Question: Physics B | 5.1 Doppler Effect Doppler Effect Background: The Doppler effect is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative

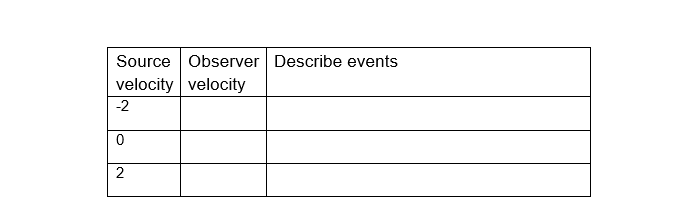
Physics B | 5.1 Doppler Effect Doppler Effect Background: The Doppler effect is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to its source. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and moves away from an observer. The received frequency is higher during the approach, it is identical at the instant of passing by, and it is lower while it moves away. Objectives: Draw pictures of high and low frequency wave fronts. . Explain why the pitch of a car horn changes as it approaches and then drives past. Explain the Doppler effect, with diagrams, and give examples of where it can be heard. Key Terms: Pitch - How low or high a tone sounds to a person Frequency - wiggles per second (moves back and forth) Doppler Effect - As the source of a wave (sound or light) approaches an observer, the observer sees/hears a higher frequency than the source actually is emitting. As the source moves away from an observer, the observer sees/hears a lower frequency wave than the source actually is emitting Procedure: 1. Go to the physics simulation entitled Doppler Effect at the website: http://physics.bu.edu/-duffy/HTML5/doppler.html 2. Press play, watch how the waves move. Experiment with altering the source velocity (in units of the speed of sound). Describe what you see in the table below. (5 points) Source Describe events velocity -2 0 2 . Now experiment with the observer velocity and source velocity. Explain what you observed below, you change observer velocity: (5 points)\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


