Question: Please answer all parts and code preferably in Python. And provide explanation to every part of the question. Thanks 2.4. Write a routine for estimating
Please answer all parts and code preferably in Python. And provide explanation to every part of the question. Thanks
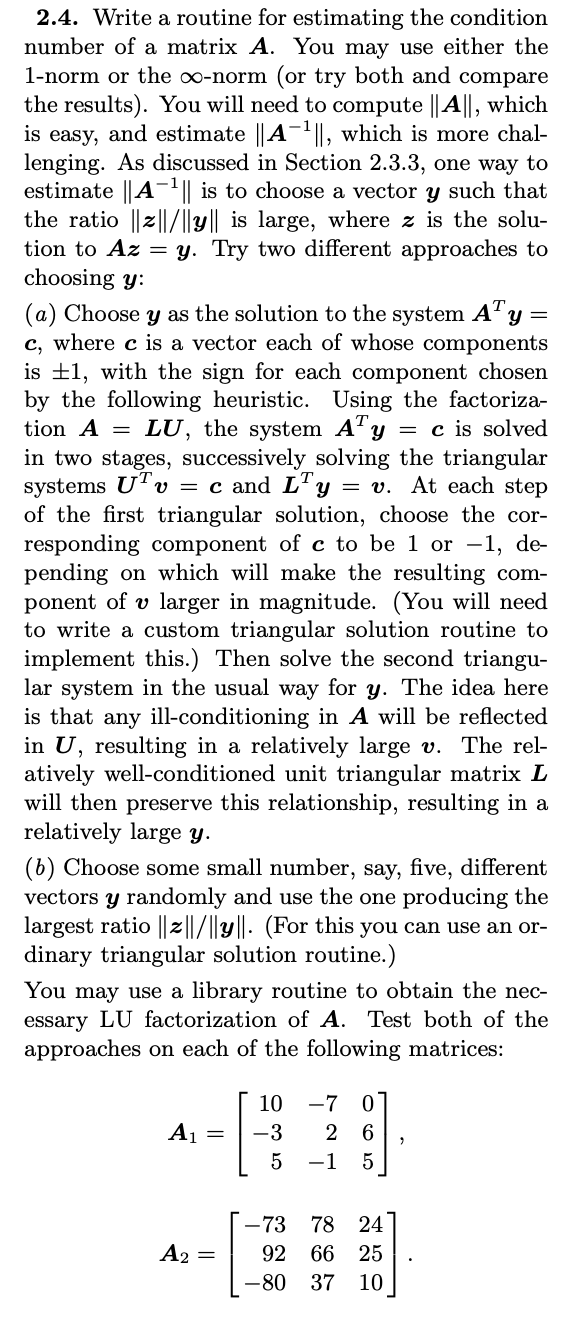
 2.4. Write a routine for estimating the condition number of a matrix A. You may use either the 1-norm or the -norm (or try both and compare the results). You will need to compute A, which is easy, and estimate A1, which is more chal- lenging. As discussed in Section 2.3.3, one way to estimate A1 is to choose a vector y such that the ratio z/y is large, where z is the solu- tion to Az = y. Try two different approaches to choosing y: (a) Choose y as the solution to the system AT y = c, where c is a vector each of whose components is 1, with the sign for each component chosen by the following heuristic. Using the factoriza- tion A = LU, the system ATy = c is solved in two stages, successively solving the triangular systems UTv = c and LTy = v. At each step of the first triangular solution, choose the cor- responding component of c to be 1 or 1, de- pending on which will make the resulting com- ponent of v larger in magnitude. (You will need to write a custom triangular solution routine to implement this.) Then solve the second triangu- lar system in the usual way for y. The idea here is that any ill-conditioning in A will be reflected in U, resulting in a relatively large v. The rel- atively well-conditioned unit triangular matrix L will then preserve this relationship, resulting in a relatively large y. (b) Choose some small number, say, five, different vectors y randomly and use the one producing the largest ratio z/y. (For this you can use an or- dinary triangular solution routine.) You may use a library routine to obtain the nec- essary LU factorization of A. Test both of the approaches on each of the following matrices:
2.4. Write a routine for estimating the condition number of a matrix A. You may use either the 1-norm or the -norm (or try both and compare the results). You will need to compute A, which is easy, and estimate A1, which is more chal- lenging. As discussed in Section 2.3.3, one way to estimate A1 is to choose a vector y such that the ratio z/y is large, where z is the solu- tion to Az = y. Try two different approaches to choosing y: (a) Choose y as the solution to the system AT y = c, where c is a vector each of whose components is 1, with the sign for each component chosen by the following heuristic. Using the factoriza- tion A = LU, the system ATy = c is solved in two stages, successively solving the triangular systems UTv = c and LTy = v. At each step of the first triangular solution, choose the cor- responding component of c to be 1 or 1, de- pending on which will make the resulting com- ponent of v larger in magnitude. (You will need to write a custom triangular solution routine to implement this.) Then solve the second triangu- lar system in the usual way for y. The idea here is that any ill-conditioning in A will be reflected in U, resulting in a relatively large v. The rel- atively well-conditioned unit triangular matrix L will then preserve this relationship, resulting in a relatively large y. (b) Choose some small number, say, five, different vectors y randomly and use the one producing the largest ratio z/y. (For this you can use an or- dinary triangular solution routine.) You may use a library routine to obtain the nec- essary LU factorization of A. Test both of the approaches on each of the following matrices:
2.4. Write a routine for estimating the condition number of a matrix A. You may use either the 1-norm or the o-norm (or try both and compare the results). You will need to compute || A||, which is easy, and estimate || A-1||, which is more chal- lenging. As discussed in Section 2.3.3, one way to estimate || A--|| is to choose a vector y such that the ratio ||2|\/||y|| is large, where z is the solu- tion to Az = y. Try two different approaches to choosing y: (a) Choose y as the solution to the system Aly= c, where c is a vector each of whose components is +1, with the sign for each component chosen by the following heuristic. Using the factoriza- tion A = LU, the system Any = c is solved in two stages, successively solving the triangular systems U?v = c and L'y = v. At each step of the first triangular solution, choose the cor- responding component of c to be 1 or -1, de- pending on which will make the resulting com- ponent of v larger in magnitude. (You will need to write a custom triangular solution routine to implement this.) Then solve the second triangu- lar system in the usual way for y. The idea here is that any ill-conditioning in A will be reflected in U, resulting in a relatively large v. The rel- atively well-conditioned unit triangular matrix L will then preserve this relationship, resulting in a relatively large y. (6) Choose some small number, say, five, different vectors y randomly and use the one producing the largest ratio || 21/lyl. (For this you can use an or- dinary triangular solution routine.) You may use a library routine to obtain the nec- essary LU factorization of A. Test both of the approaches on each of the following matrices: A1 = [ 10 -3 5 -7 07 2 6 -1 A2 = 73 78 92 66 -80 37 24 25 10 | How do the results using these two methods com- pare? To check the quality of your estimates, com- pute A- explicitly to determine its true norm (this computation can also make use of the LU factorization already computed). If you have ac- cess to linear equations software that already in- cludes a condition estimator, how do your results compare with its? 2.4. Write a routine for estimating the condition number of a matrix A. You may use either the 1-norm or the o-norm (or try both and compare the results). You will need to compute || A||, which is easy, and estimate || A-1||, which is more chal- lenging. As discussed in Section 2.3.3, one way to estimate || A--|| is to choose a vector y such that the ratio ||2|\/||y|| is large, where z is the solu- tion to Az = y. Try two different approaches to choosing y: (a) Choose y as the solution to the system Aly= c, where c is a vector each of whose components is +1, with the sign for each component chosen by the following heuristic. Using the factoriza- tion A = LU, the system Any = c is solved in two stages, successively solving the triangular systems U?v = c and L'y = v. At each step of the first triangular solution, choose the cor- responding component of c to be 1 or -1, de- pending on which will make the resulting com- ponent of v larger in magnitude. (You will need to write a custom triangular solution routine to implement this.) Then solve the second triangu- lar system in the usual way for y. The idea here is that any ill-conditioning in A will be reflected in U, resulting in a relatively large v. The rel- atively well-conditioned unit triangular matrix L will then preserve this relationship, resulting in a relatively large y. (6) Choose some small number, say, five, different vectors y randomly and use the one producing the largest ratio || 21/lyl. (For this you can use an or- dinary triangular solution routine.) You may use a library routine to obtain the nec- essary LU factorization of A. Test both of the approaches on each of the following matrices: A1 = [ 10 -3 5 -7 07 2 6 -1 A2 = 73 78 92 66 -80 37 24 25 10 | How do the results using these two methods com- pare? To check the quality of your estimates, com- pute A- explicitly to determine its true norm (this computation can also make use of the LU factorization already computed). If you have ac- cess to linear equations software that already in- cludes a condition estimator, how do your results compare with its
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


