Question: pleas ehellp 6. (6 points) A common representation of data uses matrices and vectors, so it is helpful to familiarize ourselves with linear algebra notation,
pleas ehellp

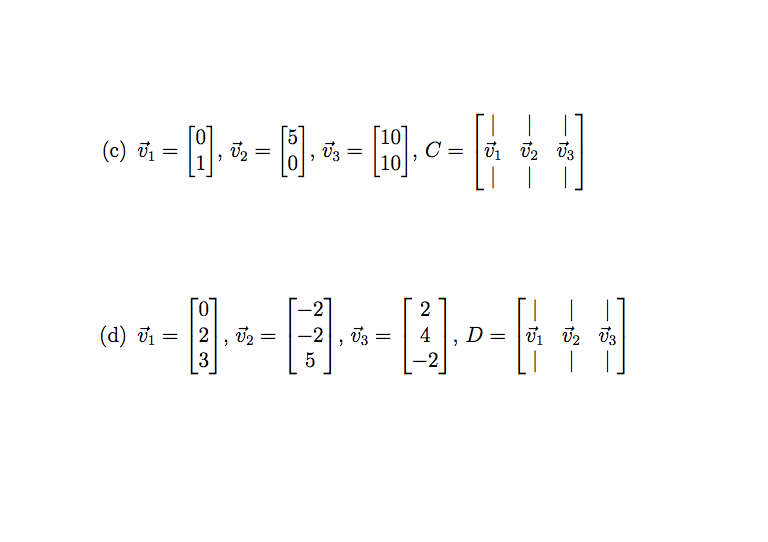
6. (6 points) A common representation of data uses matrices and vectors, so it is helpful to familiarize ourselves with linear algebra notation, as well as some simple operations. Dene a vector 13" to be a column vector. Then, the following properties hold: 0 or? with 0 some constant, is equal to a new vector where every element in of} is equal to the corresponding element in 13' multiplied by c. For example, 2 [g] = [i] o '31 +133 is equal to a new vector with elements equal to the elementwise addition of 4 a 1 _2 1:1 and 1:2. For example, [2] + [ 43] = [6 ] The above properties form our denition for a linear combination of vectors. 1713 is a linear combination of 133 and fig if g 2 as} + b172, where a and b are some constants. Oftentimes, we stack column vectors to form a matrix. Dene the rank of a matrix A to be equal to the maximal number of linearly independent columns in A. A set of columns is linearly independent if no column can be written as a linear combination of any other column(s) within the set. For example, let A be a matrix with 4 columns. If three of these columns are linearly independent, but the fourth can be written as a linear combination of the other three, then rank(A) = 3. For each part below, you will be presented with a set of vectors, and a matrix consisting of those vectors stacked in columns. State the rank of the matrix, and whether or not the matrix is full rank. If the matrix is not full rank, state a linear relationship among the vectorsfor example: 131 2 g. | | (a).=[3].a.=[,A= a. | | \f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


