Question: Please answer all questions. Thank you! Please answer the 7 questions on the last page. what is not clear? Can you explain what is not

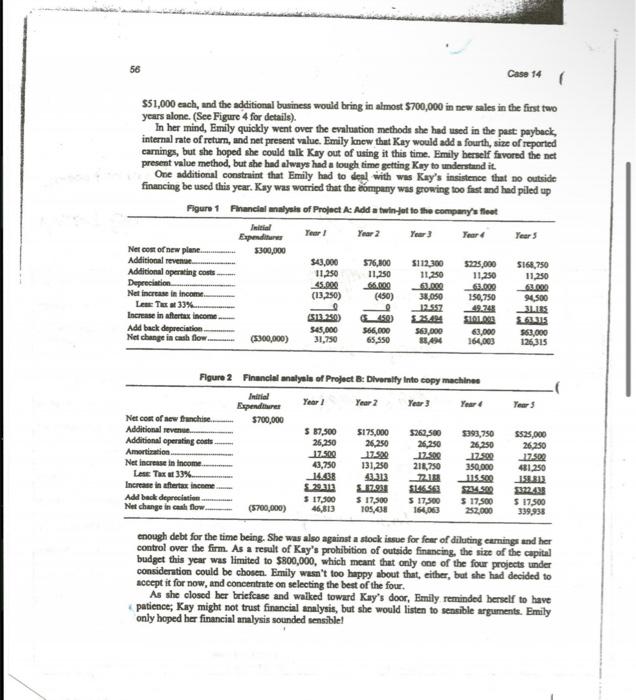
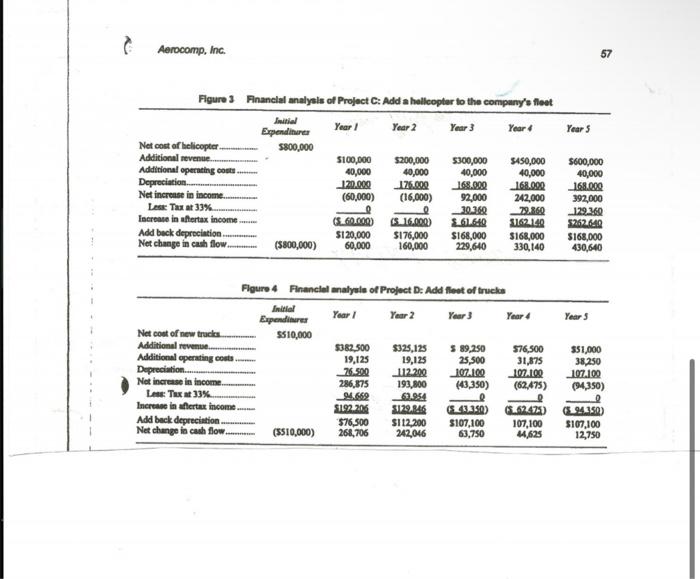

Aerocomp, Inc. As ahe beaded soward her bosi's office, Emily Hamilton, ehief operating officer for the Aerocoenp CorporitionA. A proponal to add a jet b the competter services frm that opecielired in airberne ipport-wished ine coeld oompeny's flect. The pinne wat only lie years old wod wat eonsidered a remember more of her training in good bey at 3300,000 . Hn retum, the finascial theory that she had bece plane would bring over 5600,000 in expesed to in collige. Emily had jost completed summartxing the fimuncial additional stevenoe turing the nett five yean with oely about 556,000 in mapeets of four eapital investment projects that were open to Aeroconp during the coming year, and the was B. A proposal to diveraily inte copy froed with the tatk of rooomenening which should be seloctod. What machines. The franchise wat to cont 5700,000 , shich would be amortized concerned ber was the knowledge that over a 40-year period. The new her boss, Kay Manth, "ntrset imart" burinese wa erpected to genernte over chief executive, with no background in \$1.4 million in sales over the nett five financial theory, would ferimedintely your, ead over $800,000 in aflertar favor the project that promised the C. emingn. (Soe Figare 2 for details.) highest gain in reported net ineome. Emily luow that melectiog projects parely on that besis would be incerroct; bet she Wasn't aure of her ability to ooevinot Kay, who tended to asuase fintncien thought up fancy methods jut to show how emat they were. As ahe prepared to enter Kxy's oftice, Emily pulled her summary sheots from ber briefease and quicidy reviewed the details of the four projects, all of which she considered to be equally risky. D. A propeeal to begin operating a fleet of truck. Ten sould be bought for anly $51,000 each, and the additional business would bring in almont $700,000 in new sales in the first two years alone. (See Figure 4 for details). In her mind, Emily quickly went over the evaluation methods she had used in the past paybeck, internal rate of return, and net present value. Emily lonew thut Kay would add a fourth, size of reported carnings, but she boped she coald tnlk Kay out of using it this time. Emily berself frvored the net present value method, but ahe had always had a tough time getting Kay to understand it. One additional constraint that Emily had to deal with was Kary's insistence that no outside financing be used this year. Kay was worried that the eompany was growing too fast and had piled up Figure 1 Financiol malysit of Projoct Ac Add a twin-lot to the comoany'u fleet enough debt for the time being. She was also against a stock iesue for fear of diluting earnings and her control over the firm. As a result of Kay s prohibition of outside financing, the size of the capital budget this year was limited to $800,000, which meant that only one of the four projects under consideration could be chosen. Emily wasn't too happy about that, either, but she had decided to accept it for now, and concentrate on selecting the best of the four. As she elosed ber briefcase and walked toward Kay's door, Emily reminded berself to have patience, Kay might not trust financial analysis, but she would listen to sensible arguments. Emily only boped her financial amalysis sounded sensiblel Aerocomp, Inc. Figure 3 Financlal analysis of Project C: Add a hollcopter to the company's neet 1. Refer to Figures 1 through 4. Add up the total increase in after-tax income for each project. Given what you know about Kay Mash, to which project do you think she will be attracted? 2. Computer the Payback Period, Discounted Payback Period, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Productivity Index of all four alternatives based on cash flow. User 10 percent for the cost of capital in your calculations. For the Payback Period and for the Discounted Payback Period, compute to the midyear points as discussed in class. 3. a. According to the payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 4. a. According to the Discounted Payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 5. a. According to the Net Present Value method, which project should be selected? b. What are the major advantages of the Net Present Value method? c. What are any disadvantages of the Net Present Value Method? d. If Kay had not put a limit on the size of the capital budget, under the NPV method which projects would have been accepted? 6. a. According to the IRR method, which project should be chosen? b. What is the major disadvantage of the IRR method that occurs when HIGH IRR projects are selected? c. Can you think of another disadvantage of the IRR method? (Hint: Look over the four alternatives and compare the sizes of the projects. Ask yourself whether you would prefer to make a large percent return on a small amount of money or a small percent gain on a large amount of money.) d. Do the NPV and IRR both reject the same projects - Why? 7. a. According to the Productivity Index, which project should be chosen? b. Explain why people use the Productivity Index. c. Explain why a Productivity Index so closely correlates with the results of NPV. Aerocomp, Inc. As ahe beaded soward her bosi's office, Emily Hamilton, ehief operating officer for the Aerocoenp CorporitionA. A proponal to add a jet b the competter services frm that opecielired in airberne ipport-wished ine coeld oompeny's flect. The pinne wat only lie years old wod wat eonsidered a remember more of her training in good bey at 3300,000 . Hn retum, the finascial theory that she had bece plane would bring over 5600,000 in expesed to in collige. Emily had jost completed summartxing the fimuncial additional stevenoe turing the nett five yean with oely about 556,000 in mapeets of four eapital investment projects that were open to Aeroconp during the coming year, and the was B. A proposal to diveraily inte copy froed with the tatk of rooomenening which should be seloctod. What machines. The franchise wat to cont 5700,000 , shich would be amortized concerned ber was the knowledge that over a 40-year period. The new her boss, Kay Manth, "ntrset imart" burinese wa erpected to genernte over chief executive, with no background in \$1.4 million in sales over the nett five financial theory, would ferimedintely your, ead over $800,000 in aflertar favor the project that promised the C. emingn. (Soe Figare 2 for details.) highest gain in reported net ineome. Emily luow that melectiog projects parely on that besis would be incerroct; bet she Wasn't aure of her ability to ooevinot Kay, who tended to asuase fintncien thought up fancy methods jut to show how emat they were. As ahe prepared to enter Kxy's oftice, Emily pulled her summary sheots from ber briefease and quicidy reviewed the details of the four projects, all of which she considered to be equally risky. D. A propeeal to begin operating a fleet of truck. Ten sould be bought for anly $51,000 each, and the additional business would bring in almont $700,000 in new sales in the first two years alone. (See Figure 4 for details). In her mind, Emily quickly went over the evaluation methods she had used in the past paybeck, internal rate of return, and net present value. Emily lonew thut Kay would add a fourth, size of reported carnings, but she boped she coald tnlk Kay out of using it this time. Emily berself frvored the net present value method, but ahe had always had a tough time getting Kay to understand it. One additional constraint that Emily had to deal with was Kary's insistence that no outside financing be used this year. Kay was worried that the eompany was growing too fast and had piled up Figure 1 Financiol malysit of Projoct Ac Add a twin-lot to the comoany'u fleet enough debt for the time being. She was also against a stock iesue for fear of diluting earnings and her control over the firm. As a result of Kay s prohibition of outside financing, the size of the capital budget this year was limited to $800,000, which meant that only one of the four projects under consideration could be chosen. Emily wasn't too happy about that, either, but she had decided to accept it for now, and concentrate on selecting the best of the four. As she elosed ber briefcase and walked toward Kay's door, Emily reminded berself to have patience, Kay might not trust financial analysis, but she would listen to sensible arguments. Emily only boped her financial amalysis sounded sensiblel Aerocomp, Inc. Figure 3 Financlal analysis of Project C: Add a hollcopter to the company's neet 1. Refer to Figures 1 through 4. Add up the total increase in after-tax income for each project. Given what you know about Kay Mash, to which project do you think she will be attracted? 2. Computer the Payback Period, Discounted Payback Period, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Productivity Index of all four alternatives based on cash flow. User 10 percent for the cost of capital in your calculations. For the Payback Period and for the Discounted Payback Period, compute to the midyear points as discussed in class. 3. a. According to the payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 4. a. According to the Discounted Payback method, which project should be selected? b. What is the chief disadvantage of this method? c. Why would anyone want to use this method? 5. a. According to the Net Present Value method, which project should be selected? b. What are the major advantages of the Net Present Value method? c. What are any disadvantages of the Net Present Value Method? d. If Kay had not put a limit on the size of the capital budget, under the NPV method which projects would have been accepted? 6. a. According to the IRR method, which project should be chosen? b. What is the major disadvantage of the IRR method that occurs when HIGH IRR projects are selected? c. Can you think of another disadvantage of the IRR method? (Hint: Look over the four alternatives and compare the sizes of the projects. Ask yourself whether you would prefer to make a large percent return on a small amount of money or a small percent gain on a large amount of money.) d. Do the NPV and IRR both reject the same projects - Why? 7. a. According to the Productivity Index, which project should be chosen? b. Explain why people use the Productivity Index. c. Explain why a Productivity Index so closely correlates with the results of NPV
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


