Question: Please answer clearly! Long Problem 2: General Equilibrium in an Exchange Economy (38 points) Romeo's preferences for pizza (good 1) and wine (good 2) are



Please answer clearly!
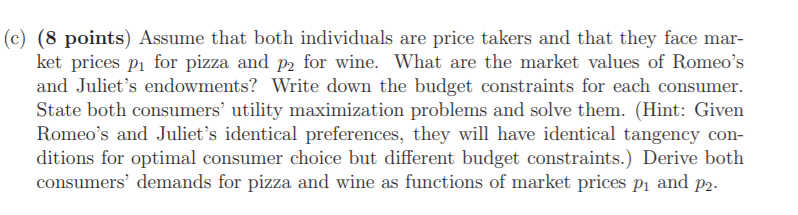
Long Problem 2: General Equilibrium in an Exchange Economy (38 points) Romeo's preferences for pizza (good 1) and wine (good 2) are represented by the utility function uR(XR, 2) = 272. Juliet's utility function is given by u"(21,2) RR %= zz. Romeo's initial endowment consists of 3 pizzas and 1 bottles of wine whereas Juliet's initial endowment consists of 7 pizzas and 9 bottles of wine. (c) (8 points) Assume that both individuals are price takers and that they face mar- ket prices p for pizza and p2 for wine. What are the market values of Romeo's and Juliet's endowments? Write down the budget constraints for each consumer. State both consumers' utility maximization problems and solve them. (Hint: Given Romeo's and Juliet's identical preferences, they will have identical tangency con- ditions for optimal consumer choice but different budget constraints.) Derive both consumers' demands for pizza and wine as functions of market prices P1 and 22. (d) (7 points) State the market clearing conditions for any one of the markets in this economy. Using your results from (C), find the equilibrium price ratio between pizza and wine. Explain why it is not necessary to consider the other market. (e) (7 points) Calculate the equilibrium allocations. Is the market equilibrium found in (d) and (e) Pareto-efficient? Why or why not? Illustrate your answer graphically. Long Problem 2: General Equilibrium in an Exchange Economy (38 points) Romeo's preferences for pizza (good 1) and wine (good 2) are represented by the utility function uR(XR, 2) = 272. Juliet's utility function is given by u"(21,2) RR %= zz. Romeo's initial endowment consists of 3 pizzas and 1 bottles of wine whereas Juliet's initial endowment consists of 7 pizzas and 9 bottles of wine. (c) (8 points) Assume that both individuals are price takers and that they face mar- ket prices p for pizza and p2 for wine. What are the market values of Romeo's and Juliet's endowments? Write down the budget constraints for each consumer. State both consumers' utility maximization problems and solve them. (Hint: Given Romeo's and Juliet's identical preferences, they will have identical tangency con- ditions for optimal consumer choice but different budget constraints.) Derive both consumers' demands for pizza and wine as functions of market prices P1 and 22. (d) (7 points) State the market clearing conditions for any one of the markets in this economy. Using your results from (C), find the equilibrium price ratio between pizza and wine. Explain why it is not necessary to consider the other market. (e) (7 points) Calculate the equilibrium allocations. Is the market equilibrium found in (d) and (e) Pareto-efficient? Why or why not? Illustrate your answer graphically
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


