Question: Planar biaxial tests ( Fig 1 ( a ) ) are typically used to extract the mechanical properties of a wide range of materials, including
Planar biaxial tests Fig a are typically used to extract the mechanical properties of a wide range of materials, including metals, polymers, and biological tissues, especially if the properties are anisotropic. For biological tissue samples, the specimen is stretched with hooks that are connected to linear actuators. During the test, biaxial forces are measured from load cells, displacement can be measured by optically tracking markers that are placed on the surface of the specimen. This forcedisplacement data can then be converted to stressstrain curves, which reveal the underlying mechanical behavior of the tissue specimen.
Computational models, such as finite element analysis FEA can be used to simulate and compute key mechanical variables during planar biaxial tests. Fig b shows a FEA model of biaxial test. From the FEA simulation, the stressstrain of the two directions and can be obtained Fig c
In this project, you will work with the stressstrain data and complete a series of tasks outlined below. In the real world, these tasks are useful for finding the stiffness of material at various loading conditions, the strain energy density of the material, stress distribution in the deformable body, etc.
To begin with, the stressstrain data can be found in Data.mat. Use the PYTHON code below to import the data.
import scipy
DataReadscipy.ioloadmatC:Datamat' # replace with the directory containing 'Data.mat' DataDataReadData
Or
from scipy import io
DataReadioloadmatC:Datamat' # replace with the directory containing 'Data.mat'
DataDataReadData
In the D array 'Data', rows correspond to data points, to columns correspond to time, strain E strain E stress S and stress S respectively. and stand for two directions in the biaxial test. For the following questions, use builtin functions whenever possible.
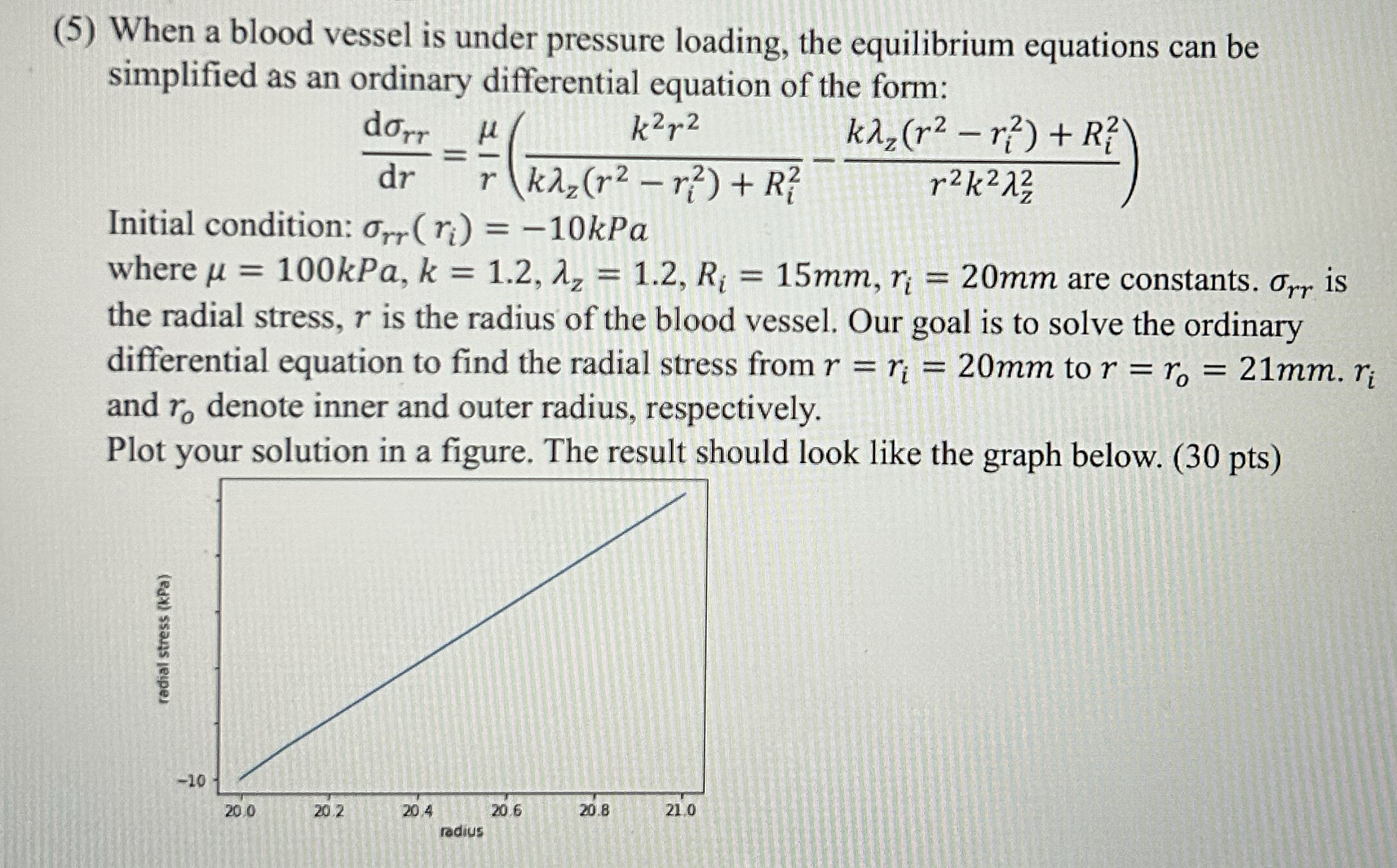
When a blood vessel is under pressure loading, the equilibrium equations can be simplified as an ordinary differential equation of the form:
Initial condition: kPa
where kPa, are constants. is the radial stress, is the radius of the blood vessel. Our goal is to solve the ordinary differential equation to find the radial stress from to and denote inner and outer radius, respectively.
Plot your solution in a figure. The result should look like the graph below. pts
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


