Question: Please answer step by step 2. Use your results from Question 1 to analyze the RLC Ai(t) circuit from Question 1. 0.5 A- a. Draw
Please answer step by step
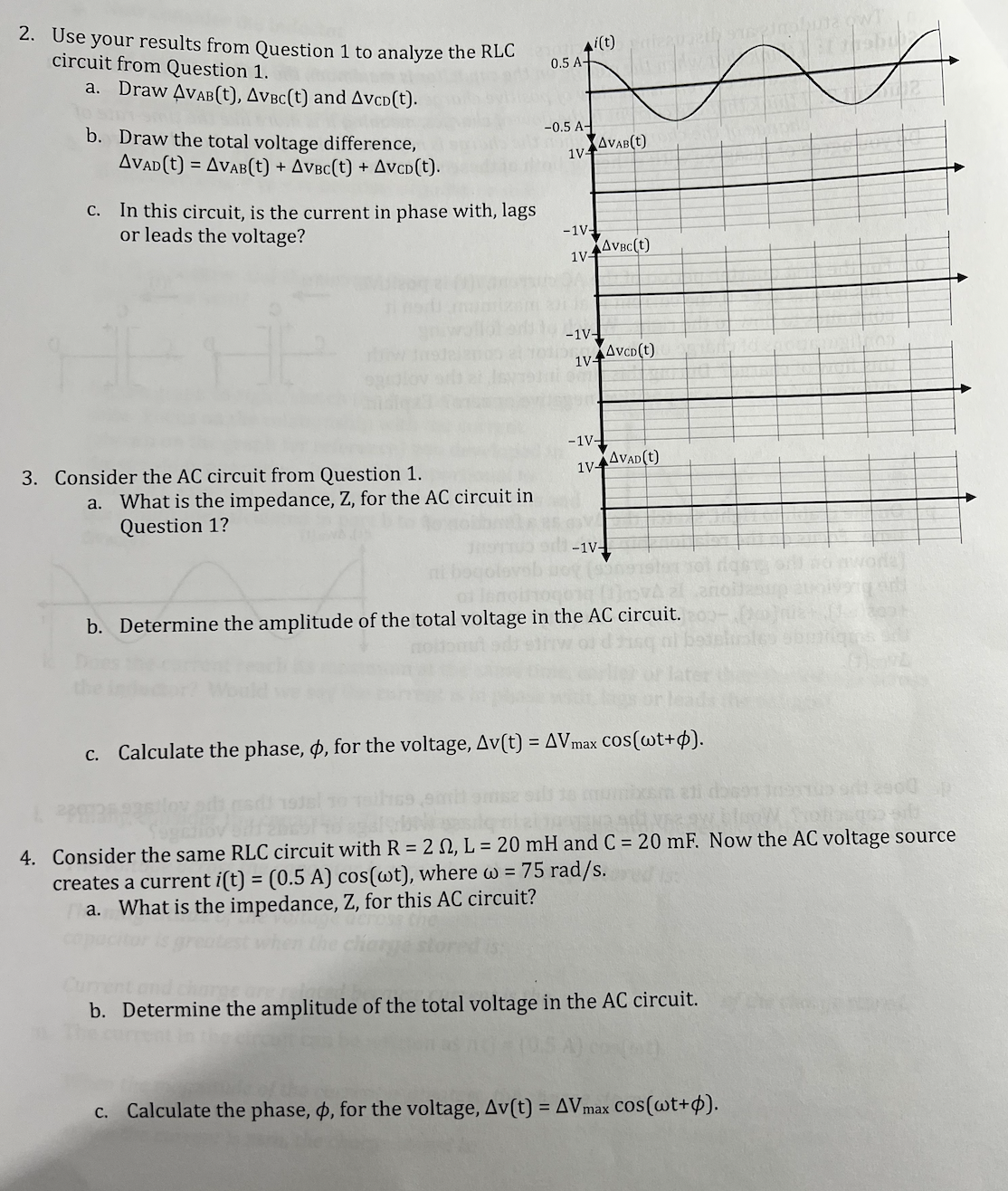
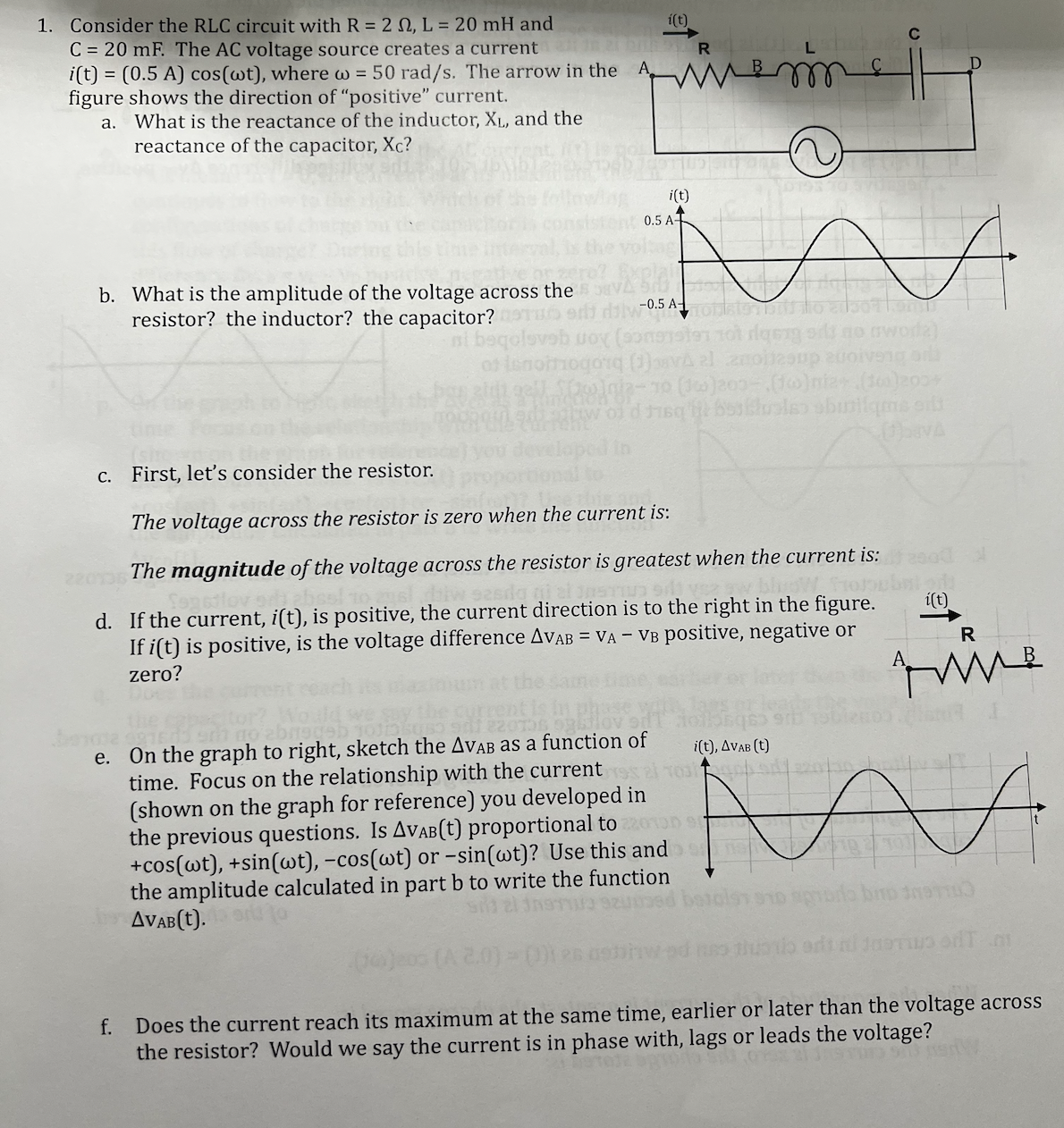
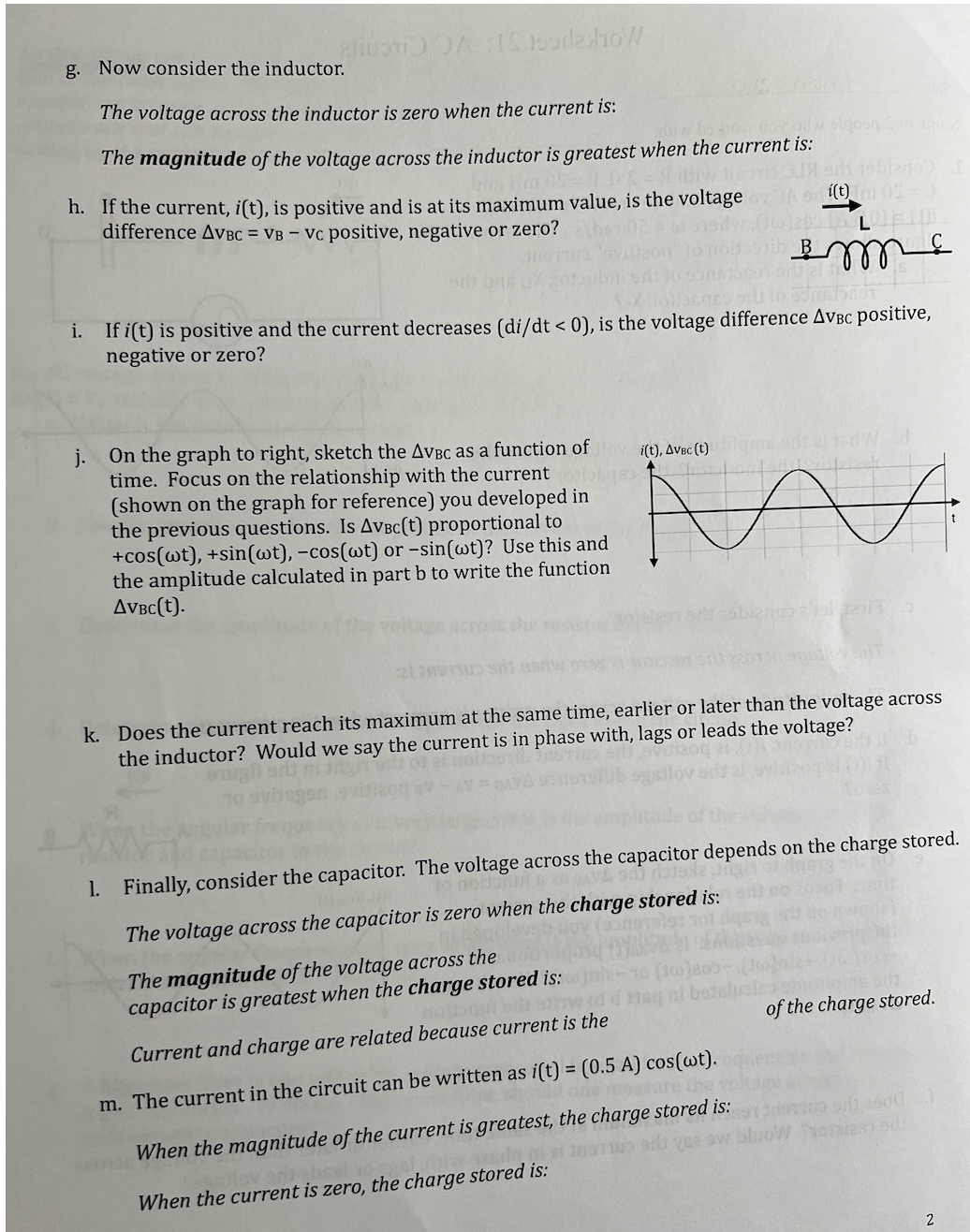
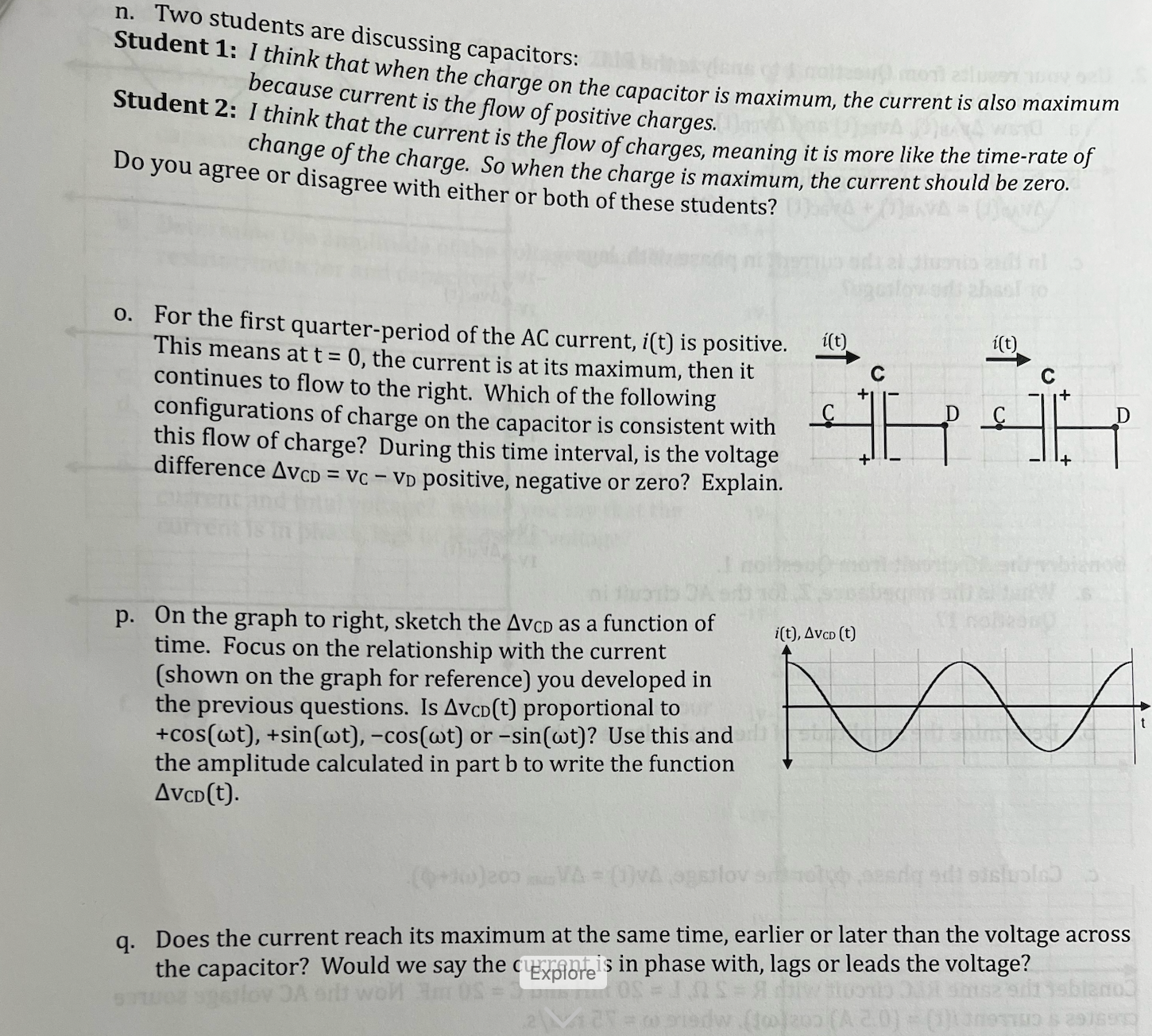
2. Use your results from Question 1 to analyze the RLC Ai(t) circuit from Question 1. 0.5 A- a. Draw AVAB(t), AVBc(t) and AVCD(t). b. Draw the total voltage difference, -0.5 A- AVAD(t) = AVAB(t) + AVBC(t) + AVCD(t). 1VAVAB (t) c. In this circuit, is the current in phase with, lags or leads the voltage? -1V- 1VAVBC(t) -1V- 1VVCD(t) -1V- 3. Consider the AC circuit from Question 1. 1VAVAD(t) a. What is the impedance, Z, for the AC circuit in Question 1? 13-1V- anoida b. Determine the amplitude of the total voltage in the AC circuit. of later c. Calculate the phase, , for the voltage, Av(t) = AVmax cos(wt+p). 4. Consider the same RLC circuit with R = 2 0, L = 20 mH and C = 20 mF. Now the AC voltage source creates a current i(t) = (0.5 A) cos(wt), where w = 75 rad/s. a. What is the impedance, Z, for this AC circuit? he charge store b. Determine the amplitude of the total voltage in the AC circuit. c. Calculate the phase, o, for the voltage, Av(t) = AVmax cos(wt+p).1. Consider the RLC circuit with R = 2 0, L = 20 mH and i(t) C = 20 mF. The AC voltage source creates a current i(t) = (0.5 A) cos(wt), where w = 50 rad/s. The arrow in the A figure shows the direction of "positive" current. a. What is the reactance of the inductor, XL, and the reactance of the capacitor, Xc? b. What is the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor? the inductor? the capacitor? off day-0.5 A- beqolovebuoy (songmolen To1 rigeng sil no aword) of linorhogand (Java al znoblesup egoiverig ord c. First, let's consider the resistor. The voltage across the resistor is zero when the current is: The magnitude of the voltage across the resistor is greatest when the current is: esad d. If the current, i(t), is positive, the current direction is to the right in the figure. i(t) If i(t) is positive, is the voltage difference AVAB = VA - VB positive, negative or zero? e. On the graph to right, sketch the AVAB as a function of time. Focus on the relationship with the current (shown on the graph for reference) you developed in the previous questions. Is AVAB(t) proportional to +cos(wt), +sin(wt), -cos(wt) or -sin(wt)? Use this and AAA the amplitude calculated in part b to write the function AVAB (t). f. Does the current reach its maximum at the same time, earlier or later than the voltage across the resistor? Would we say the current is in phase with, lags or leads the voltage?g. Now consider the inductor. along DA IS josdeshow The voltage across the inductor is zero when the current is: The magnitude of the voltage across the inductor is greatest when the current is: h. If the current, i(t), is positive and is at its maximum value, is the voltage (isbiznod JA or i(t) mos difference AVBC = VB - Vc positive, negative or zero? L If i(t) is positive and the current decreases (di/dt
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


