Question: Please answer the following questions using the background given- this was all I was given. BACKGROUND and PROBLEM (1): Numerical Integration Introduction We have learned

Please answer the following questions using the background given- this was all I was given.
BACKGROUND and PROBLEM (1):
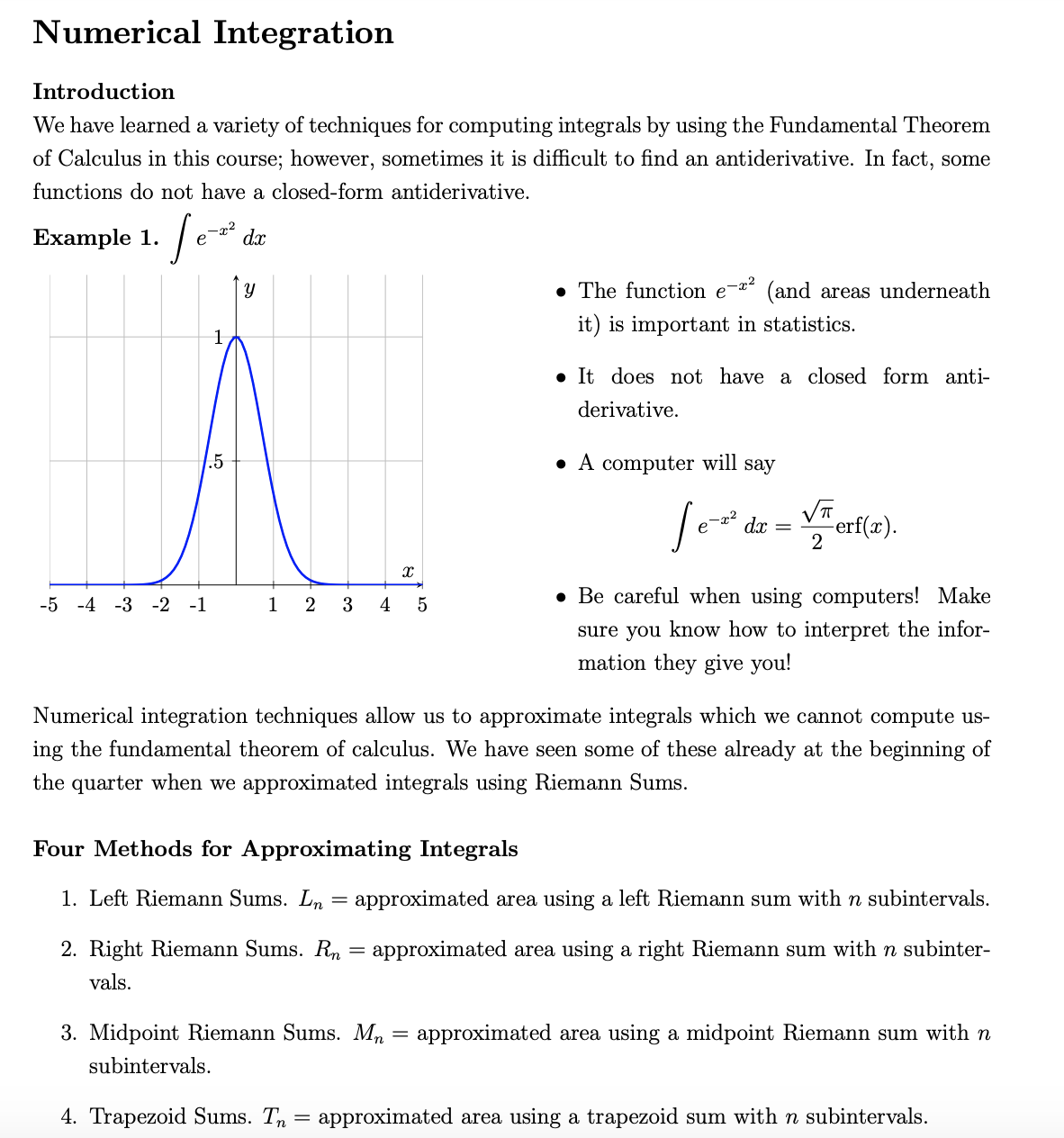

Numerical Integration Introduction We have learned a variety of techniques for computing integrals by using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus in this course; however, sometimes it is difficult to find an antiderivative. In fact, some functions do not have a closed-form antiderivative. Example 1. / e- dx . The function e- (and areas underneath it) is important in statistics. . It does not have a closed form anti- derivative. 1.5 . A computer will say ex dx = VR 2 " erf ( x ) . -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 . Be careful when using computers! Make sure you know how to interpret the infor- mation they give you! Numerical integration techniques allow us to approximate integrals which we cannot compute us- ing the fundamental theorem of calculus. We have seen some of these already at the beginning of the quarter when we approximated integrals using Riemann Sums. Four Methods for Approximative Integrals 1. Left Riemann Sums. In = approximated area using a left Riemann sum with n subintervals. 2. Right Riemann Sums. An = approximated area using a right Riemann sum with n subinter- vals. 3. Midpoint Riemann Sums. Mn = approximated area using a midpoint Riemann sum with n subintervals. 4. Trapezoid Sums. In = approximated area using a trapezoid sum with n subintervals.\f(b) For each of the functions in problem (1), compute [ f(2) dr. (c) Compute Li and R1 for each function in problem (1) and compare their values to the true value of the corresponding definite integral. What patterns do you observe? Hint: Think about the growth of these functions. Which functions are increasing on [0, 1] ? Which functions are decreasing on [0, 1] ? (d) Compute Mi and T, for each function in problem (1) and compare their values to the true value of the corresponding definite integral. What patterns do you observe? Hint: Think about the concavity of these functions. Which functions are concave up on [0, 1] ? Which functions are concave down on [0, 1]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


