Question: plase help me solve this. II. Problem - You have to show your work. No credit without an explanation (60 marks). 1. The two most-used
plase help me solve this.
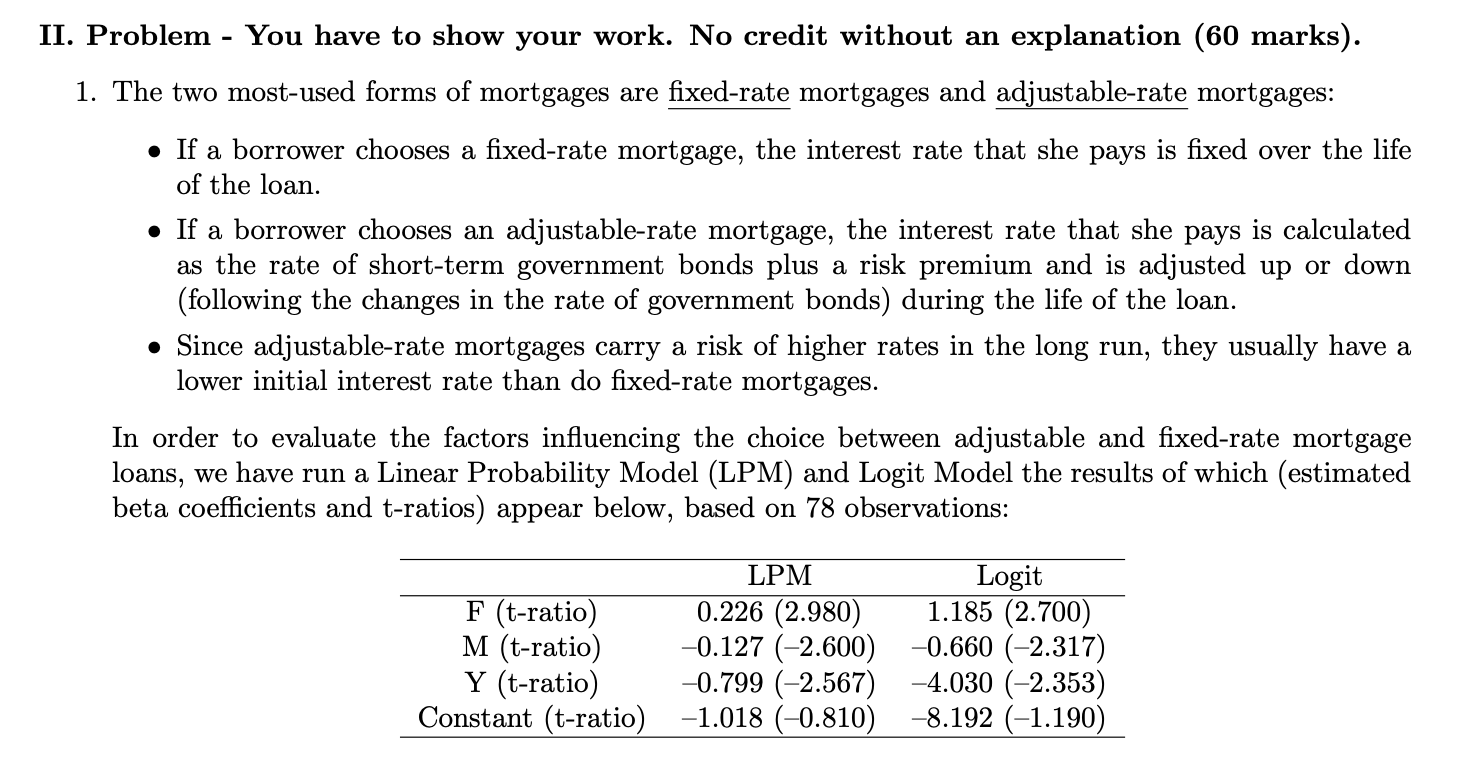
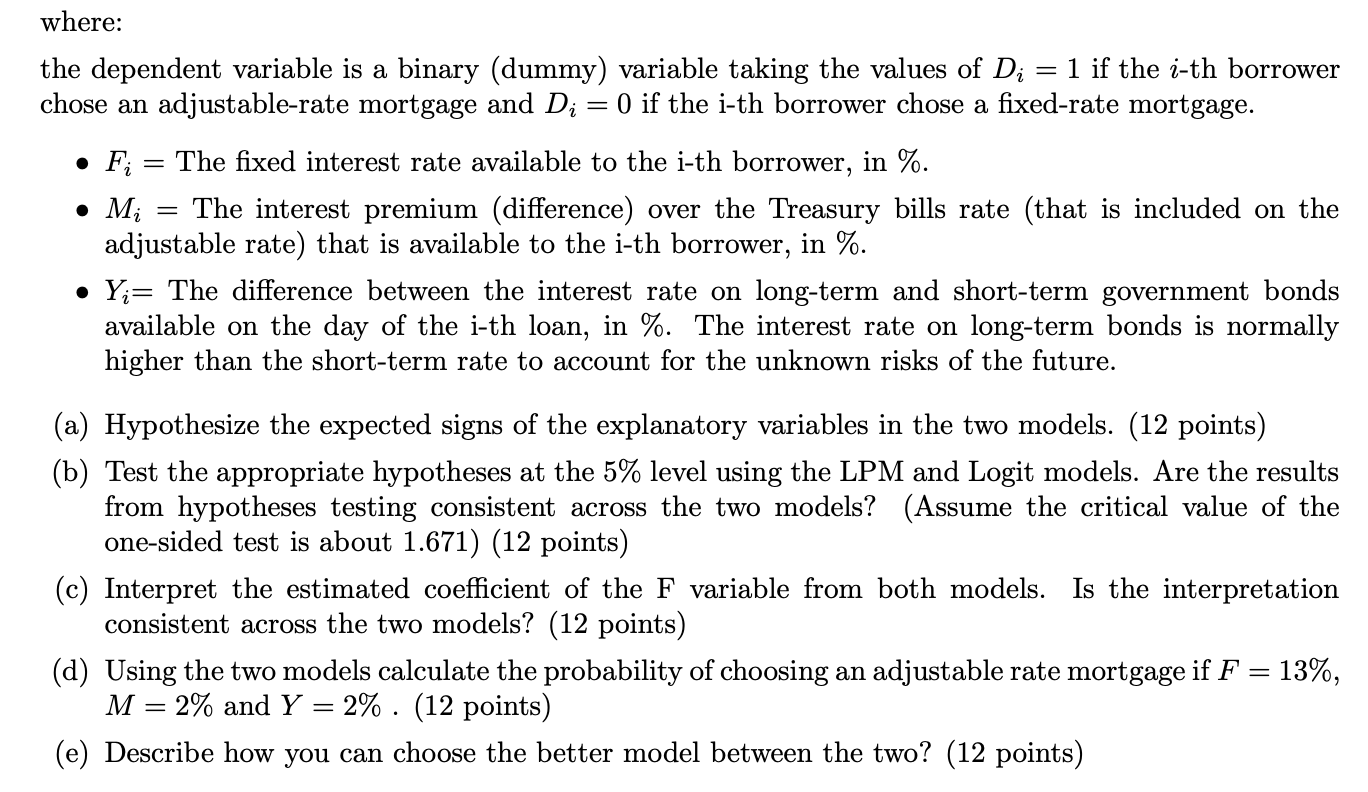
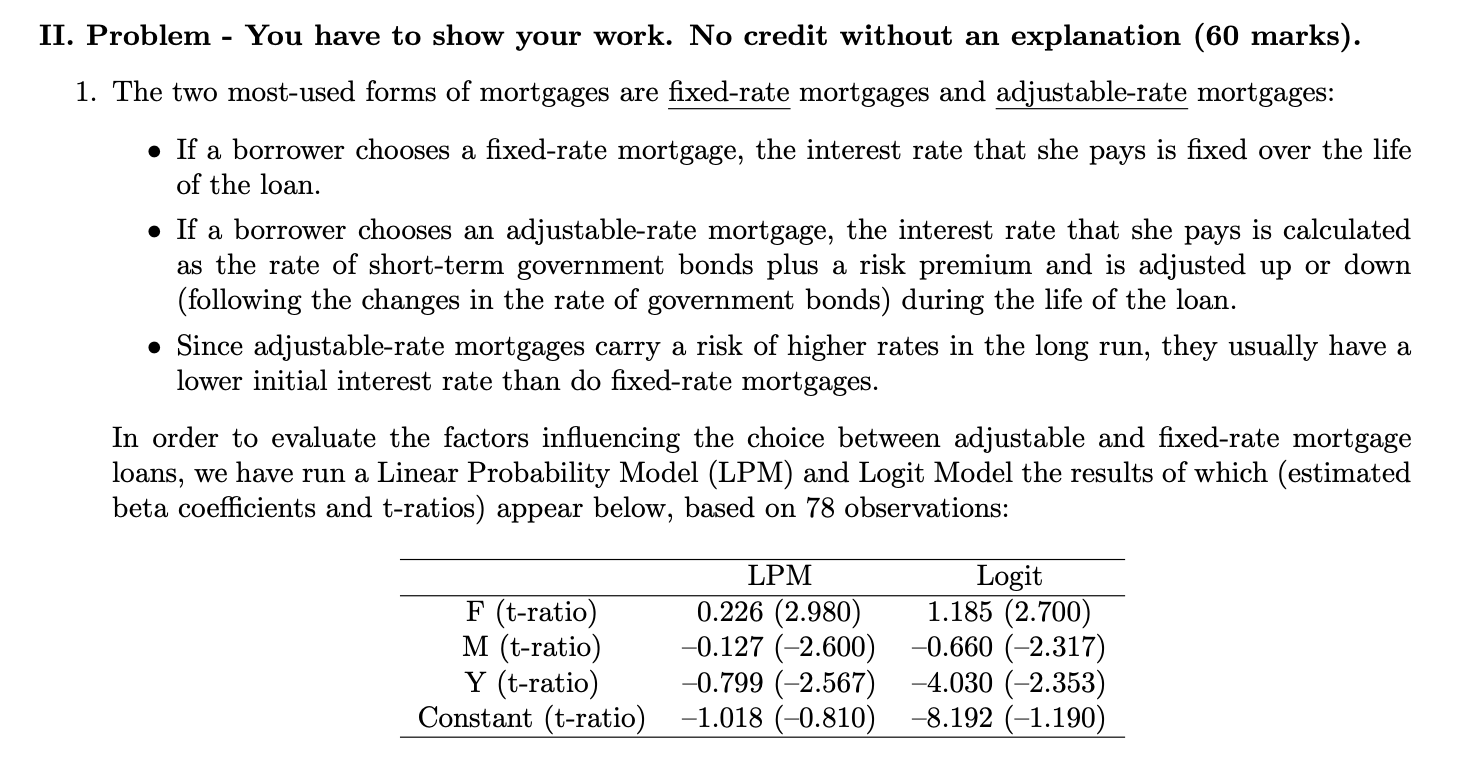
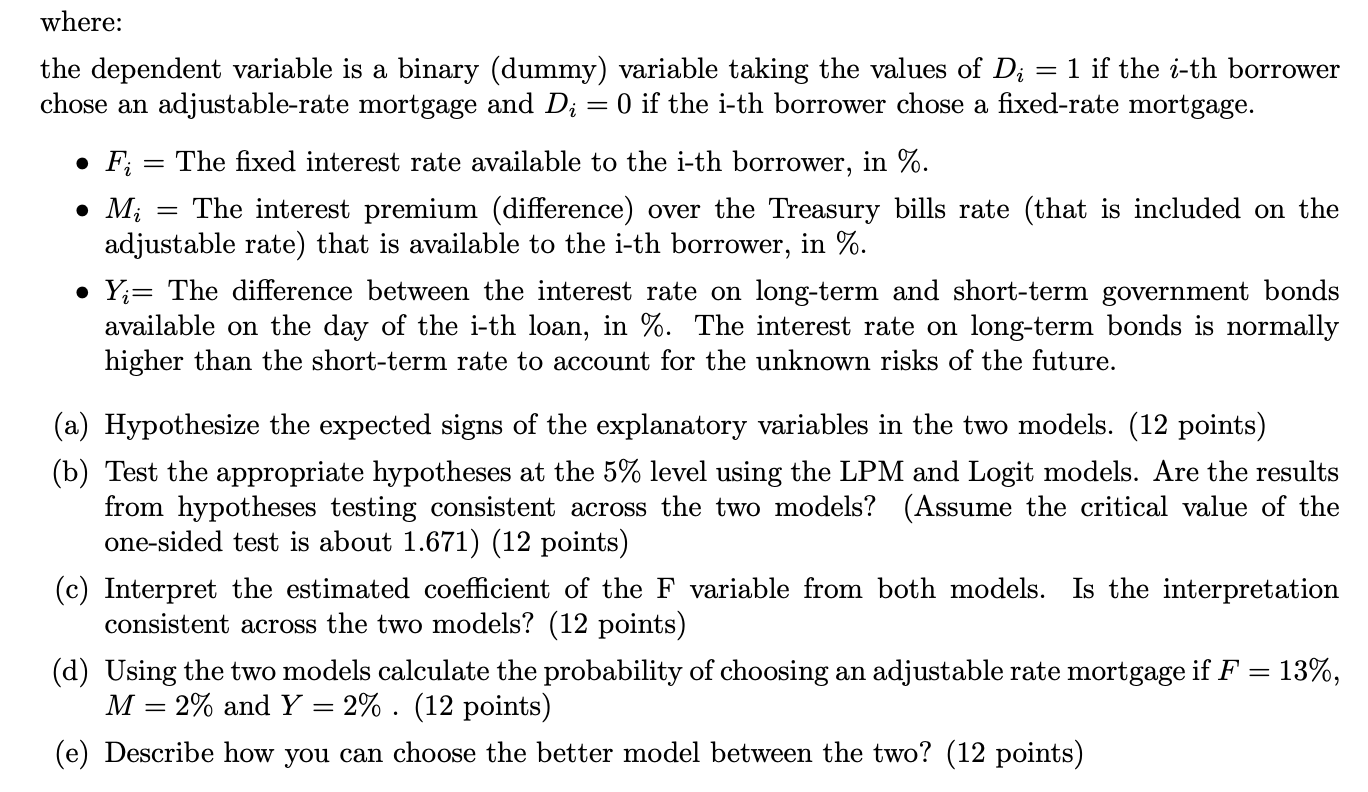
II. Problem - You have to show your work. No credit without an explanation (60 marks). 1. The two most-used forms of mortgages are fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages: . If a borrower chooses a fixed-rate mortgage, the interest rate that she pays is fixed over the life of the loan. . If a borrower chooses an adjustable-rate mortgage, the interest rate that she pays is calculated as the rate of short-term government bonds plus a risk premium and is adjusted up or down (following the changes in the rate of government bonds) during the life of the loan. . Since adjustable-rate mortgages carry a risk of higher rates in the long run, they usually have a lower initial interest rate than do fixed-rate mortgages. In order to evaluate the factors influencing the choice between adjustable and fixed-rate mortgage loans, we have run a Linear Probability Model (LPM) and Logit Model the results of which (estimated beta coefficients and t-ratios) appear below, based on 78 observations: LPM Logit F (t-ratio) 0.226 (2.980) 1.185 (2.700) M (t-ratio) -0.127 (-2.600) -0.660 (-2.317) Y (t-ratio) 0.799 (-2.567) -4.030 (-2.353 Constant (t-ratio) -1.018 (-0.810) -8.192 (-1.190)where: the dependent variable is a binary (dummy) variable taking the values of D; = 1 if the i-th borrower chose an adjustable-rate mortgage and D.- = 0 if the i-th borrower chose a xed-rate mortgage. 0 P;- = The xed interest rate available to the i-th borrower, in %. o M:- = The interest premium (difference) over the Treasury bills rate (that is included on the adjustable rate) that is available to the i-th borrower, in %. 0 Yr: The difference between the interest rate on long-term and short-term government bonds available on the day of the i-th loan, in %. The interest rate on long-term bonds is normally higher than the short-term rate to accOunt for the unknown risks of the future. (a) Hypothesize the expected signs of the explanatory variables in the two models. (12 points) (b) Test the appropriate hypotheses at the 5% level using the LPM and Logit models. Are the results from hypotheses testing consistent across the two models? (Assume the critical value of the one-sided test is about 1.671) (12 points) (0) Interpret the estimated coefcient of the F variable from both models. Is the interpretation consistent across the two models? (12 points) (d) Using the two models calculate the probability of choosing an adjustable rate mortgage if F = 13%, M = 2% and Y = 2% . (12 points) (e) Describe how you can choose the better model between the two? (12 points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


