Question: Part I - Channel Coding and Encryption (50 marks) You have studied Hamming codes in Lecture 3. In Part I of this assignment, you will
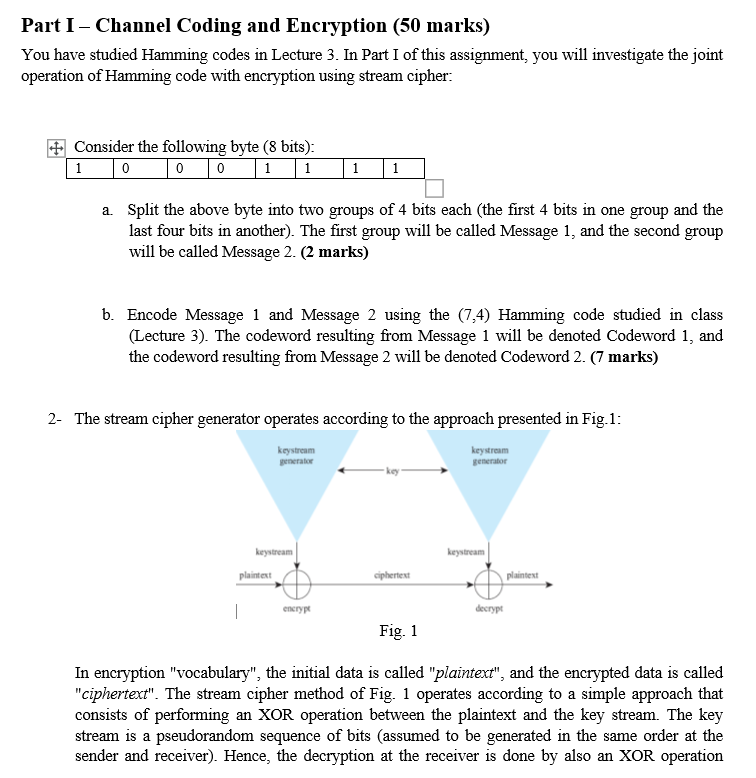


Part I - Channel Coding and Encryption (50 marks) You have studied Hamming codes in Lecture 3. In Part I of this assignment, you will investigate the joint operation of Hamming code with encryption using stream cipher: + Consider the following byte (8 bits): 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 a Split the above byte into two groups of 4 bits each (the first 4 bits in one group and the last four bits in another). The first group will be called Message 1, and the second group will be called Message 2. (2 marks) b. Encode Message 1 and Message 2 using the (7,4) Hamming code studied in class (Lecture 3). The codeword resulting from Message 1 will be denoted Codeword 1, and the codeword resulting from Message 2 will be denoted Codeword 2. (7 marks) 2- The stream cipher generator operates according to the approach presented in Fig.1: keystream generator keystream generator keystream keystream plaintext ciphertent plaintext 1 encrypt decrypt Fig. 1 In encryption "vocabulary", the initial data is called "plaintext", and the encrypted data is called "ciphertext". The stream cipher method of Fig. 1 operates according to a simple approach that consists of performing an XOR operation between the plaintext and the key stream. The key stream is a pseudorandom sequence of bits (assumed to be generated in the same order at the sender and receiver). Hence, the decryption at the receiver is done by also an XOR operation between the received ciphertext and the same key stream in order to recover the plaintext. The resulting codewords from the previous Question (1) will form a plaintext that will be encrypted using a stream cipher. The first bit of Codeword 1 will be the first bit of the plaintext, the second bit of Codeword 1 will be the second bit of the plaintext, ..., the first bit of Codeword 2 will be the 8th bit of the plaintext (after the 7 bits of Codeword 1), the second bit of Codeword 2 will be the 9th bit of the plaintext, - ... and the last bit of Codeword 2 will be the 14th bit of the plaintext. The first 14 bits of the keystream are given by: Key | 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 Derive the ciphertext resulting from the encryption of Codewords 1 and 2 with the Key stream shown above. (7 marks) 3- Assume the ciphertext you derived in Question 2 arrives to the receiver with no errors. Assume also that the receiver generates the same key stream as the sender. Perform a XOR operation between the received Ciphertext and the Key stream. What is the result? (7 marks) 4- Now assume that the channel induces some errors. After transmission over this channel, the following ciphertext is received: Received 0100 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 Ciphertext (with errors) a Decrypt the received ciphertext using the same Key stream (7 marks) b. The obtained plaintext is the concatenation of two Codewords that are the results of a (7,4) Hamming encoding operation: Codeword 1 and Codeword 2, each consisting of 7 bits. The first 7 bits correspond to Codeword 1, and the last 7 bits correspond to Codeword 2. List Codeword 1 and Codeword 2. (2 marks) C. Verify if the codewords are correct. Show your calculations in detail for each codeword. If any of the codewords is in error, perform the correction (assuming that the probability of more than one bit error per codeword is negligible). (10 marks) d. Extract the message corresponding to each corrected codeword. (3 marks) 5- In this problem, a synchronous stream cipher was considered. Another method for using a stream cipher is to implement a self-synchronizing cipher. Describe the operation of such a cipher
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


