Question: PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK 2. THANK YOU! PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK 2. THANK YOU! PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK 2. THANK YOU! PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK
PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK 2. THANK YOU!
PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK 2. THANK YOU!
PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK 2. THANK YOU!
PLEASE ANSWER ONLY TASK 2. THANK YOU!
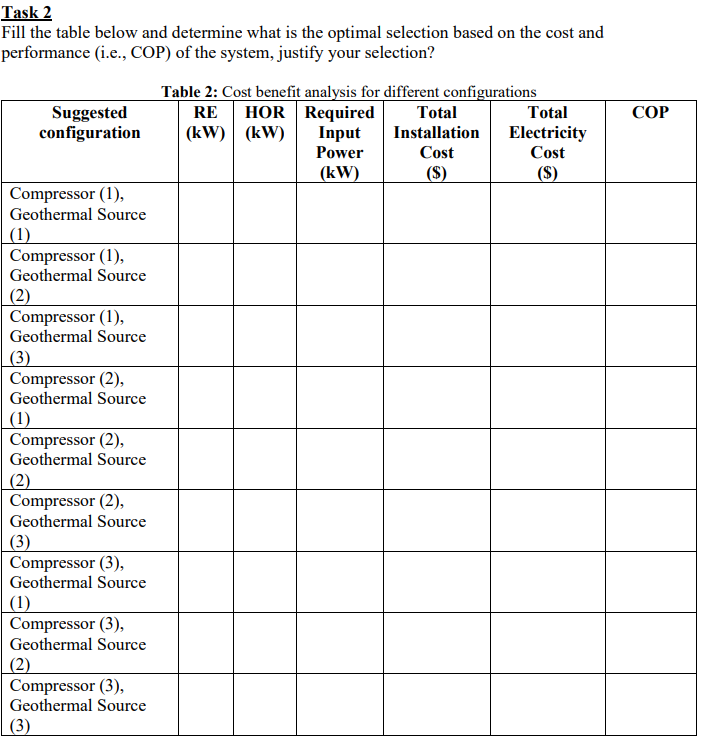

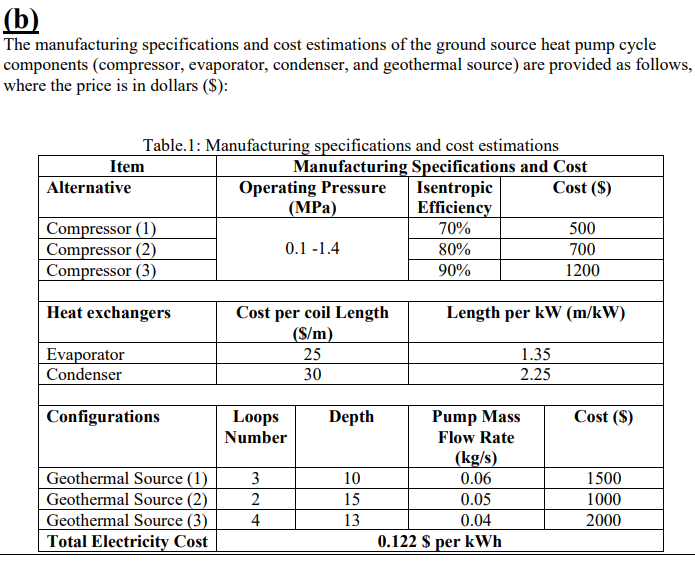
Task 2 Fill the table below and determine what is the optimal selection based on the cost and performance (i.e., COP) of the system, justify your selection? COP Suggested configuration Table 2: Cost benefit analysis for different configurations RE HOR Required Total Total (kW) (kW) Input Installation Electricity Power Cost Cost (kW) ($) ($) Compressor (1), Geothermal Source (1) Compressor (1), Geothermal Source (2) Compressor (1), Geothermal Source Compressor (2), Geothermal Source (1) Compressor (2) Geothermal Source (2) Compressor (2), Geothermal Source (3) Compressor (3), Geothermal Source (1) Compressor (3), Geothermal Source (2) Compressor (3), Geothermal Source (3) The geothermal source manufacturing provides the following information to determine the inlet (Tin) and outlet (Tout) temperatures, Tin = 20 + N 3D, Tout = Tin - 5*N where, N is the loop number and D is the depth of the geothermal network. Your design team put a set of assumptions related to the irreversibilities that will affect the performance of the heat pump system, which include the following . A pressure drop in the pipeline that goes through the condenser of 10% of its inlet pressure at the exist of compressor point, where all the other pipelines are assumed to have a negligible pressure drop Expansion valve is capable to decrease the fluid pressure by 7% above the original low pressure of cycle The ground source water at the inlet and outlet is assumed to be saturated liquid Where the R134-A refrigerant enters the compressor as superheated at -12 C and cooled in the condenser to 24 C. Your role is to conduct a cost-benefit analysis of the ground source heat pump through selecting the best set of compressor alternatives and ground-source configurations that give the end user the optimum cost. (b) The manufacturing specifications and cost estimations of the ground source heat pump cycle components (compressor, evaporator, condenser, and geothermal source) are provided as follows, where the price is in dollars ($): Table.1: Manufacturing specifications and cost estimations Item Manufacturing Specifications and Cost Alternative Operating Pressure Isentropic Cost ($) (MPa) Efficiency Compressor (1) 70% 500 Compressor (2) 0.1 -1.4 80% 700 Compressor (3) 90% 1200 Heat exchangers Cost per coil Length (S/m) Length per kW (m/kW) 25 Evaporator Condenser 1.35 2.25 30 Configurations Cost (S) Loops Number Geothermal Source (1) Geothermal Source (2) Geothermal Source (3) Total Electricity Cost 3 2 4 Depth Pump Mass Flow Rate (kg/s) 10 0.06 15 0.05 13 0.04 0.122 $ per kWh 1500 1000 2000






