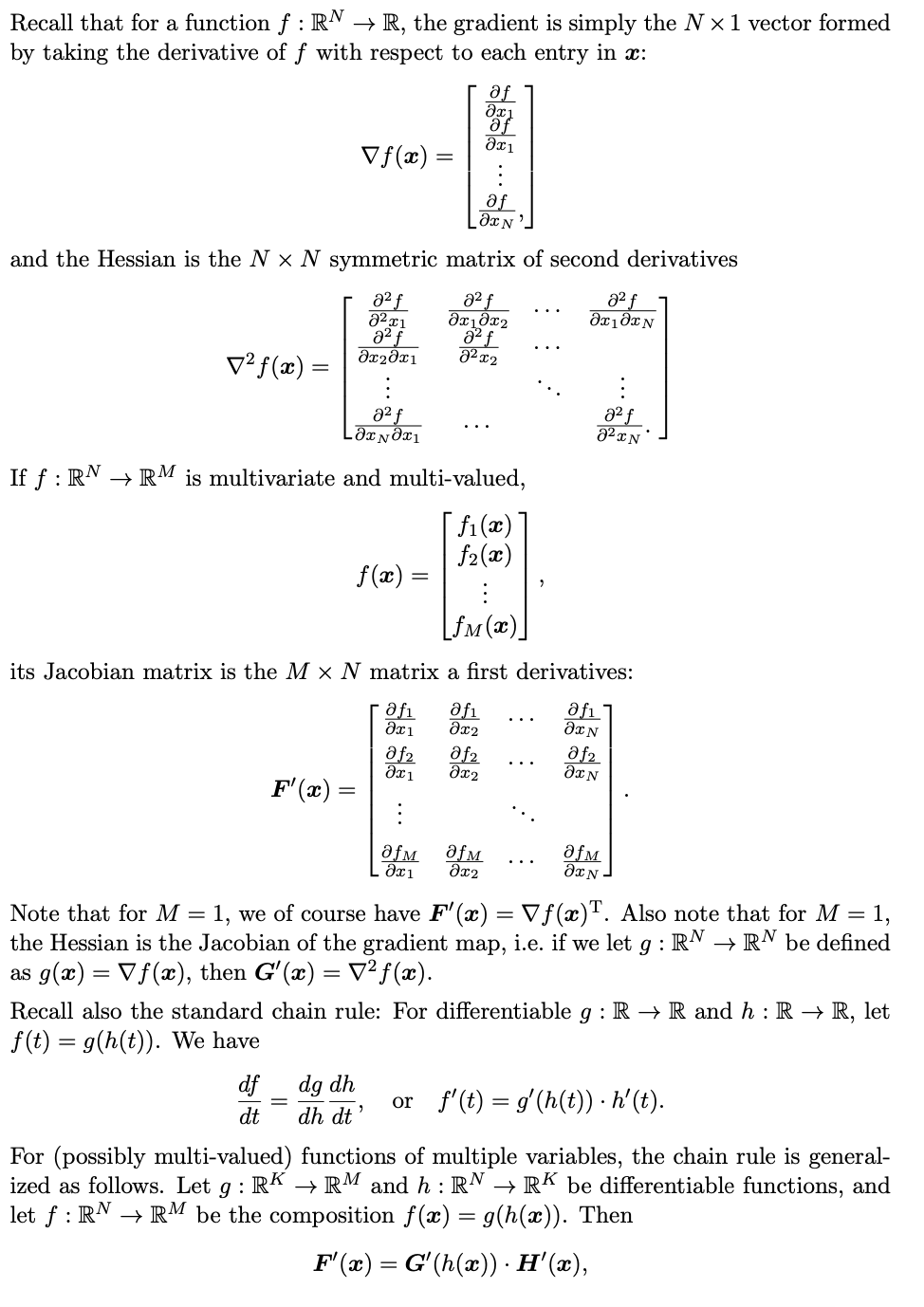
Question: Please answer questions a to e according to the following formula, and give detailed steps and explanations Recall that for a function f : RN
Please answer questions a to e according to the following formula, and give detailed steps and explanations

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


