Question: Part D: Problem Solving in One Dimension Exercises Below are three Conservation of Momentum problems. The first one has been done for you. The next
Part D: Problem Solving in One Dimension
Exercises
Below are three Conservation of Momentum problems. The first one has been
done for you. The next two you must complete.
Question : so here image is the the thing Im looking for, like, i want to know what type of collisions are taking place in here in the questions given below
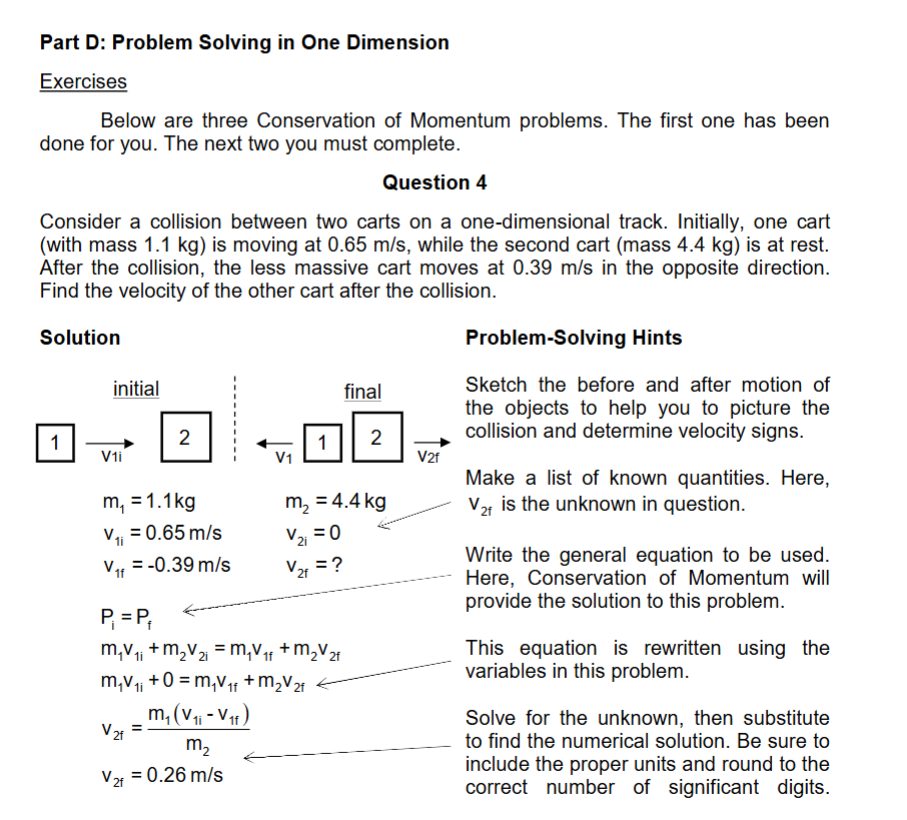
Consider a collision between two carts on a onedimensional track. Initially, one cart
with mass kg is moving at ms while the second cart mass kg is at rest.
After the collision, the less massive cart moves at ms in the opposite direction.
Find the velocity of the other cart after the collision.
Solution
PiPf
mvimvimvfmvf
mvimvfmvf
vfmvivfm
vfms
ProblemSolving Hints
Sketch the before and after motion of
the objects to help you to picture the
collision and determine velocity signs.
Make a list of known quantities. Here,
Vf is the unknown in question.
Write the general equation to be used.
Here, Conservation of Momentum will
provide the solution to this problem.
This equation is rewritten using the
variables in this problem.
Solve for the unknown, then substitute
to find the numerical solution. Be sure to
include the proper units and round to the
correct number of significant digits. For the type of collilsoin kg ms while the other boxcar
moves at ms in the same direction. After the collision, the two boxcars are coupled
and move together at ms Find the mass of the other boxcar.
Question
Cannons in the past were often mounted on rails such that they rolled backwards when
fired, as shown below. Consider a kg cannon firing a kg cannonball. When
fired, the cannonball travels at ms Find the velocity of the cannon.
State whether each of the following interactions is explosive, elastic, inelastic, or
perfectly inelastic. Give supporting calculations andor explanations. a Activity
Question b Activity Question and c Activity Question
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


