Since the P-value > a, we reject the null hypothesis. O Since the P-value s a, we reject the null hypothesis. O Since the P-value s a, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. (e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application. O At the 5% level of significance, the evidence is sufficient to conclude that the subject distribution of books in the library is different from that of books checked out by students. O At the 5% level of significance, the evidence is insufficient to conclude that the subject distribution of books in the library is different from that of books checked out by students
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


