Question: PLEASE ANSWER ALL 6 !! WILL !!!! Bunnell Corporation is a manufacturer that uses job-order costing. On January 1, the company's inventory balances were as

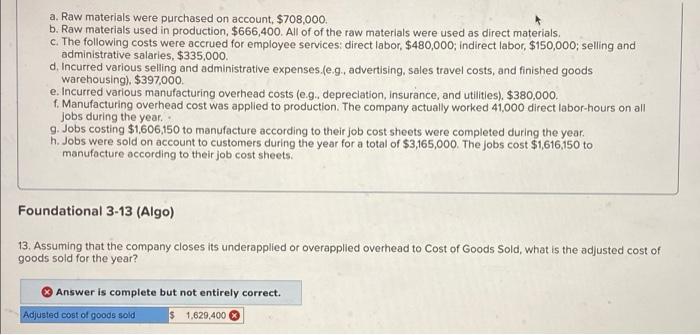

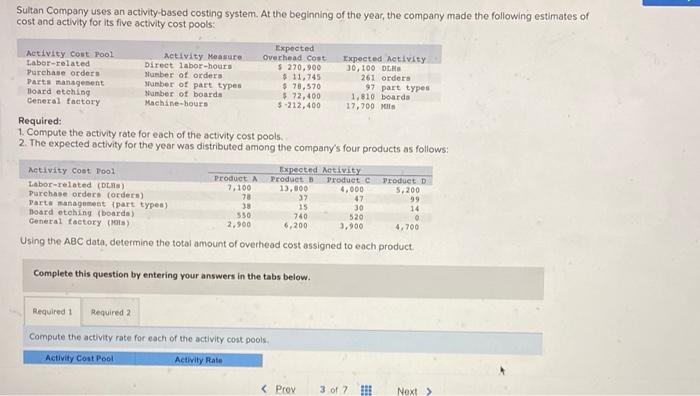
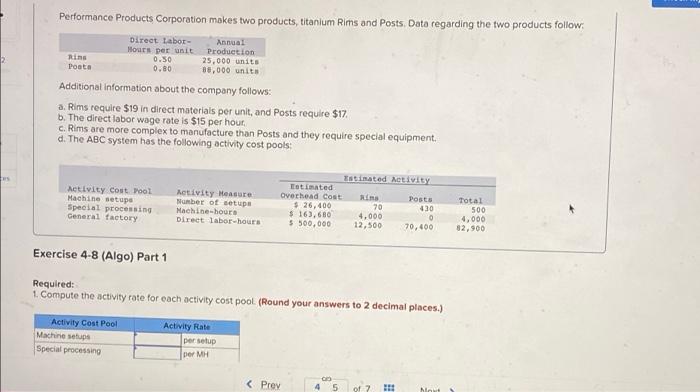
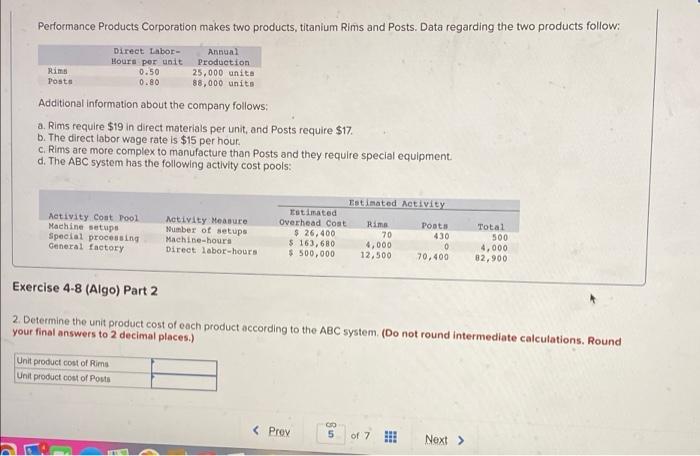
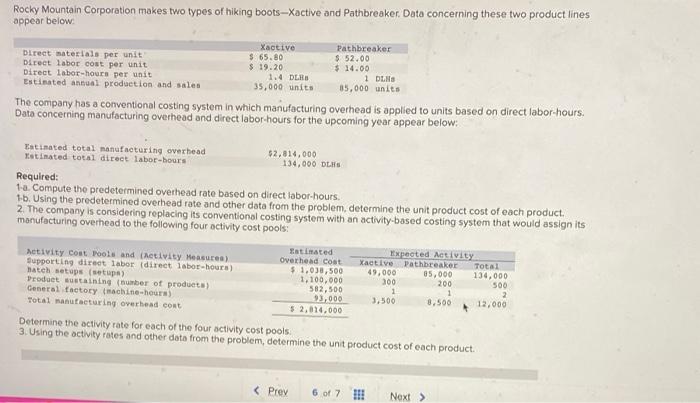
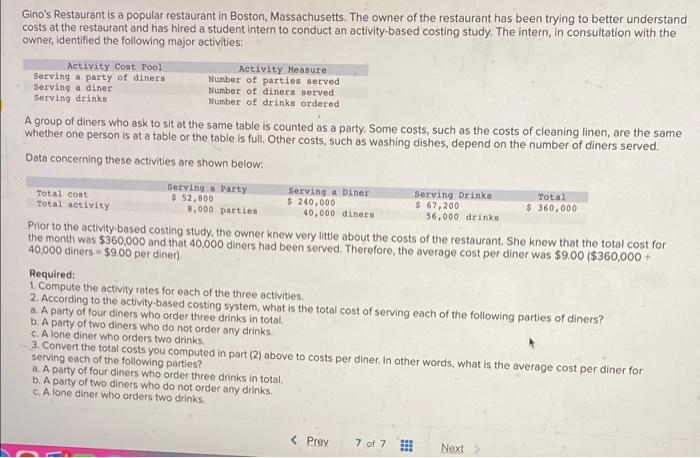
Bunnell Corporation is a manufacturer that uses job-order costing. On January 1, the company's inventory balances were as follows: Raw materials $ 77,000 Work in process $ 29,000 Finished goods $ 59,400 The company applies overhead cost to jobs on the basis of direct labor-hours. For the current year, the company's predetermined overhead rate of $13.25 per direct labor hour was based on a cost formula that estimated $530,000 of total manufacturing overhead for an estimated activity level of 40,000 direct labor-hours. The following transactions were recorded for the year o. Raw materials were purchased on account $708,000, b. Raw materials used in production, $666,400. All of of the raw materials were used as direct materials c. The following costs were accrued for employee services: direct labor, $480,000, indirect labor, $150,000; selling and administrative salaries, $335,000 d. Incurred various selling and administrative expenses (e.g., advertising, sales travel costs, and finished goods warehousing), $397,000. e. Incurred various manufacturing overhead costs (eg, depreciation, insurance, and utilities). $380,000 f. Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to production. The company actually worked 41,000 direct labor-hours on all jobs during the year. 9. Jobs costing $1606,150 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets were completed during the year h. Jobs were sold on account to customers during the year for a total of $3,165,000. The jobs cost $1616,150 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets. a. Raw materials were purchased on account, $708,000. b. Raw materials used in production, $666,400. All of of the raw materials were used as direct materials c. The following costs were accrued for employee services: direct labor, $480,000; indirect labor, $150,000; selling and administrative salaries, $335,000. d. Incurred various selling and administrative expenses.(e.g., advertising, sales travel costs, and finished goods warehousing) $397,000 e. Incurred various manufacturing overhead costs (e.g. depreciation, Insurance, and utilities). $380,000. f. Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to production. The company actually worked 41,000 direct labor-hours on all Jobs during the year. 9. Jobs costing $1,606,150 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets were completed during the year. h. Jobs were sold on account to customers during the year for a total of $3,165,000. The jobs cost $1,616,150 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets. Foundational 3-13 (Algo) 13. Assuming that the company closes its underapplied or overapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold, what is the adjusted cost of goods sold for the year? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Adjusted cost of goods sold $ 1,629,400 Retu MIL U HUYUUUUUUUUUU total manufacturing overhead for an estimated activity level of 40,000 direct labor-hours. The following transactions were recorded for the year a. Raw materials were purchased on account, $708,000 b. Raw materials used in production, $666,400. All of of the raw materials were used as direct materials c. The following costs were accrued for employee services: direct labor, $480,000; indirect labor, $150,000; selling and administrative salaries, $335,000 d. Incurred various selling and administrative expenses (0.9., advertising, sales travel costs, and finished goods warehousing). $397,000. e. Incurred various manufacturing overhead costs (eg., depreciation, insurance, and utilities), $380,000 1. Manufacturing overhead cost was applied to production. The company actually worked 41.000 direct labor-hours on all Jobs during the year. g. Jobs costing $1606,150 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets were completed during the year, h Jobs were sold on account to customers during the year for a total of $3,165,000. The jobs cost $1,616,150 to manufacture according to their job cost sheets, Foundational 3-14 (Algo) 14. What is the gross margin for the year? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Gross margin $ 1,535,600 Sultan Company uses an activity-based costing system. At the beginning of the year, the company made the following estimates of cost and activity for its five activity cost pools: Expected Activity cost Pool Activity Measure Overhead cost Expected Activity Labor-related Direct labor-hours $ 270,900 10, 100 DLHH Purchase orders Number of orders $ 11,745 261 orders Parts management umber of part types $78,570 97 part types Board etching Number of boards $ 72,400 1,810 boards General factory Machine-hours 5-212,400 17,700 M Required: 1. Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools 2. The expected activity for the year was distributed among the company's four products as follows: Activity Cost Pool Expected Activity Labor-related (RS) Product Products Product Product D. 7.100 Purchase orders (orders) 13,800 4.000 5,200 70 37 47 99 Parts management part types) 38 15 Doard etching boards) 30 14 550 740 520 General factory (1) 2.900 6.200 3,900 4.700 Using the ABC data, determine the total amount of overhead cost assigned to each product Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools Activity Cost Pool Activity Rate Performance Products Corporation makes two products, titanium Rims and Posts Data regarding the two products follow Direct Labor- Annual Houts per unit Production Rins 0.50 25,000 units Posta 0.80 88,000 units Additional Information about the company follows: a. Rims require $19 in direct materials per unit, and Posts require $17. b. The direct labor wage rate is $15 per hour c. Rims are more complex to manufacture than Posts and they require special equipment. d. The ABC system has the following activity cost pools: Activity Cost Pool Machine stupe Special processing General factory Activity Mercure Number of setup Machine hours Direct labor-hours Isticated activity Totiated Overhead cost Ruins Posts $.26,400 70 430 $ 163,680 4,000 $ 500,000 12,500 70,400 Total 500 4,000 82,900 Exercise 4-8 (Algo) Part 1 Required: 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Activity Cost Pool Machine sebe Special processing Activity Rate per setup per MH Rocky Mountain Corporation makes two types of biking boots-Xactive and Pathbreaker. Data concerning these two product lines appear below Xactive Pathbreaker Direct materials per unit $ 65.80 $ 52.00 Direct labor cost per unit $ 19.20 Direct labor-hours per unit $14.00 1.4 DLR 1 DLNA Estimated annual production and sales 35,000 units 85,000 units The company has a conventional costing system in which manufacturing overhead is applied to units based on direct labor-hours. Data concerning manufacturing overhead and direct labor hours for the upcoming year appear below: Estimated total manufacturing overhead $2.814,000 Estimated total direct labor-hours 134,000 DI Required: 1-a. Compute the predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. 1-5. Using the predetermined overhead rate and other data from the problem, determine the unit product cost of each product. 2. The company is considering replacing its conventional costing system with an activity-based costing system that would assign its manufacturing overhead to the following four activity cost pools: Estimated Activity Controls and Activity Measures) Expected Activity Supporting direct labor direct labor-hours) overhead coat Xactive Pathbreaker Total match setups (setups) $ 1.030,500 49,000 85,000 134,000 Product sustaining (umber of products) 1.100,000 200 200 500 General factory machine-hours) 582,500 1 1 93,000 Total manufacturing overhead cost 3,500 8,500 12,000 52,614.000 Determine the activity rate for each of the four activity cost pools 3. Using the activity rates and other data from the problem, determine the unit product cost of each product Prev 6 of 7 1. Next > Gino's Restaurant is a popular restaurant in Boston, Massachusetts. The owner of the restaurant has been trying to better understand costs at the restaurant and has hired a student intern to conduct an activity-based costing study. The intern, in consultation with the owner, identified the following major activities: Activity Cont Tool Activity Measure Serving a party of diners Number of parties served Serving a diner Number of diners served Serving drinks Number of drinks ordered A group of diners who ask to sit at the same table is counted as a party. Some costs, such as the costs of cleaning linen, are the same whether one person is at a table or the table is full. Other costs, such as washing dishes, depend on the number of diners served. Data concerning these activities are shown below: Serving a Party Serving a Diner Serving Drinko Total Total cont $ 52,800 $ 240,000 Total activity $ 67,200 $360,000 8,000 parties 40,000 diners 56.000 drinks Prior to the activity based costing study, the owner knew very little about the costs of the restaurant. She knew that the total cost for the month was $360,000 and that 40.000 diners had been served. Therefore, the average cost per diner was $9.00 ($360,000+ 40,000 diners $9.00 per diner) Required: 1. Compute the activity rates for each of the three activities, 2. According to the activity-based costing system, what is the total cost of serving each of the following parties of diners? a. A party of four diners who order three drinks in total b. A party of two diners who do not order any drinks c. A lone diner who orders two drinks 3. Convert the total costs you computed in part (2) above to costs per diner In other words, what is the average cost per diner for serving each of the following parties? a. A party of four diners who order three drinks in total, b. A party of two diners who do not order any drinks c. Alone diner who orders two drinks
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


