Question: PART B (INDEPENDENT THINKING AND APPLICATION) 5) (KEY QUESTION) A small town is served by many perfectly competing supermarkets, which have constant marginal cost. a.
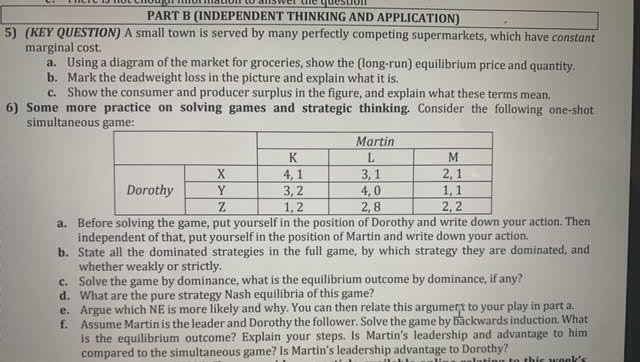
PART B (INDEPENDENT THINKING AND APPLICATION) 5) (KEY QUESTION) A small town is served by many perfectly competing supermarkets, which have constant marginal cost. a. Using a diagram of the market for groceries, show the (long-run) equilibrium price and quantity. b. Mark the deadweight loss in the picture and explain what it is. C. Show the consumer and producer surplus in the figure, and explain what these terms mean. 6) Some more practice on solving games and strategic thinking. Consider the following one-shot simultaneous game: Martin K L M X 4. 1 3, 1 2, 1 Dorothy Y 3, 2 4,0 1, 1 Z 1, 2 2, B 2, 2 a. Before solving the game, put yourself in the position of Dorothy and write down your action. Then independent of that, put yourself in the position of Martin and write down your action. b. State all the dominated strategies in the full game, by which strategy they are dominated, and whether weakly or strictly. C. Solve the game by dominance, what is the equilibrium outcome by dominance, if any? d. What are the pure strategy Nash equilibria of this game? e. Argue which NE is more likely and why. You can then relate this argument to your play in part a. f. Assume Martin is the leader and Dorothy the follower. Solve the game by backwards induction, What is the equilibrium outcome? Explain your steps. Is Martin's leadership and advantage to him compared to the simultaneous game? Is Martin's leadership advantage to Dorothy
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


