Question: Please answer A and B. Thank you. Exercise 10-24 Oriole Corporation owns and manages a small 10-store shopping centre, which it classifies as an investment

Please answer A and B. Thank you.
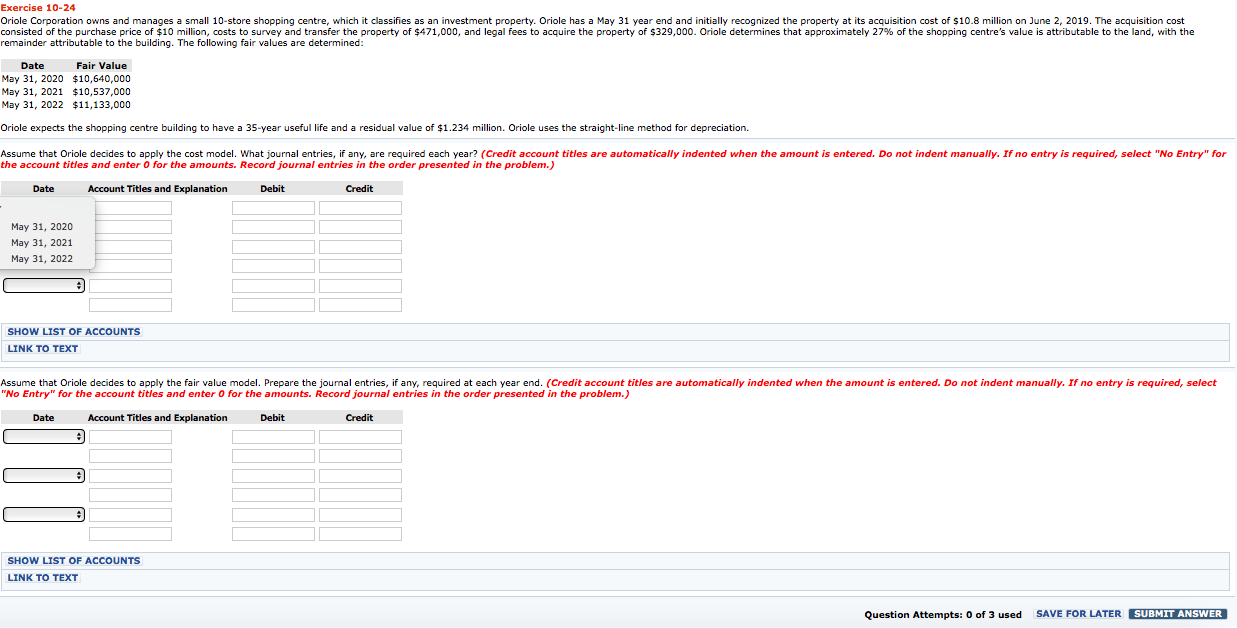
Exercise 10-24 Oriole Corporation owns and manages a small 10-store shopping centre, which it classifies as an investment property. Oriole has a May 31 year end and initially recognized the property at its acquisition cost of $10.8 million on June 2, 2019. The acquisition cost consisted of the purchase price of $10 million, costs to survey and transfer the property of $471,000, and legal fees to acquire the property of $329,000. Oriole determines that approximately 27% of the shopping centre's value is attributable to the land, with the remainder attributable to the building. The following fair values are determined: Date Fair Value May 31, 2020 $10,640,000 May 31, 2021 $10,537,000 May 31, 2022 $11,133,000 Oriole expects the shopping centre building to have a 35-year useful life and a residual value of $1.234 million. Oriole uses the straight-line method for depreciation. Assume that Oriole decides to apply the cost model. What journal entries, if any, are required each year? (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter o for the amounts. Record journal entries in the order presented in the problem.) Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit May 31, 2020 May 31, 2021 May 31, 2022 SHOW LIST OF ACCOUNTS LINK TO TEXT Assume that Oriole decides to apply the fair value model. Prepare the journal entries, if any, required at each year end. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter o for the amounts. Record journal entries in the order presented in the problem.) Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit CD SHOW LIST OF ACCOUNTS LINK TO TEXT Question Attempts: 0 of 3 used SAVE FOR LATER SUBMIT ANSWER List of Accounts Exercise 10-17 Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Accumulated Depreciation - Buildings Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment Accumulated Depreciation - Leasehold Improvements Accumulated Depreciation - Machinery Accumulated Depreciation - Vehicles Advertising Expense Asset Retirement Obligation Buildings Cash Common Shares Contributed Surplus Contributed Surplus - Donated Capital Cost of Goods Sold Deferred Revenue - Government Grants Depreciation Expense Donation Revenue Equipment Finance Expense Finance Revenue Gain or Loss in Value of Investment Property Gain on Disposal of Building Gain on Disposal of Equipment Gain on Disposal of Machinery Gain on Disposal of Vehicles GST Payable GST Receivable Interest Expense Interest Income Interest Payable Interest Receivable Inventory Investment Property Land Land Improvements Loss on Disposal of Building Loss on Disposal of Equipment Loss on Disposal of Land Loss on Disposal of Machinery Loss on Disposal of Vehicles Machinery Repairs and Maintenance Expense Mineral Resources Mortgage Payable No Entry Notes Payable Notes Receivable Office Expense Owner's Drawings Prepaid Expenses Prepaid Insurance Profit on Construction Purchase Discounts Purchase Returns and Allowances Rent Expense Revaluation Gain or Loss Revaluation Surplus (OCI) Revenue - Government Grants Salaries and Wages Expense Salaries and Wages Payable Sales Revenue Service Revenue Supplies Supplies Expense Tenant Deposits Liability Vehicles Exercise 10-24 Oriole Corporation owns and manages a small 10-store shopping centre, which it classifies as an investment property. Oriole has a May 31 year end and initially recognized the property at its acquisition cost of $10.8 million on June 2, 2019. The acquisition cost consisted of the purchase price of $10 million, costs to survey and transfer the property of $471,000, and legal fees to acquire the property of $329,000. Oriole determines that approximately 27% of the shopping centre's value is attributable to the land, with the remainder attributable to the building. The following fair values are determined: Date Fair Value May 31, 2020 $10,640,000 May 31, 2021 $10,537,000 May 31, 2022 $11,133,000 Oriole expects the shopping centre building to have a 35-year useful life and a residual value of $1.234 million. Oriole uses the straight-line method for depreciation. Assume that Oriole decides to apply the cost model. What journal entries, if any, are required each year? (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter o for the amounts. Record journal entries in the order presented in the problem.) Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit May 31, 2020 May 31, 2021 May 31, 2022 SHOW LIST OF ACCOUNTS LINK TO TEXT Assume that Oriole decides to apply the fair value model. Prepare the journal entries, if any, required at each year end. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter o for the amounts. Record journal entries in the order presented in the problem.) Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit CD SHOW LIST OF ACCOUNTS LINK TO TEXT Question Attempts: 0 of 3 used SAVE FOR LATER SUBMIT ANSWER List of Accounts Exercise 10-17 Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Accumulated Depreciation - Buildings Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment Accumulated Depreciation - Leasehold Improvements Accumulated Depreciation - Machinery Accumulated Depreciation - Vehicles Advertising Expense Asset Retirement Obligation Buildings Cash Common Shares Contributed Surplus Contributed Surplus - Donated Capital Cost of Goods Sold Deferred Revenue - Government Grants Depreciation Expense Donation Revenue Equipment Finance Expense Finance Revenue Gain or Loss in Value of Investment Property Gain on Disposal of Building Gain on Disposal of Equipment Gain on Disposal of Machinery Gain on Disposal of Vehicles GST Payable GST Receivable Interest Expense Interest Income Interest Payable Interest Receivable Inventory Investment Property Land Land Improvements Loss on Disposal of Building Loss on Disposal of Equipment Loss on Disposal of Land Loss on Disposal of Machinery Loss on Disposal of Vehicles Machinery Repairs and Maintenance Expense Mineral Resources Mortgage Payable No Entry Notes Payable Notes Receivable Office Expense Owner's Drawings Prepaid Expenses Prepaid Insurance Profit on Construction Purchase Discounts Purchase Returns and Allowances Rent Expense Revaluation Gain or Loss Revaluation Surplus (OCI) Revenue - Government Grants Salaries and Wages Expense Salaries and Wages Payable Sales Revenue Service Revenue Supplies Supplies Expense Tenant Deposits Liability Vehicles
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


