Question: Please add explanation for this. Much appreciated. Consider the incomplete function below: def selection_sort(data): for pass_num in range (len (data)-1, 0, -1): Complete the selection_sort()
Please add explanation for this. Much appreciated.
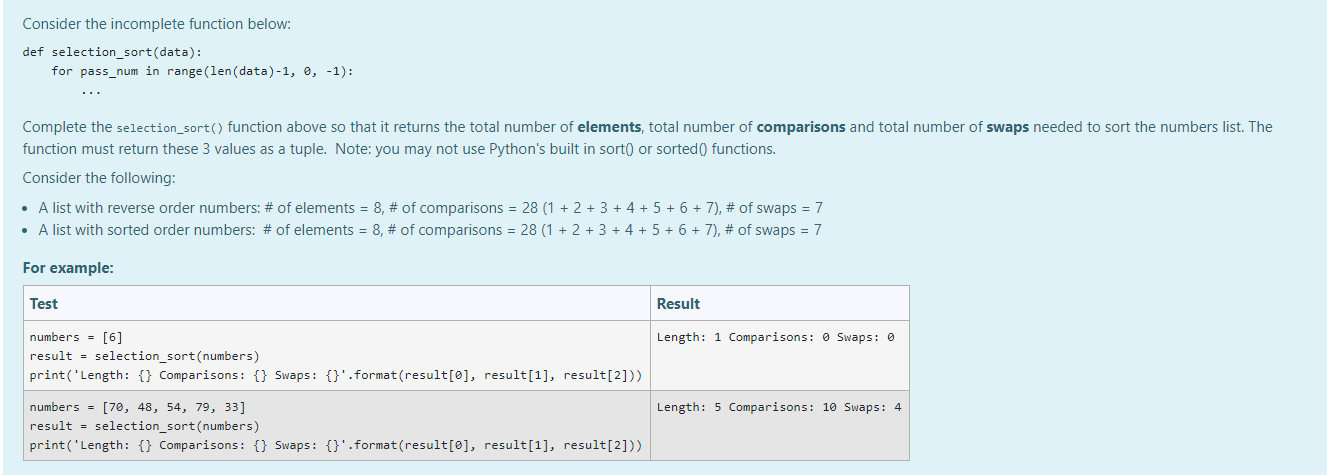
Consider the incomplete function below: def selection_sort(data): for pass_num in range (len (data)-1, 0, -1): Complete the selection_sort() function above so that it returns the total number of elements, total number of comparisons and total number of swaps needed to sort the numbers list. The function must return these 3 values as a tuple. Note: you may not use Python's built in sort( or sorted() functions. Consider the following: A list with reverse order numbers: # of elements = 8, # of comparisons = 28 (1 + 2+ 3+ 4+ 5+ 6+ 7), # of swaps = 7 A list with sorted order numbers: # of elements = 8, # of comparisons = 28 (1 + 2 +3 +4 + 5+ 6+ 7), # of swaps = 7 For example: Test Result Length: 1 Comparisons: Swaps: 0 numbers = [6] result = selection_sort(numbers) print('Length: {} Comparisons: {} Swaps: {}'.format(result[@], result[1], result[2])) numbers = [70, 48, 54, 79, 33] result = selection_sort(numbers) print('Length: {} Comparisons: {} Swaps: {}'.format(result[@], result[1], result[2])) Length: 5 Comparisons: 10 Swaps: 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


