Question: Please answer to all the questions Attemptt Keep the Highest / 2 6. 6: The Cost of Capital: Weighted Average Cost of Capital The firm's
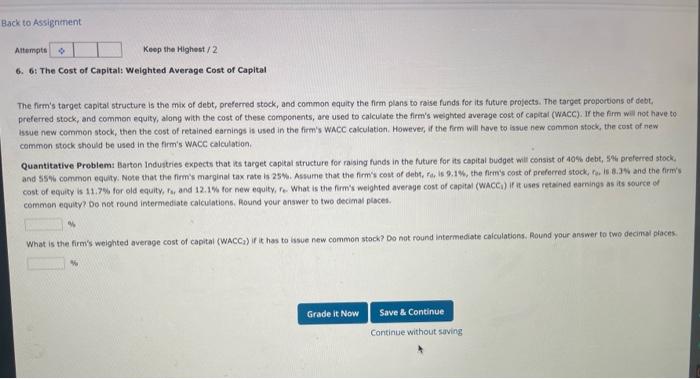
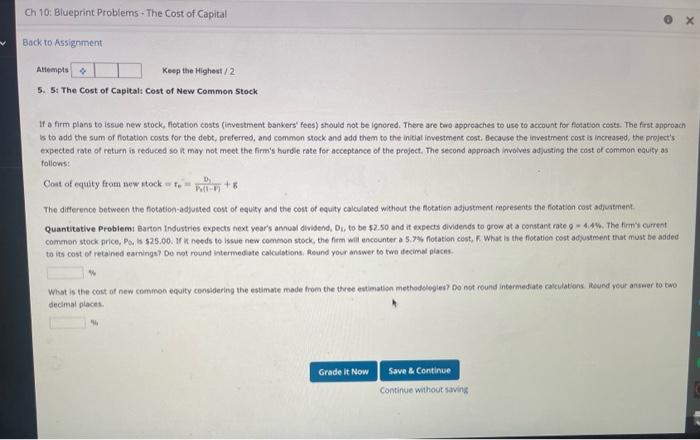
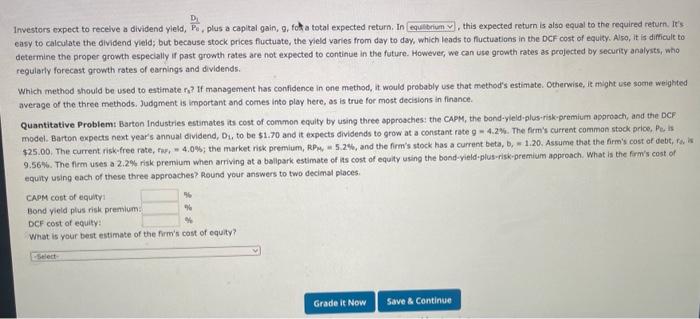
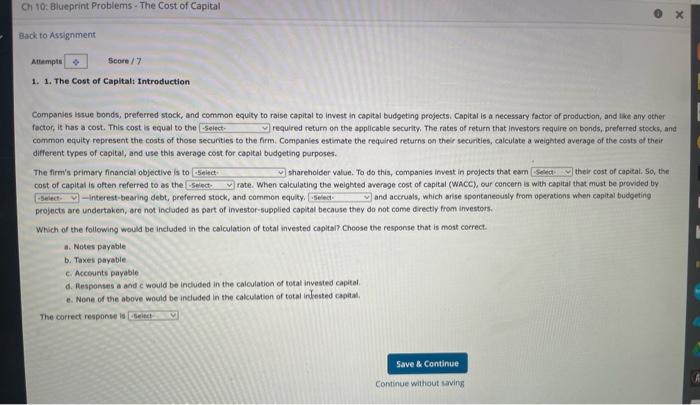
Attemptt Keep the Highest / 2 6. 6: The Cost of Capital: Weighted Average Cost of Capital The firm's target capital structure is the mix of debt, preferred stock, and common equity the firm plans to raise funds for its future projects. The target proportions of debt, preferred stock, and common equity, along with the cost of these components, are used to calculate the firm's welghted average cost of capital (Wacc). If the firm will not have to issue new common stock, then the cost of retained earnings is used in the firm's WACC calculation. However, if the firm will hove to issue hew cammen stock, the cost of new. common stock should be used in the firm's WACC calculation. Quantitative Problems Barton induitries expects that its target capital structure for raising funds in the future for its capital budget will consist of 40% debt, SNh areferred stock, and 557 common equity. Note that the firm's marginal tax rate is 25\%. Assume that the firm's cost of debr, fin, is 9.1%, the firm's cost of preferred stock, fo. is 8.a% and the firmis cost of equity is 11.7% for old equity, far and 12.1% for new equity, fe. What is the firm's weighted average cost of capital (Wacci) if it uses retaned eamings as its source of comman equityz Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. What is the firm's welghted average cost of capital (WACC) if it has to issue new common stock? Do not round intermediate calculations: Round your answer to two decimel piaces. If a firm plans to issiee new stock, fiotation costs (investment bankers' fees) should not be ignored. There are two approaches to use to account for fotation costs. The frist approach is to add the sum of fotation costs for the debt, preferred, and common steck and add them to the initiat investment cost, flecause the investment cost is increased, the project's expected rate of return is reduced so it may not meet the firm's burdie rate for acceptance of the project. The second approach inyolves asjusting the cost of conmon equity as folions: Cost of equity from new atock re=Fith2+1D1+5 The difference between the fotation-adjusted cost of equity and the cost of equity calculated without the fotatien adjustment represents the fotation cost adjutenent- Quantitative Probiemy Barton industries expects next year's annual divisend, Dy, to be 52.50 and it expects dividends to grow at a constant rate 9 = 4.44. The firmit current common stock price, Po, is $2.5.00. If it needs to issue new common stock, the firm will encounter a 5.7% fotation cost, F. What is the fotation cost adjustrent that must be added to its cost of retained eamings? De not round intermedate calculations, Reand your answer to twe decimal places. What is the cost of new common equity considering the estimate made from the three estimation methodelegles? Do not round intermedate catilations iteund your ansaer to two decimal pieces. Investors expect to receive a dividend yield, P0D1, plus a capital gain, q, fok a total expected return. In this expected return is also equal to the required return. It's easy to calculate the dividend yield; but because stock prices fuctuate, the yield varies from day to day, which leads to fluctuations in the DCF cost of equity. Aiso, it is difficult to determine the proper growth especially if past growth rates are not expected to continue in the future. However, we can use growth rates as prajected by security analysts, who regularly forecast growth rates of earnings and dividends: Which method should be used to estimate rs? If management has confidence in one method, it would probably use that method's estimate. Otherwise, it might use some weighted average of the three methods. Judgment is important and comes into play here, as is true for most decisions in finance. Quantitative Problem: Barton Industries estimates its cost of common equity by using three approachies: the CAPM, the bond-yleld-plus-risk-premium aporosch, and the DCF: model. Barton expects next year's annual dividend, Di, to be $1.70 and it expects dividends to grow at a constant rate 9=4.2%. The firm's current common stock price, Pe, is \$25.00. The current risk.free rate, tw;, =4.0s; the market risk premium, RP w. =5.2%, and the firm's stock has a current beta, b, =1.20. Assume that the firm's cost of debi, fow is 9.56%. The firm uses a 2.2%.risk premium when arriving at a balipark estimate of ats cost of equity using the bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach. What is the firm's cost of equity using each of these three approaches? Round your answers to two decimal places. CAPM cost of equityi Bond yield plus risk premium: DCF cost of equity? Winat is your best estimate of the firm's cost of equity? Companies issue bonds, peeferred stock, and common equity to raise capital to invest in capital budgeting projects, Capital is a necessary foctor of productian, and ike any other factor, it has a cost. This cost is equal to the required return on the applicable security. The rates of return that inwestors require on bonds, prefarred stocks, and comman equity represent the costs of those securities to the firm. Companies estimate the required returns ca their secuities, calculate a weighted average of the costs of their different types of capital, and use this average cost for capital budgeting purposes. The firm's primary financial objective is to shareholder value. To do this, companies invest in projects that eam their cost of capital. So, the cost of capital is often referred to as the rate. When calculating the weighted average cost of capital (Wacc), cur concern is with capital that must be provided by - interest-bearing debt, preferred stock, and common equity. and accruals, which arise spontanecusly from operations when eapital budgeting projects are undertaken, are not indaded as part of imvestor-supplied capital because they do not come drectiy from investors. Which of the following would be included in the caiculation of total invested capital? Choose the response that is most correct. a. Notes payable b. Taxes payable c. Accosints payable d. Responses a and c would be included in the calculation of total invested capital. e. None of the above would be included in the calculstion of total intested capital, The correct response is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


