Question: Please answer using python, thanks! Quicksort has an average case running time of n*log(n). This algorithm uses comparisons and is considered one of the fastest
Please answer using python, thanks!
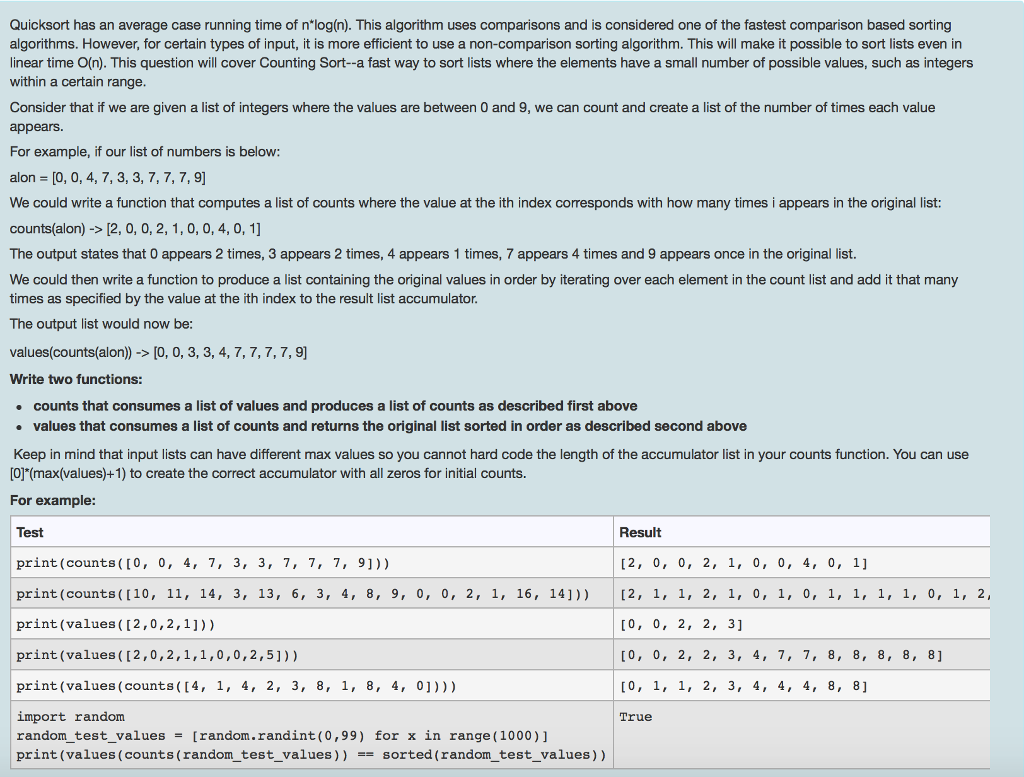
Quicksort has an average case running time of n*log(n). This algorithm uses comparisons and is considered one of the fastest comparison based sorting algorithms. However, for certain types of input, it is more efficient to use a non-comparison sorting algorithm. This will make it possible to sort lists even in linear time O(n). This question will cover Counting Sort-a fast way to sort lists where the elements have a small number of possible values, such as integers within a certain range. Consider that if we are given a list of integers where the values are between 0 and 9, we can count and create a list of the number of times each value appears. For example, if our list of numbers is below: alon = [0, 0, 4, 7, 3, 3, 7, 7, 7, 9] We could write a function that computes a list of counts where the value at the ith index corresponds with how many times i appears in the original list: counts(alon) -> [2, 0, 0, 2,1, 0, 0, 4, 0,1] The output states that 0 appears 2 times, 3 appears 2 times, 4 appears 1 times, 7 appears 4 times and 9 appears once in the original list. We could then write a function to produce a list containing the original values in order by iterating over each element in the count list and add it that many times as specified by the value at the ith index to the result list accumulator. The output list would now be: values(counts(alon)) -> [0, 0, 3, 3, 4, 7, 7, 7, 7, 9] Write two functions: counts that consumes a list of values and produces a list of counts as described first above values that consumes a list of counts and returns the original list sorted in order as described second above Keep in mind that input lists can have different max values so you cannot hard code the length of the accumulator list in your counts function. You can use [0]*(max(values)+1) to create the correct accumulator with all zeros for initial counts
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


