Question: Please answer Quantitative problem 1 and 2. Show your work, thanks! 1. 11 Multinational Financial Management Foreign Exchange Rate Quotations The role of multinational firms
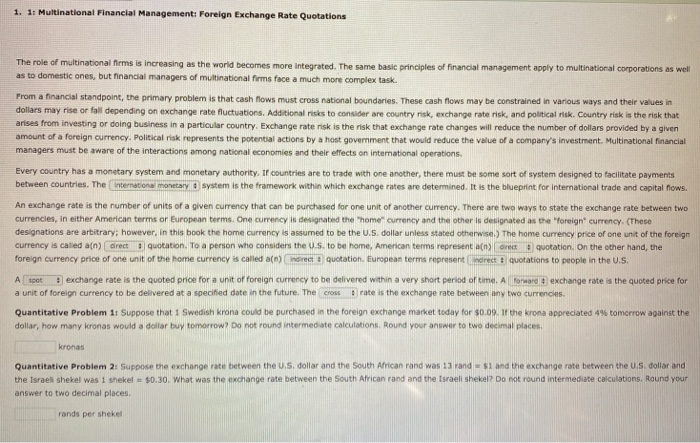
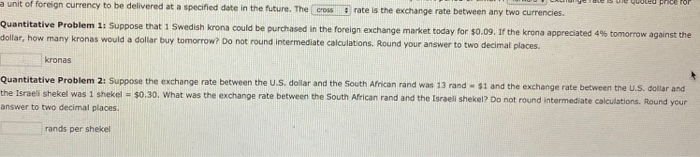
1. 11 Multinational Financial Management Foreign Exchange Rate Quotations The role of multinational firms is increasing as the world becomes more integrated. The same basic principles of financial management apply to multinational corporations as well as to domestic ones, but financial managers of multinational firms face a much more complex task. From a financial standpoint, the primary problem is that cash flows must cross national boundaries. These cash flows may be constrained in various ways and their values in dollars may rise or fall depending on exchange rate fluctuations. Additional risks to considerare country risk, exchange rate risk, and political risk. Country risk is the risk that arises from investing or doing business in a particular country. Exchange rate risk is the risk that exchange rate changes will reduce the number of dollars provided by a given amount of a foreign currency, Political risk represents the potential actions by a host government that would reduce the value of a company's investment. Multinational financial managers must be aware of the interactions among national economies and their effects on international operations Every country has a monetary system and monetary authority. If countries are to trade with one another, there must be some sort of system designed to facilitate payments between countries. The international motary system is the framework within which exchange rates are determined. It is the blueprint for international trade and capital flows. An exchange rate is the number of units of a given currency that can be purchased for one unit of another currency. There are two ways to state the exchange rate between two currencies, in either American terms or European terms. One currency is designated the home currency and the other is designated as the "oreign currency. (These designations are arbitrary; however, in this book the home currency is assumed to be the U.S. dollar unless stated otherwise) The home currency price of one unit of the foreign currency is called a(n) drect quotation. To a person who considers the U.S. to be home, American terms represent andret quotation. On the other hand, the foreign currency price of one unit of the home currency is called a(n) indirect : quotation. European terms represent recto quotations to people in the U.S. A sot exchange rate is the quoted price for a unit of foreign currency to be delivered within a very short period of time. A forward exchange rate is the quoted price for a unit of foreign currency to be delivered at a specified date in the future. The cross rate is the exchange rate between any two currencies Quantitative Problem 1. Suppose that Swedish Krona could be purchased in the foreign exchange market today for $0.09. If the krona appreciated 4% tomorrow against the dollar, how many kronas would a dollar buy tomorrow? Do not found intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places kronas Quantitative Problem 2: Suppose the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the South African rand was 13 rand - 51 and the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Israel Shekel was 1 Shekel - 50.30. What was the exchange rate between the South African rand and the Israeli Shekel? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places rands per shekel a unit of foreign currency to be delivered at a specified date in the future. The cross rate is the exchange rate between any two currencies. Quantitative Problem 1: Suppose that 1 Swedish Krona could be purchased in the foreign exchange market today for $0.09. If the krona appreciated 4% tomorrow against the dollar, how many kronas would a dollar buy tomorrow? Do not round Intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. kronas Quantitative Problem 2: Suppose the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the South African rand was 13 rand - $1 and the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Israeli Shekel was 1 shekel = $0.30. What was the exchange rate between the South African rand and the Israeli Shekel? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places rands per shekel
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


