Question: PLEASE ANSWER PART D THANK U BHP Billiton is the world's largest mining firm. BHP expects to produce 2.25 billion pounds of copper next year,
 PLEASE ANSWER PART D THANK U
PLEASE ANSWER PART D THANK U
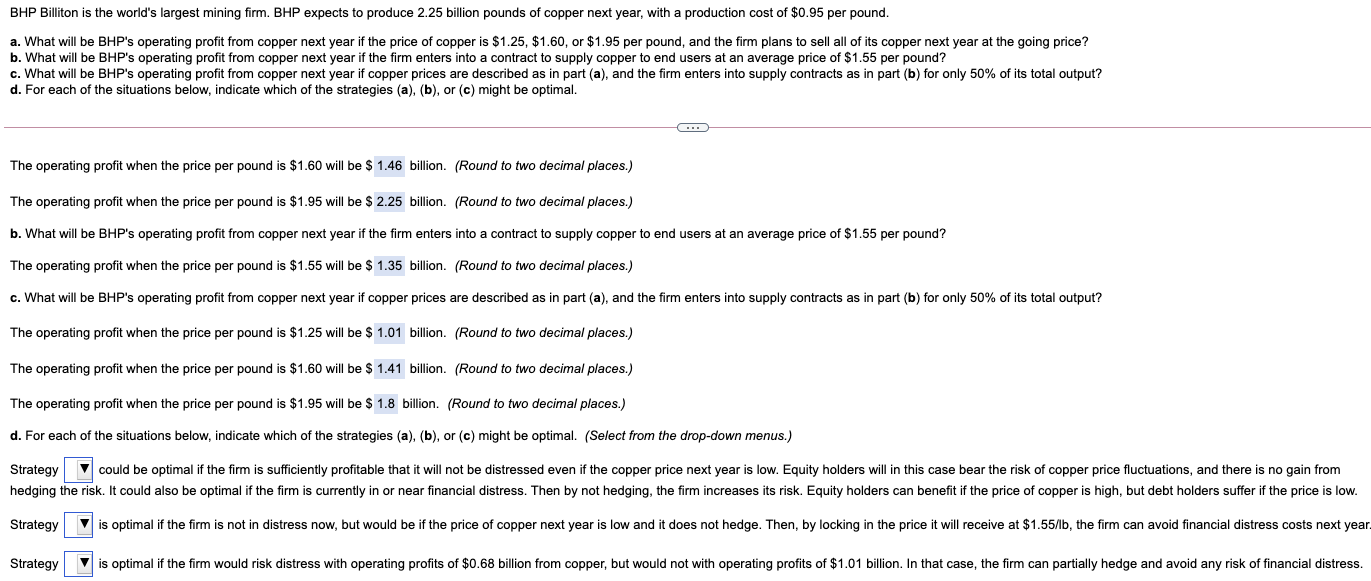
BHP Billiton is the world's largest mining firm. BHP expects to produce 2.25 billion pounds of copper next year, with a production cost of $0.95 per pound. a. What will be BHP's operating profit from copper next year if the price of copper is $1.25, $1.60, or $1.95 per pound, and the firm plans to sell all of its copper next year at the going price? b. What will be BHP's operating profit from copper next year if the firm enters into a contract to supply copper to end users at an average price of $1.55 per pound? c. What will be BHP's operating profit from copper next year if copper prices are described as in part (a), and the firm enters into supply contracts as in part (b) for only 50% of its total output? d. For each of the situations below, indicate which of the strategies (a), (b), or (c) might be optimal. C. The operating profit when the price per pound is $1.60 will be $ 1.46 billion. (Round to two decimal places.) The operating profit when the price per pound is $1.95 will be $ 2.25 billion. (Round to two decimal places.) b. What will be BHP's operating profit from copper next year if the firm enters into a contract to supply copper to end users at an average price of $1.55 per pound? The operating profit when the price per pound is $1.55 will be $ 1.35 billion. (Round to two decimal places.) c. What will be BHP's operating profit from copper next year if copper prices are described as in part (a), and the firm enters into supply contracts as in part (b) for only 50% of its total output? The operating profit when the price per pound is $1.25 will be $ 1.01 billion. (Round to two decimal places.) The operating profit when the price per pound is $1.60 will be $ 1.41 billion. (Round to two decimal places.) The operating profit when the price per pound is $1.95 will be $ 1.8 billion. (Round to two decimal places.) d. For each of the situations below, indicate which of the strategies (a), (b), or (c) might be optimal. (Select from the drop-down menus.) Strategy could be optimal if the firm is sufficiently profitable that it will not be distressed even if the copper price next year is low. Equity holders will in this case bear the risk of copper price fluctuations, and there is no gain from hedging the risk. It could also be optimal if the firm is currently in or near financial distress. Then by not hedging, the firm increases its risk. Equity holders can benefit if the price of copper is high, but debt holders suffer if the price is low. Strategy is optimal if the firm is not in distress now, but would be if the price of copper next year is low and it does not hedge. Then, by locking in the price it will receive at $1.55/lb, the firm can avoid financial distress costs next year. Strategy is optimal if the firm would risk distress with operating profits of $0.68 billion from copper, but would not with operating profits of $1.01 billion. In that case, the firm can partially hedge and avoid any risk of financial distress
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


