Question: Part IV In Part III, an array multiplier was implemented using full adder modules. At a higher level, a row of full adders functions as
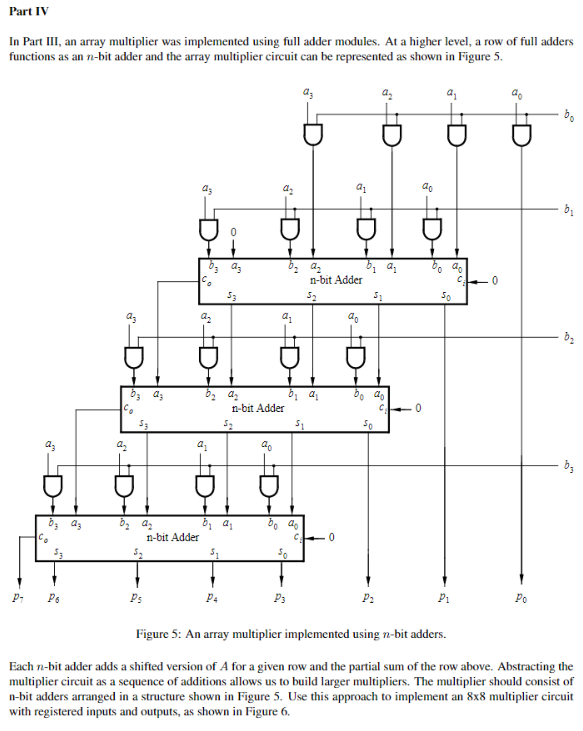
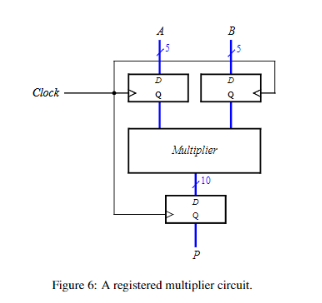
Part IV In Part III, an array multiplier was implemented using full adder modules. At a higher level, a row of full adders functions as annbi adder and the array multiplier circuit can be represented as shown in Figure 5. n-bit Adder az do 0 a ay 3 43 n-bit Adder a2 03 b, a n-bit Adder Ps P3 Figure 5: An array multiplier implemented using n-bit adders Each n-bit adder adds a shifted version of A for a given row and the partial sum of the row above. Abstracting the multiplier circuit as a sequence of additions allows us to build larger multipliers. The multiplier should consist of n-bit adders arranged in a structure shown in Figure 5. Use this approach to implement an 8x8 multiplier circuit with registered inputs and outputs, as shown in Figure 6. Part IV In Part III, an array multiplier was implemented using full adder modules. At a higher level, a row of full adders functions as annbi adder and the array multiplier circuit can be represented as shown in Figure 5. n-bit Adder az do 0 a ay 3 43 n-bit Adder a2 03 b, a n-bit Adder Ps P3 Figure 5: An array multiplier implemented using n-bit adders Each n-bit adder adds a shifted version of A for a given row and the partial sum of the row above. Abstracting the multiplier circuit as a sequence of additions allows us to build larger multipliers. The multiplier should consist of n-bit adders arranged in a structure shown in Figure 5. Use this approach to implement an 8x8 multiplier circuit with registered inputs and outputs, as shown in Figure 6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


