Question: please answer as many as you can. thanks When does a common stock investor gets back his or her initial investment? (3) When he sells
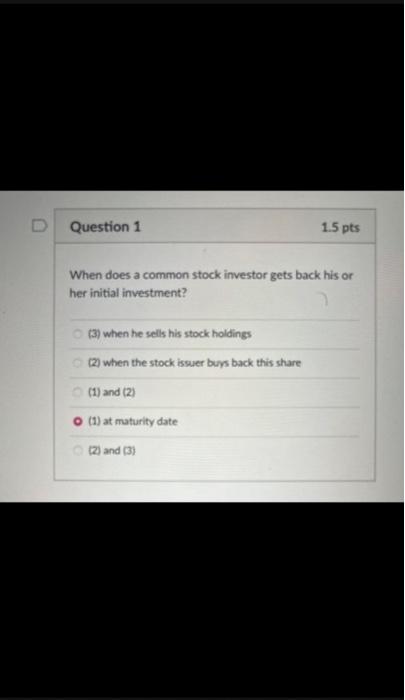
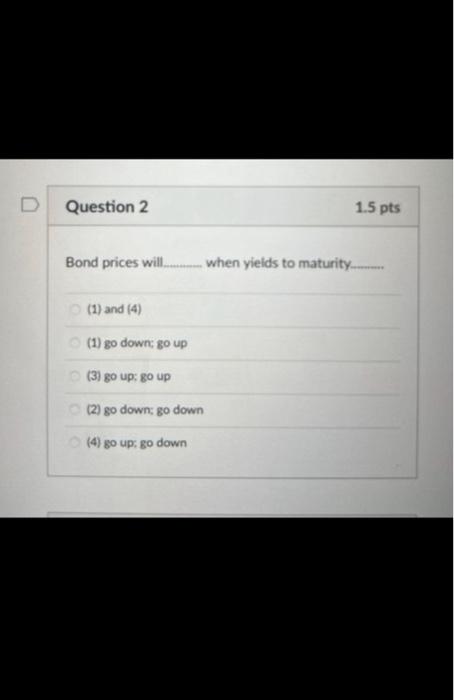
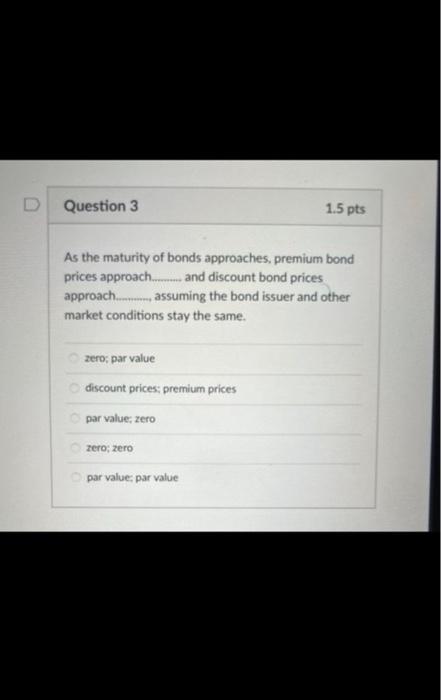
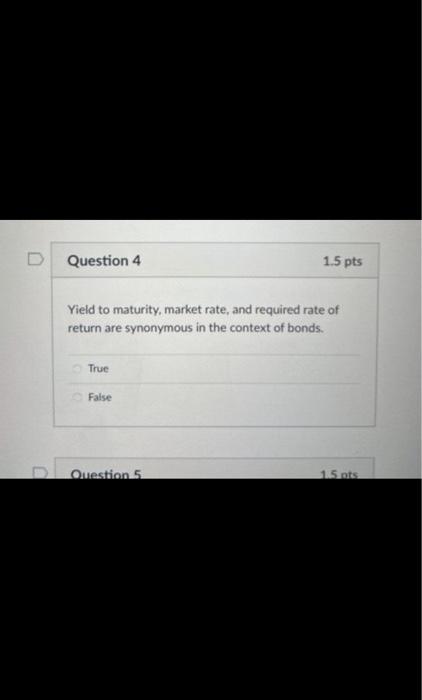
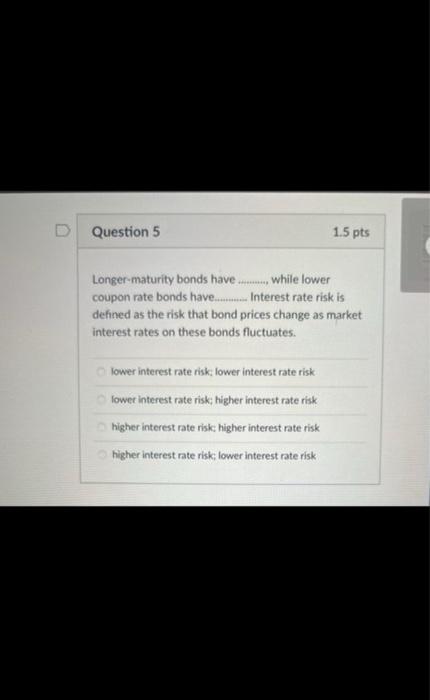
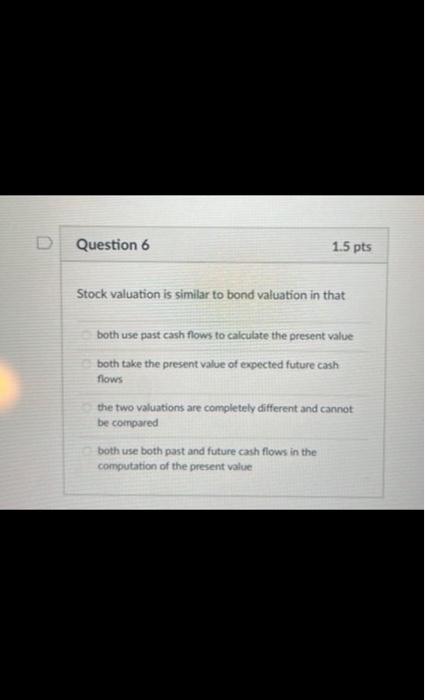
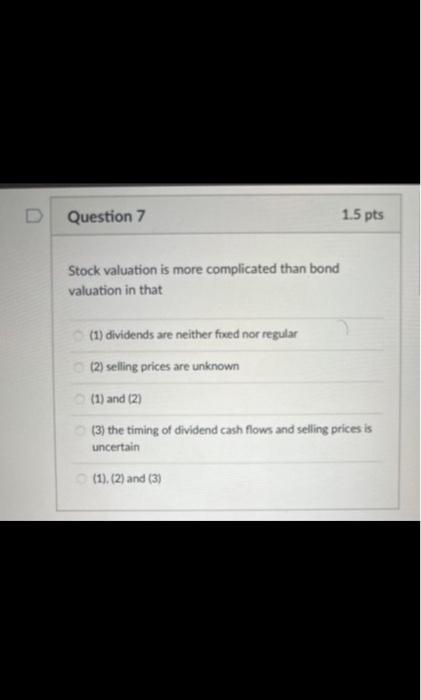
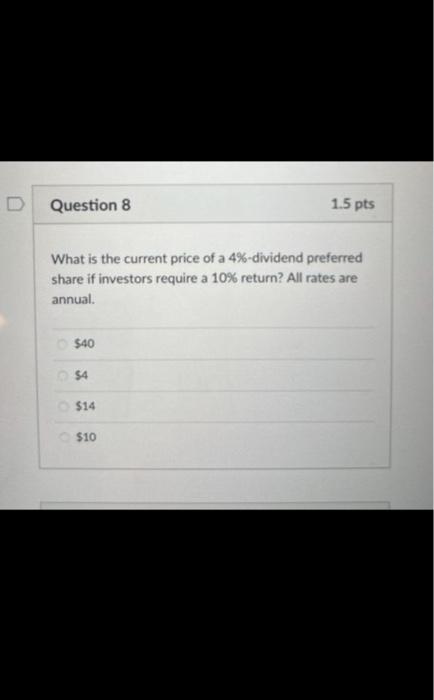
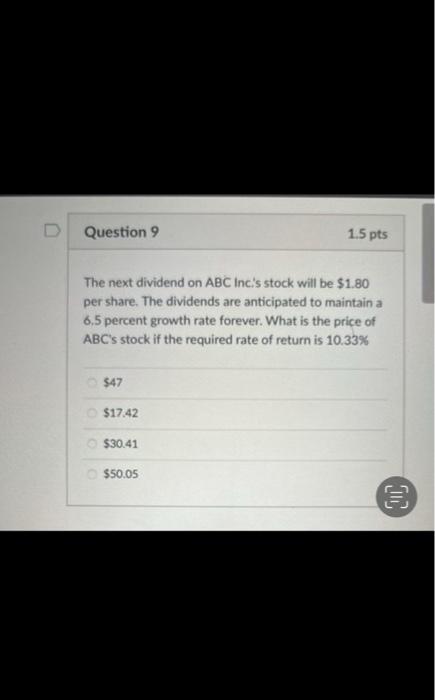
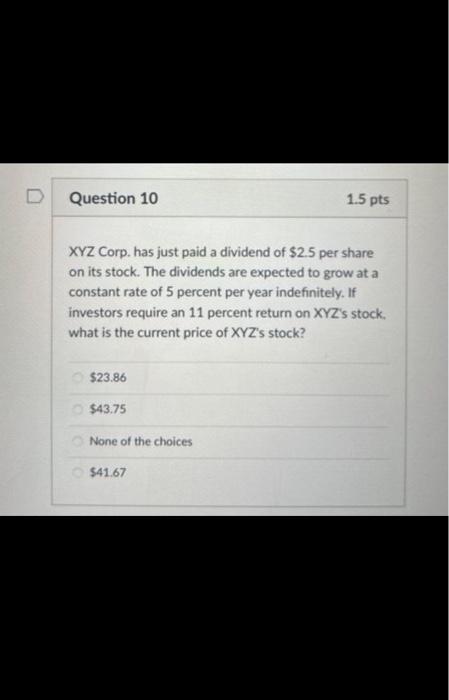
When does a common stock investor gets back his or her initial investment? (3) When he sells his stock holdings (2) when the stock issuer burs back this share (1) and (2) (1) at maturity date (2) and (3) Bond prices will. when yields to maturity. (1) and (4) (1) go down; go up (3) go up: go up (2) go down: go down (4) go up; go down As the maturity of bonds approaches, premium bond prices approach. and discount bond prices approach.._... assuming the bond issuer and other market conditions stay the same. zero; par value discount prices; premium prices par value: zero zero; zero par value: par value Yield to maturity, market rate, and required rate of return are synonymous in the context of bonds. True False Longer-maturity bonds have while lower coupon rate bonds have. Interest rate risk is defined as the risk that bond prices change as market interest rates on these bonds fluctuates. lower interest rate risk: lower interest rate risk lowet interest rate risk; higher interest rate risk higher interest rate risk higher interest rate risk higher interest rate risk; lower interest rate risk Stock valuation is similar to bond valuation in that both use past cash flows to calculate the present value both take the present value of expected future cash flows the two valuations are completely different and cannot be compared both use both past and future cach flows in the computation of the present value Stock valuation is more complicated than bond valuation in that (1) dividends are neither foxed nor regular (2) selling prices are unknown (1) and (2) (3) the timing of dividend cash flows and selling prices is uncertain (1). (2) and (3) What is the current price of a 4%-dividend preferred share if investors require a 10% return? All rates are annual. $40 $4 $14 $10 The next dividend on ABC Incis stock will be $1.80 per share. The dividends are anticipated to maintain a 6.5 percent growth rate forever. What is the price of ABC's stock if the required rate of return is 10.33% $47 $17.42 $30.41 $50.05 XYZ Corp. has just paid a dividend of $2.5 per share on its stock. The dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 5 percent per year indefinitely. If investors require an 11 percent return on XYZ's stock, what is the current price of XYZ's stock? $23.86$43.75 None of the choices $41.67
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


