Question: Please answer in full solutions Consider the horizontal, laminar flow of a non-Newtonian fluid (K=2Pasn and n=0.35) that is subjected to a constant pressure gradient
Please answer in full solutions

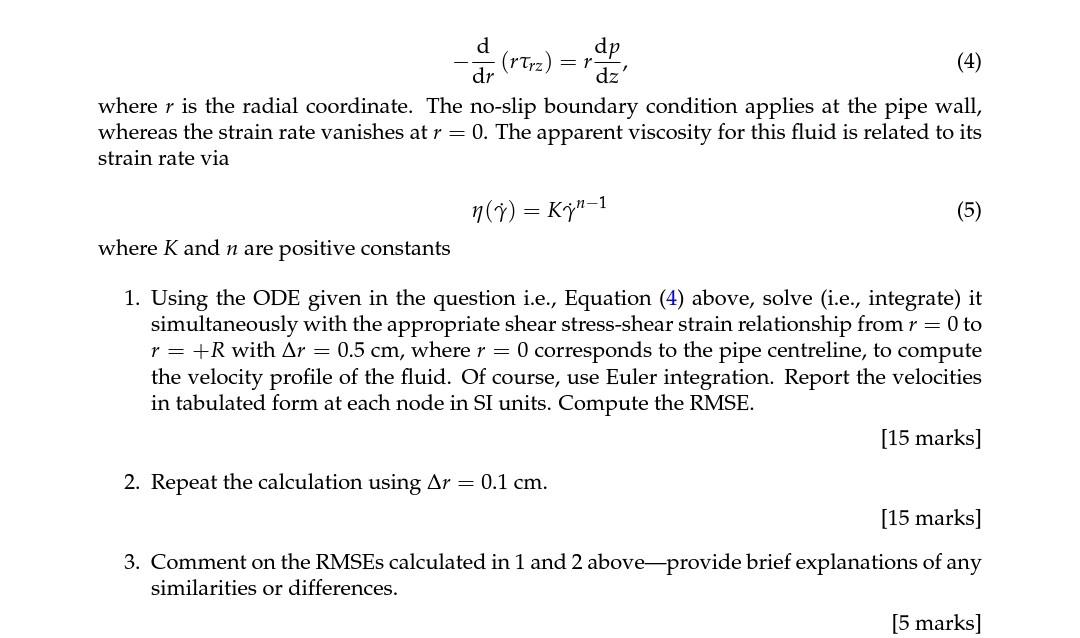
Consider the horizontal, laminar flow of a non-Newtonian fluid (K=2Pasn and n=0.35) that is subjected to a constant pressure gradient of 500Pa/m in a pipe of circular cross-section (radius R=5cm ). Performing a momentum balance on an annular fluid element (length dz and thickness dr ) leads to the differential equation (DE) drd(rrz)=rdzdp where r is the radial coordinate. The no-slip boundary condition applies at the pipe wall, whereas the strain rate vanishes at r=0. The apparent viscosity for this fluid is related to its strain rate via ()=Kn1 where K and n are positive constants 1. Using the ODE given in the question i.e., Equation (4) above, solve (i.e., integrate) it simultaneously with the appropriate shear stress-shear strain relationship from r=0 to r=+R with r=0.5cm, where r=0 corresponds to the pipe centreline, to compute the velocity profile of the fluid. Of course, use Euler integration. Report the velocities in tabulated form at each node in SI units. Compute the RMSE. [15 marks] 2. Repeat the calculation using r=0.1cm. [15 marks] 3. Comment on the RMSEs calculated in 1 and 2 above-provide brief explanations of any similarities or differences
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


