Question: Part-I Inheritance: Extending a Class (50 marks) Given the following startup code of a Java class: 1. Adding Setter & Getter Methods (8 marks) (a)
Part-I Inheritance: Extending a Class (50 marks) Given the following startup code of a Java class:

1. Adding Setter & Getter Methods (8 marks) (a) Add a getter method to access the protected field x (2 marks) (b) Add a setter method to set the protected field x (2 marks) (c) Add a getter method to access the protected field y (2 marks) (d) Add a setter method to set the protected field y (2 marks) 2. Adding Constructors (7 marks) (a) Add a default constructor Point() that initializes a point at the origin (0, 0) (2 marks) (b) Add a constructor with two parameters Point(double x,double y) that initializes a point at the specified (x, y) coordinates (2 marks) (c) Add a constructor with one parameter Point(Point p) that initializes a point at the (x, y) coordinates of the given point p (3 marks)
3. Adding Methods (9 marks) (a) Add a method computeDistance(double x,double y) that computes the Euclidean distance between this point and point with (x, y) coordinates (use equation 1 on page 3) (3 marks) A Euclidean distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is given by the formula
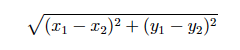 (b) Add a method computeDistance(Point p) that computes the Euclidean distance between this point and point p (3 marks) (c) Add a method toString() that returns a string representation of this point in the format (x, y) (3 marks) 4. Method Overloading (2 marks) (a) List the methods of the Point class that are overloaded?
(b) Add a method computeDistance(Point p) that computes the Euclidean distance between this point and point p (3 marks) (c) Add a method toString() that returns a string representation of this point in the format (x, y) (3 marks) 4. Method Overloading (2 marks) (a) List the methods of the Point class that are overloaded?
5. Extending The Point class (24 marks) Add Point3D class that extends the Point class to represent a point with (x, y, z) coordinates (a) Add a getter method to access the protected field z (2 marks) (b) Add a setter method to set the protected field z (2 marks) (c) Add a default constructor Point3D() that initializes a point at the origin (0, 0, 0) (2 marks) (d) Add a constructor with two parameters Point3D(double x,double y,double z) that initializes a point at the specified (x, y, z) coordinates (3 marks) (e) Add a constructor with one parameter Point3D(Point3D p) that initializes a point at the (x, y, z) coordinates of the given point p (3 marks) (f) Add a method computeDistance(double x,double y,double z) that computes the Euclidean distance between this point and 3D point with (x, y, z) coordinates (use equation 2 on page 4) (3 marks) A Euclidean distance between two 3D points (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) is given by the formula
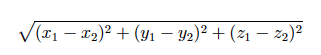 (g) Add a method computeDistance(Point3D p) that computes the Euclidean distance between this point and 3D point p (3 marks) (h) Add a method toString() that returns a string representation of this 3D point in the format (x, y, z) (3 marks) (i) List the methods of the Point3D class that override methods of the Point class? (3 marks)
(g) Add a method computeDistance(Point3D p) that computes the Euclidean distance between this point and 3D point p (3 marks) (h) Add a method toString() that returns a string representation of this 3D point in the format (x, y, z) (3 marks) (i) List the methods of the Point3D class that override methods of the Point class? (3 marks)
Part-II Inheritance: Implementing an Interface (42 marks) Irrational number is any real number that cannot expressed as a ratio of two whole numbers. The decimal expansion of an irrational number never repeats or ends.
1. BigDecimal Class (12 marks) BigDecimal class represents large floating-point numbers with high precision. Read the Java documentation of BigDecimal (see link BigDecimal) BigDecimal class can be used in Question of this part Bonus points are awarded for using BigDecimal class
(a) What is the superclass of BigDecimal class? (2 marks) (b) What is the package of BigDecimal class? (2 marks) (c) Which interface the BigDecimal class implements? (2 marks) (d) How many instance variables the BigDecimal has? (2 marks) (e) How many class variables the BigDecimal has? (2 marks) (f) How many constructors the BigDecimal has? (2 marks)
2. Implementing Java Interface (30 marks) Given the following Java interface:

Add IrrationalApproximation Java class that implements the interface Irrational?
(a) To implement public double computePI(int precision) abstract method use Leibniz formula for (use equation 3 on page 6) (10 marks)
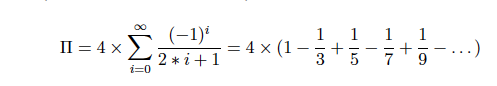
(b) To implement public double computeEulerConstant(int precision) abstract method use the formula for e given by equation 4 on page 6: (10 marks)
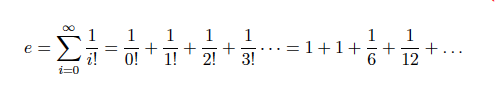
Factorial of non-negative integer N is denoted by N! is given by the following formulae (see equations 5 & 6)
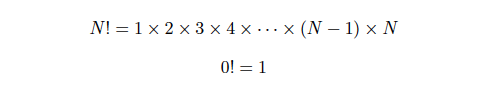
(c) To implement public double computeSquareRootOfTwo(int precision) abstract method use the Babylonian method for approximating 2 (see equation 7 on page 6) (10 marks)
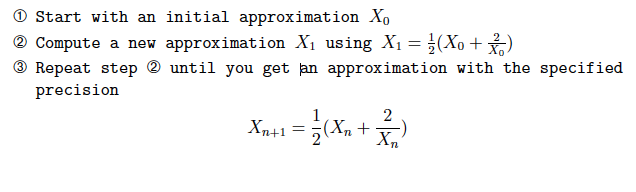
\begin{tabular}{l|l} 1 & public class Point \\ 2 & // The X coordinate of this Point \\ 3 & protected double x; \\ 4 & // The Y coordinate of this Point \\ 5 & protected double y; \\ 6 & \\ 7 & \} \end{tabular} (x1x2)2+(y1y2)2 (x1x2)2+(y1y2)2+(z1z2)2 \begin{tabular}{l|l} 1 & public interface Irrationalf \\ 2 & public double computePI (int precision); \\ 3 & public double computeEulerConstant(int precision); \\ 4 & public double computeSquareRoot0fTwo(int precision); \\ 5 & \} \end{tabular} =4i=02i+1(1)i=4(131+5171+91) e=i=0i!1=0!1+1!1+2!1+3!1=1+1+61+121+ N!=1234(N1)N0!=1 (1) Start with an initial approximation X0 (2) Compute a new approximation X1 using X1=21(X0+X02) (3) Repeat step (2) until you get an approximation with the specified precision Xn+1=21(Xn+Xn2)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


