Question: pl: LC-3 assembly code To start you off with this homework, we are implementing the multiply function! Store the result of the operation in the

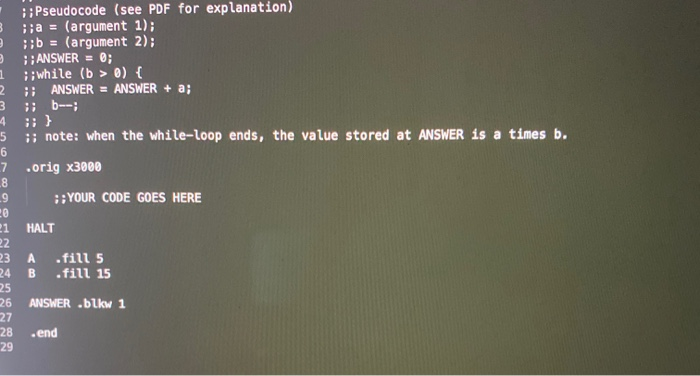
To start you off with this homework, we are implementing the multiply function! Store the result of the operation in the label ANSWER. Arguments A and B are stored in memory, and you will load them from there to perform this operation. Assume the values of A and B are positive integers. Implement your assembly code in mult.asm. Suggested Pseudocode: a = (argument 1); b = (argument 2); ANSWER = 0; while (b > 0) { ANSWER - ANSWER + a; b--; // note: when the while-loop ends, the value stored at ANSWER is a times b. 3 ::Pseudocode (see PDF for explanation) ; a = (argument 1); ;b = (argument 2); ANSWER = 0; ;; while (b > 0) { ANSWER = ANSWER + a; ; b--; 1 2 3 5 i note: when the while-loop ends, the value stored at ANSWER is a times b. .orig x3000 ::YOUR CODE GOES HERE HALT 23 A B SAW fill 5 fill 15 ANSWER .blkw 1 .end To start you off with this homework, we are implementing the multiply function! Store the result of the operation in the label ANSWER. Arguments A and B are stored in memory, and you will load them from there to perform this operation. Assume the values of A and B are positive integers. Implement your assembly code in mult.asm. Suggested Pseudocode: a = (argument 1); b = (argument 2); ANSWER = 0; while (b > 0) { ANSWER - ANSWER + a; b--; // note: when the while-loop ends, the value stored at ANSWER is a times b. 3 ::Pseudocode (see PDF for explanation) ; a = (argument 1); ;b = (argument 2); ANSWER = 0; ;; while (b > 0) { ANSWER = ANSWER + a; ; b--; 1 2 3 5 i note: when the while-loop ends, the value stored at ANSWER is a times b. .orig x3000 ::YOUR CODE GOES HERE HALT 23 A B SAW fill 5 fill 15 ANSWER .blkw 1 .end
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


