Question: Please answer using R code # load packages library(tibble) library(caret) library(rpart) # set seed set.seed (90058) = #define function to simulate data gen_nonlin_data function(sample_size 200)
Please answer using R code

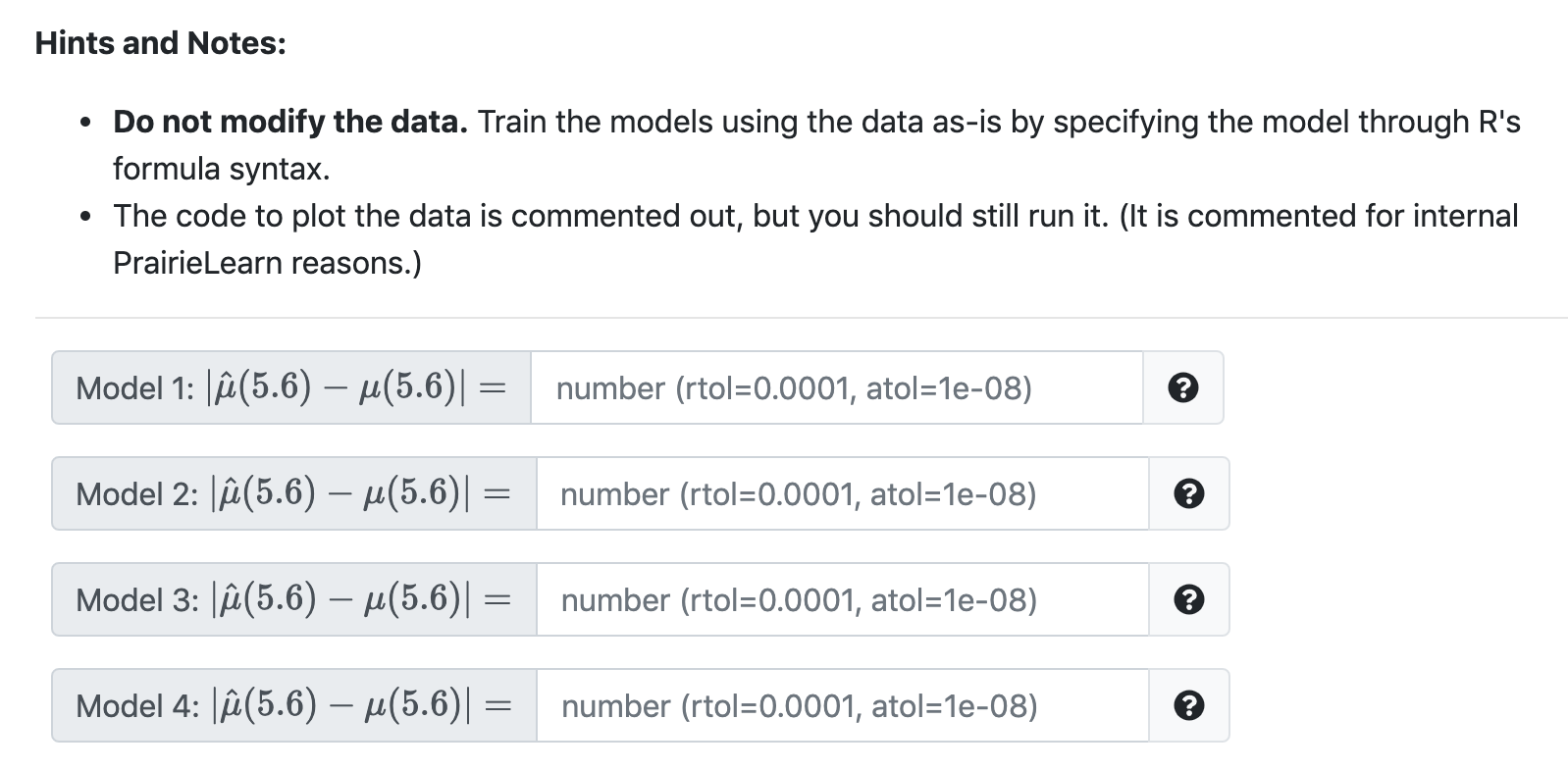
# load packages library("tibble") library("caret") library("rpart") # set seed set.seed (90058) = #define function to simulate data gen_nonlin_data function(sample_size 200) { x = runif(n. sample_size, min = 0, max = 10) mu = 0 + 3 * 2. ^ (x - 1) eps rnorman sample_size, mean = 0, sd = 100) y = mu + eps tibble(x, y) } # simulate (training) data sim_trn gen_nonlin_data() # check data (numerically) head (sim_trn) # check data (visually) # plot(sim_trn, pch 20, col # grid() "darkgrey") The code above simulates data from the data generating process defined in the function gen_nonlin_data and stores it in sim_trn. Specifically, the gen_nonlin_data function generates data according to the probability model Y = u(x) + where . . u(x) = Bo + B1 27-1 Bo = 0 B1 = 3 N(0, 1002) - U(0, 10) EN . Fit four models to the training data: Model 1: A linear model that assumes u(x) = Bo + B12 Model 2: A linear model that assumes u(x) = Bo + B1 22-1 Model 3: A KNN model with k = 10 using the only feature : Model 4: A decision tree model with default parameters using the only feature x With each, calculate (5.6) u(5.6)| where (5.6) is the estimate of the regression (mean) function at x = 5.6 for the model considered. u(5.6) is the true value of regression (mean) function for the (in this case known) data generating process Hints and Notes: Do not modify the data. Train the models using the data as-is by specifying the model through R's formula syntax. The code to plot the data is commented out, but you should still run it. (It is commented for internal Prairie Learn reasons.) Model 1: S(5.6) u(5.6)| = = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=1e-08) Model 2: (5.6) (5.6) = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=14-08) e Model 3: (5.6) 4(5.6)| = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=1e-08) Model 4: S(5.6) M(5.6)| = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=1e-08) # load packages library("tibble") library("caret") library("rpart") # set seed set.seed (90058) = #define function to simulate data gen_nonlin_data function(sample_size 200) { x = runif(n. sample_size, min = 0, max = 10) mu = 0 + 3 * 2. ^ (x - 1) eps rnorman sample_size, mean = 0, sd = 100) y = mu + eps tibble(x, y) } # simulate (training) data sim_trn gen_nonlin_data() # check data (numerically) head (sim_trn) # check data (visually) # plot(sim_trn, pch 20, col # grid() "darkgrey") The code above simulates data from the data generating process defined in the function gen_nonlin_data and stores it in sim_trn. Specifically, the gen_nonlin_data function generates data according to the probability model Y = u(x) + where . . u(x) = Bo + B1 27-1 Bo = 0 B1 = 3 N(0, 1002) - U(0, 10) EN . Fit four models to the training data: Model 1: A linear model that assumes u(x) = Bo + B12 Model 2: A linear model that assumes u(x) = Bo + B1 22-1 Model 3: A KNN model with k = 10 using the only feature : Model 4: A decision tree model with default parameters using the only feature x With each, calculate (5.6) u(5.6)| where (5.6) is the estimate of the regression (mean) function at x = 5.6 for the model considered. u(5.6) is the true value of regression (mean) function for the (in this case known) data generating process Hints and Notes: Do not modify the data. Train the models using the data as-is by specifying the model through R's formula syntax. The code to plot the data is commented out, but you should still run it. (It is commented for internal Prairie Learn reasons.) Model 1: S(5.6) u(5.6)| = = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=1e-08) Model 2: (5.6) (5.6) = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=14-08) e Model 3: (5.6) 4(5.6)| = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=1e-08) Model 4: S(5.6) M(5.6)| = number (rtol=0.0001, atol=1e-08)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


