Question: PLEASE ANSWER ALL !!! WILL on my last question Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct
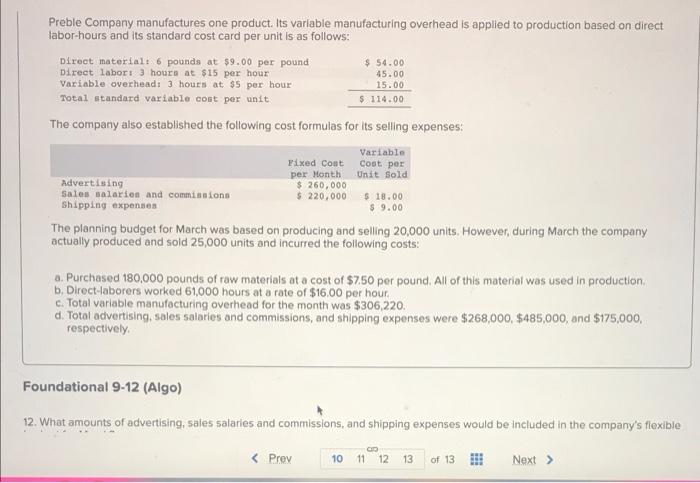
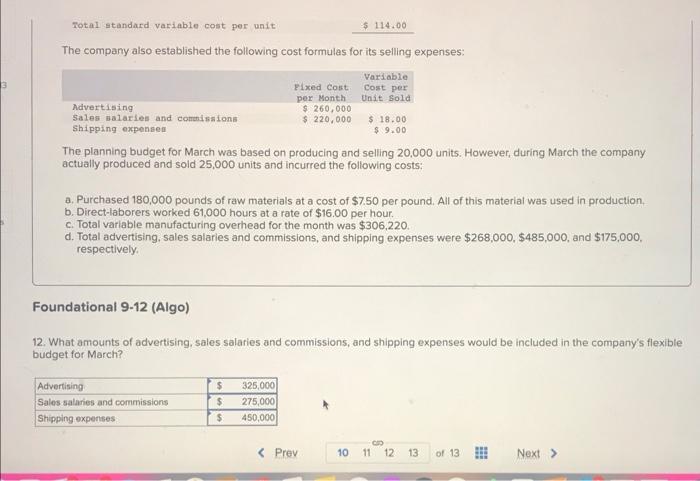


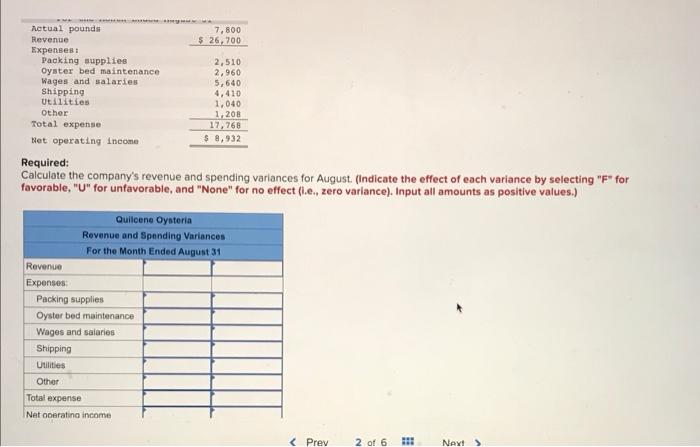
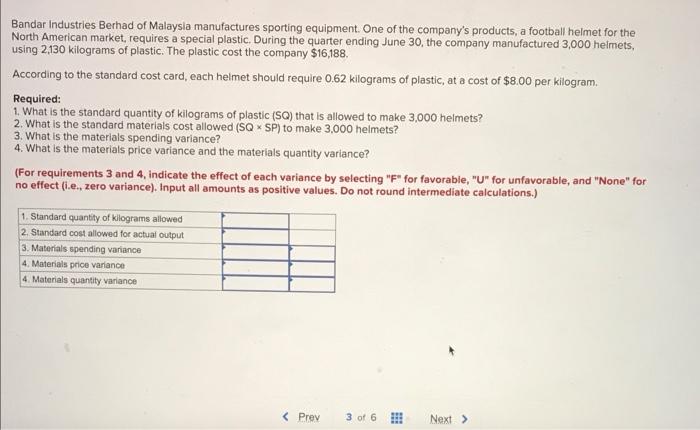


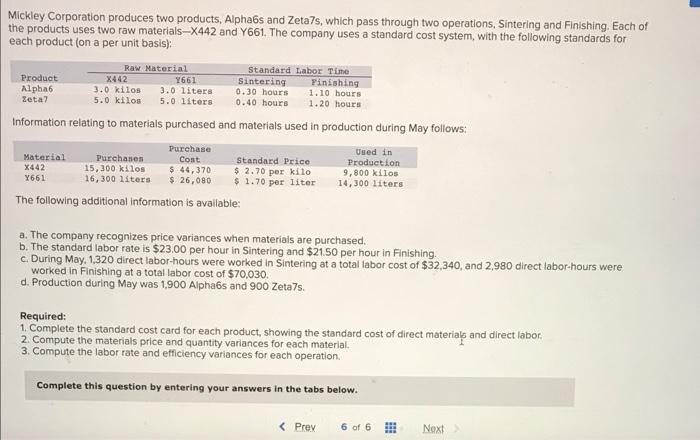
Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 6 pounds at $9.00 per pound Direct labor: 3 hours at $15 per hour $ 54.00 45.00 15.00 Variable overhead: 3 hours at $5 per hour Total standard variable cost per unit $ 114.00 The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Fixed Cost per Month Variable Cost per Unit Sold Advertising Sales salaries and commissions $ 260,000 $ 220,000 Shipping expenses $18.00 $ 9.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 20,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 25,000 units and incurred the following costs: a. Purchased 180,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.50 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-laborers worked 61,000 hours at a rate of $16.00 per hour. c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was $306,220. d. Total advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses were $268,000, $485,000, and $175,000, respectively. Foundational 9-12 (Algo) 12. What amounts of advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses would be included in the company's flexible BD 3 Total standard variable cost per unit $ 114.00 The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Fixed Cost Variable Cost per Unit Sold Advertising per Month $ 260,000 $ 220,000 Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses $ 18.00 $ 9.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 20,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 25,000 units and incurred the following costs: a. Purchased 180,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.50 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-laborers worked 61,000 hours at a rate of $16.00 per hour. c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was $306,220. d. Total advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses were $268,000, $485,000, and $175,000, respectively. Foundational 9-12 (Algo) 12. What amounts of advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses would be included in the company's flexible budget for March? Advertising $ 325,000 Sales salaries and commissions $ 275,000 Shipping expenses $ 450,000 C 10 11 12 13 of 13 Next > Quilcene Oysteria farms and sells oysters in the Pacific Northwest. The company harvested and sold 7,800 pounds of oysters in August. The company's flexible budget for August appears below: Quilcene Oysteria Flexible Budget For the Month Ended August 31 7,800 Actual pounds (g) Revenue ($4.15g) Expenses: $ 32,370 Packing supplies ($0.30g) 2,340 3,100 Oyster bed maintenance ($3,100) Wages and salaries ($2,500+ $0.35g) Shipping ($0.60g) 5,230 4,680 Utilities ($1,230) 1,230 588 Other ($510+ $0.019) Total expense 17,168 $ 15,202 Net operating income The actual results for August appear below: Quilcene Oysteria Income Statement For the Month Ended August 31 Actual pounds Revenue Expenses: Packing supplies Oyster bed maintenance Wages and salaries Shipping Utilities Other Total expense Net operating income Required: 7,800 $ 26,700 2,510 2,960 5,640 4,410 1,040 1,208 17,768 $8,932 SELESA, KARENA ME Actual pounds 7,800 $ 26,700 Revenue Expenses: 2,510 Packing supplies Oyster bed maintenance 2,960 5,640 Wages and salaries Shipping 4,410 Utilities 1,040 Other 1,208 Total expense 17,768 Net operating income $ 8,932 Required: Calculate the company's revenue and spending variances for August. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Quilcene Oysteria Revenue and Spending Variances For the Month Ended August 31 Revenue Expenses: SkyChefs, Incorporated, prepares in-flight meals for a number of major airlines. One of the company's products is grilled salmon in dill sauce with baby new potatoes and spring vegetables. During the most recent week, the company prepared 6,200 of these meals using 1,200 direct labor-hours. The company paid its direct labor workers a total of $10,800 for this work, or $9.00 per hour. According to the standard cost card for this meal, it should require 0.20 direct labor-hours at a cost of $8.50 per hour. Required: 1. What is the standard labor-hours allowed (SH) to prepare 6,200 meals? 2. What is the standard labor cost allowed (SH SR) to prepare 6,200 meals? 3. What is the labor spending variance? 4. What is the labor rate variance and the labor efficiency variance? (For requirements 3 and 4, indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations.) 1. Standard labor-hours allowed 2. Standard labor cost allowed 3. Labor spending variance 4. Labor rate variance 4. Labor efficiency variance Logistics Solutions provides order fulfillment services for dot.com merchants. The company maintains warehouses that stock items carried by its dot.com clients. When a client receives an order from a customer, the order is forwarded to Logistics Solutions, which pulls the item from storage, packs it, and ships it to the customer. The company uses a predetermined variable overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. In the most recent month, 190,000 items were shipped to customers using 8,300 direct labor-hours. The company incurred a total of $29,050 in variable overhead costs. According to the company's standards, 0.03 direct labor-hours are required to fulfill an order for one item and the variable overhead rate is $3.55 per direct labor-hour. Required: 1. What is the standard labor-hours allowed (SH) to ship 190,000 items to customers? 2. What is the standard variable overhead cost allowed (SH x SR) to ship 190,000 items to customers? 3. What is the variable overhead spending variance? 4. What is the variable overhead rate variance and the variable overhead efficiency variance? (For requirements 3 and 4, indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations.) 1. Standard quantity of labor-hours allowed 2. Standard variable overhead cost allowed 3. Variable overhead spending variance 4. Variable overhead rate variance 4. Variable overhead efficiency variance Mickley Corporation produces two products, Alpha6s and Zeta7s, which pass through two operations, Sintering and Finishing. Each of the products uses two raw materials-X442 and Y661. The company uses a standard cost system, with the following standards for each product (on a per unit basis): Standard Labor Time Raw Material 1661 Sintering Finishing Product Alpha6 X442 3.0 kilos 3.0 liters: 0.30 hours 1.10 hours Zeta7 5.0 kilos 5.0 liters 0.40 hours 1.20 hours Information relating to materials purchased and materials used in production during May follows: Purchase Cost Material Purchases 15,300 kilos Standard Price $2.70 per kilo Used in Production 9,800 kilos $ 44,370 X442 Y661 16,300 liters $ 26,080 $ 1.70 per liter 14,300 liters The following additional information is available: a. The company recognizes price variances when materials are purchased. b. The standard labor rate is $23.00 per hour in Sintering and $21.50 per hour in Finishing. c. During May, 1,320 direct labor-hours were worked in Sintering at a total labor cost of $32,340, and 2,980 direct labor-hours were worked in Finishing at a total labor cost of $70,030. d. Production during May was 1,900 Alpha6s and 900 Zeta7s. Required: 1. Complete the standard cost card for each product, showing the standard cost of direct materials and direct labor. 2. Compute the materials price and quantity variances for each material. 3. Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances for each operation. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


