Question: Part b) A simplified process control block diagram is shown as: XF(S) MS) Gl(s) wt% %TO R(S) E(S) Ms) C(s) G(s) Gp(s) %TO %TO %CO
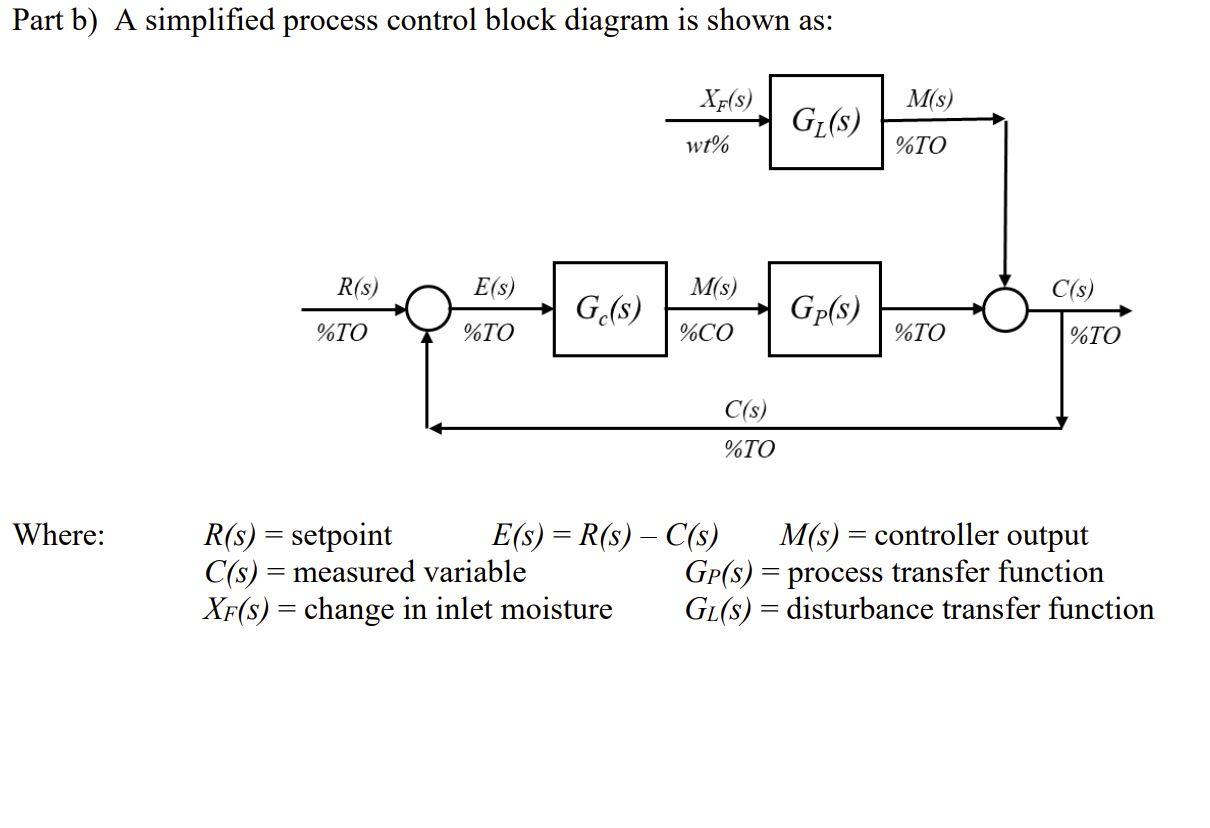

Part b) A simplified process control block diagram is shown as: XF(S) MS) Gl(s) wt% %TO R(S) E(S) Ms) C(s) G(s) Gp(s) %TO %TO %CO %TO %TO C(s) %TO Where: = R(s) = setpoint E(s) = R(s) C(s) M(s) = controller output C(s) = measured variable GP(s) = process transfer function XF(s) = change in inlet moisture Gl(s) = disturbance transfer function = The process transfer function and the disturbance transfer function were each approximated by a FOPDT model, so: Gp(s) Kpe-tops G(s) K e-tols TLS+1 Tp5+1 Where: top = the process deadtime, and tol = the disturbance deadtime. The figures below show the exiting moisture pebble wt% response (open loop) to an 8% step change in the controller output, and the exiting pebble moisture wt% response (open loop) to a disturbance step change of a 3 wt% moisture increase in the feed, respectively. 5.0 - 5.0- 4.5 4.5 4.0 4.0 Moisture, % Moisture, % 3.5 3.5 3.0 3.0 0 50 400 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 Time, s 1 100 150 200 250 300 350 Time, s Exiting pebble moisture (wt%) responding to a step change in the controller output of an 8% incr. Exiting pebble moisture (wt%) response to a step change incr of the entering pebble moisture concentration of 3 wt%. From the graphs the following FOPDT values were found: %TO Kp = 4.688 %CO Tp = 120 sec top = 70 sec %TO K= 16.67 wt% Ti = 105 sec ToL = 65 sec b) (71.4%) Determine the PI tuning parameters for this process using the IMC method for aggressive tuning. Show your work. Include the units on the PI tuned constants
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


