Question: please answer will rate no work needed Madison Meats Inc. produces sausages in three production departments-Mixing, Casing and Curing, and Packaging. In the Mixing Department,
please answer will rate no work needed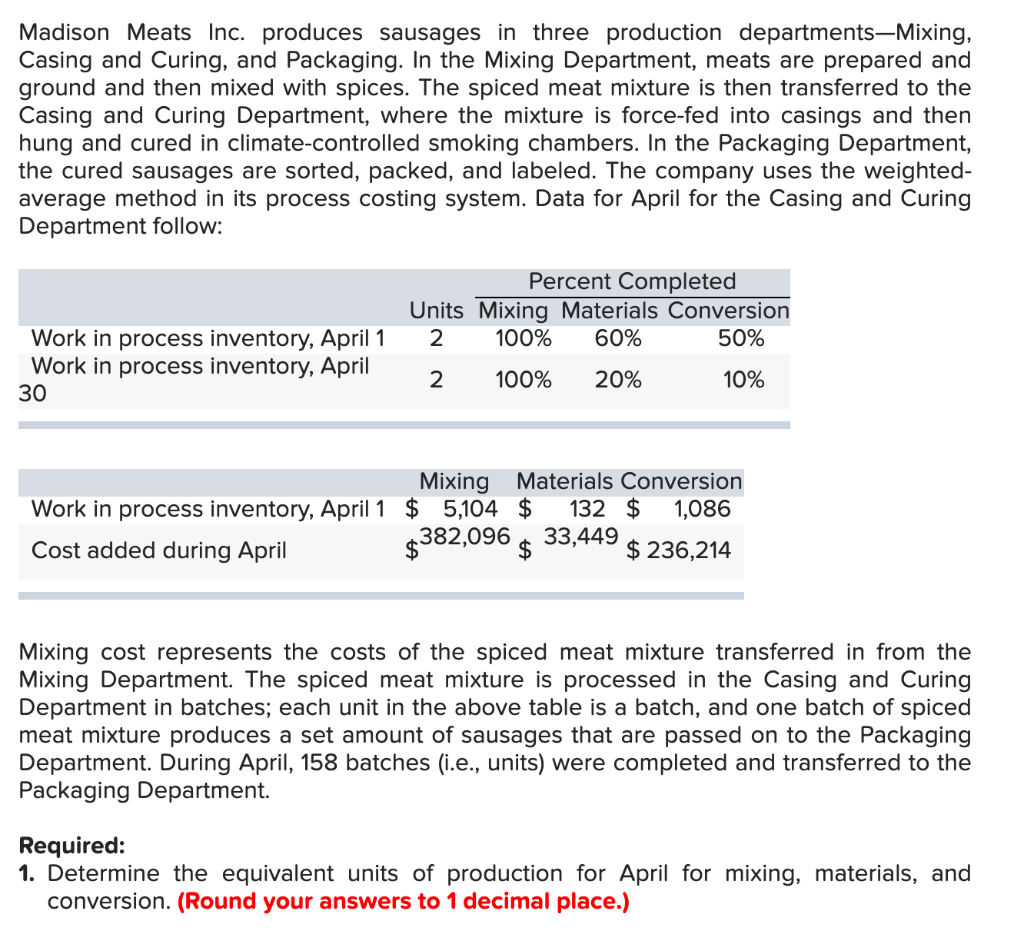
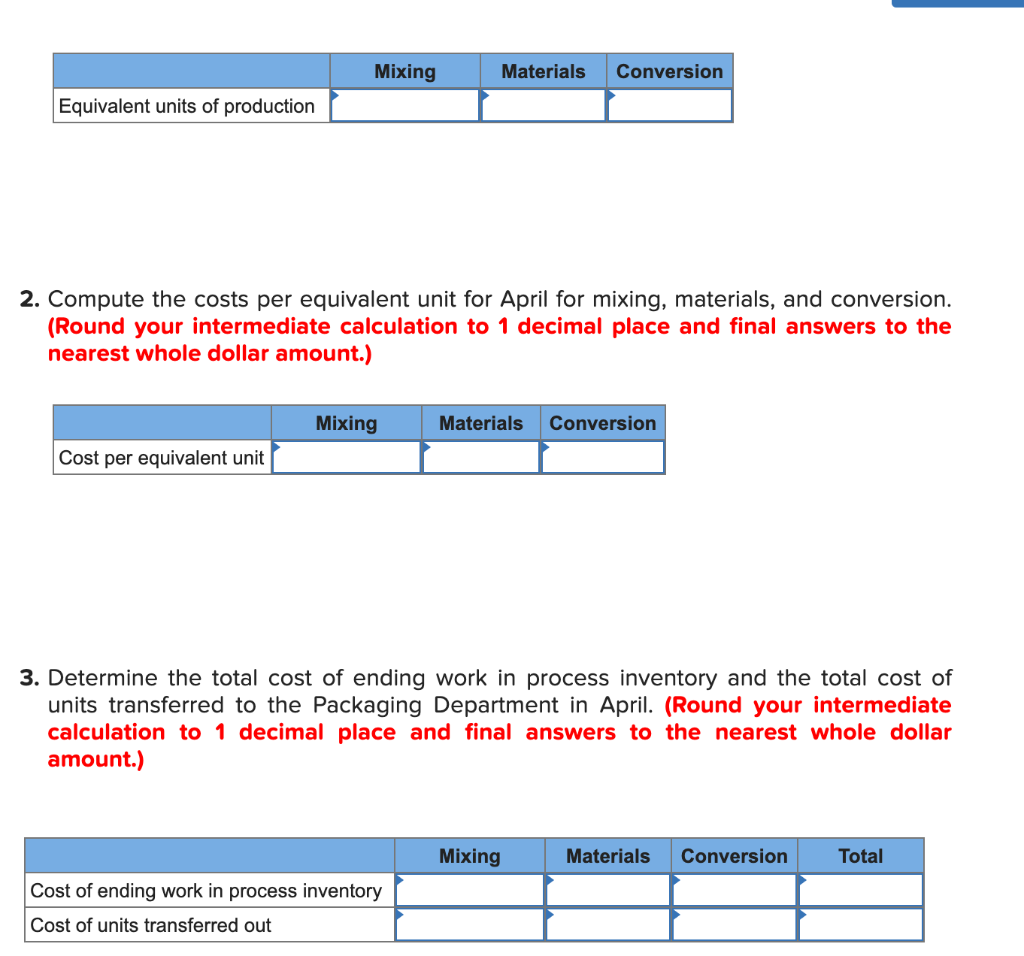
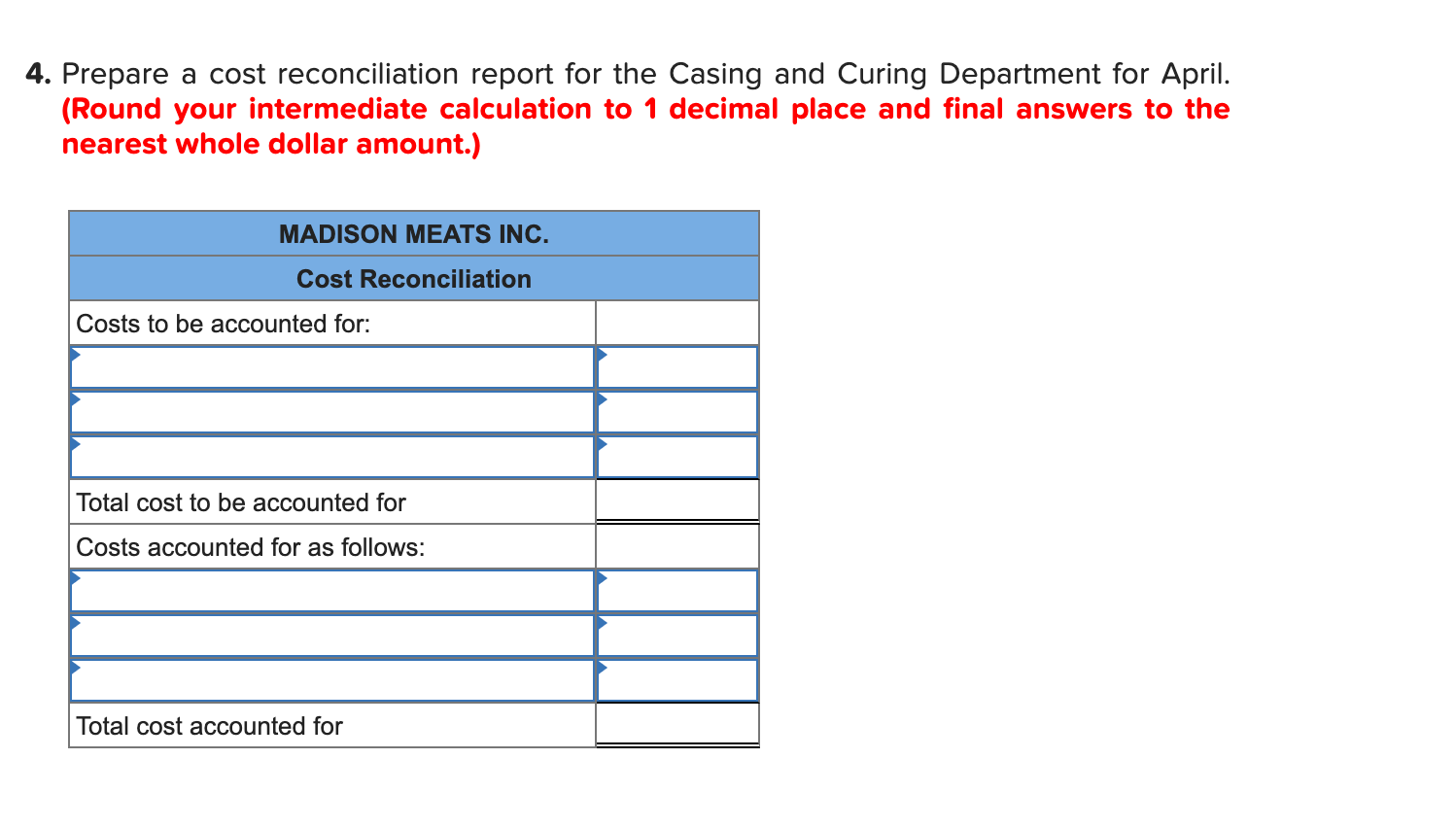
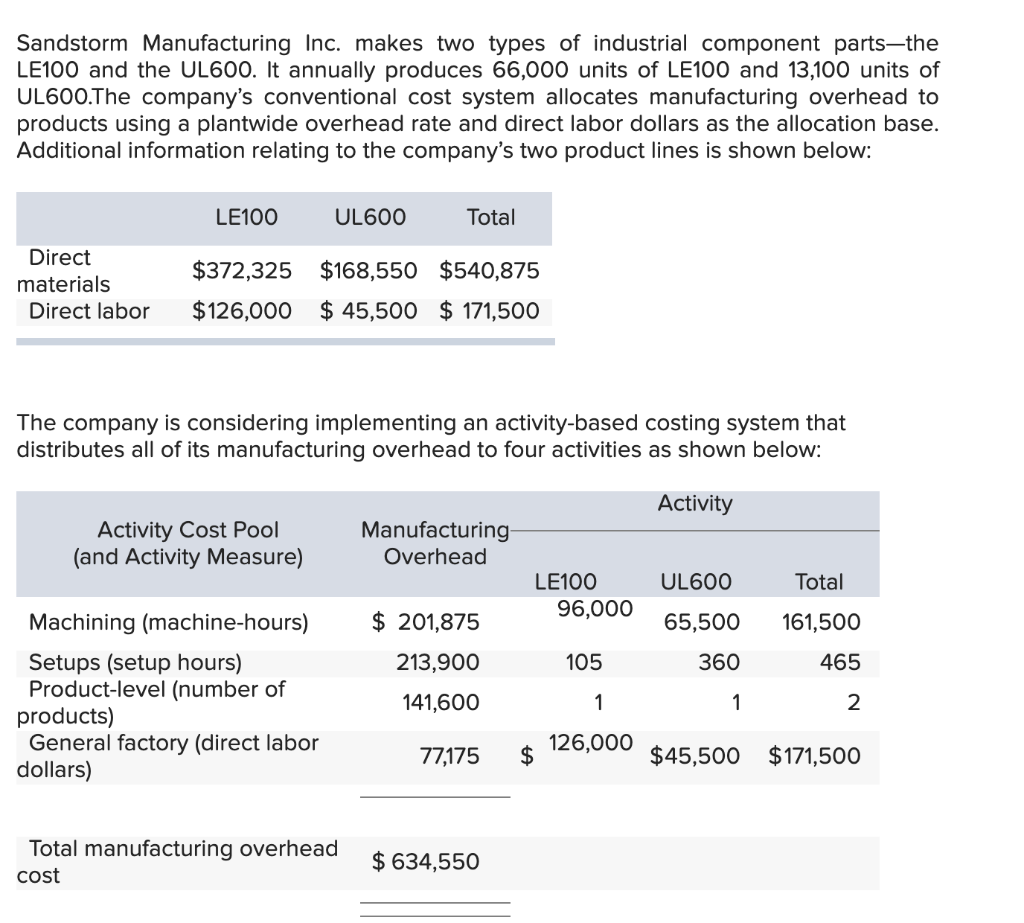
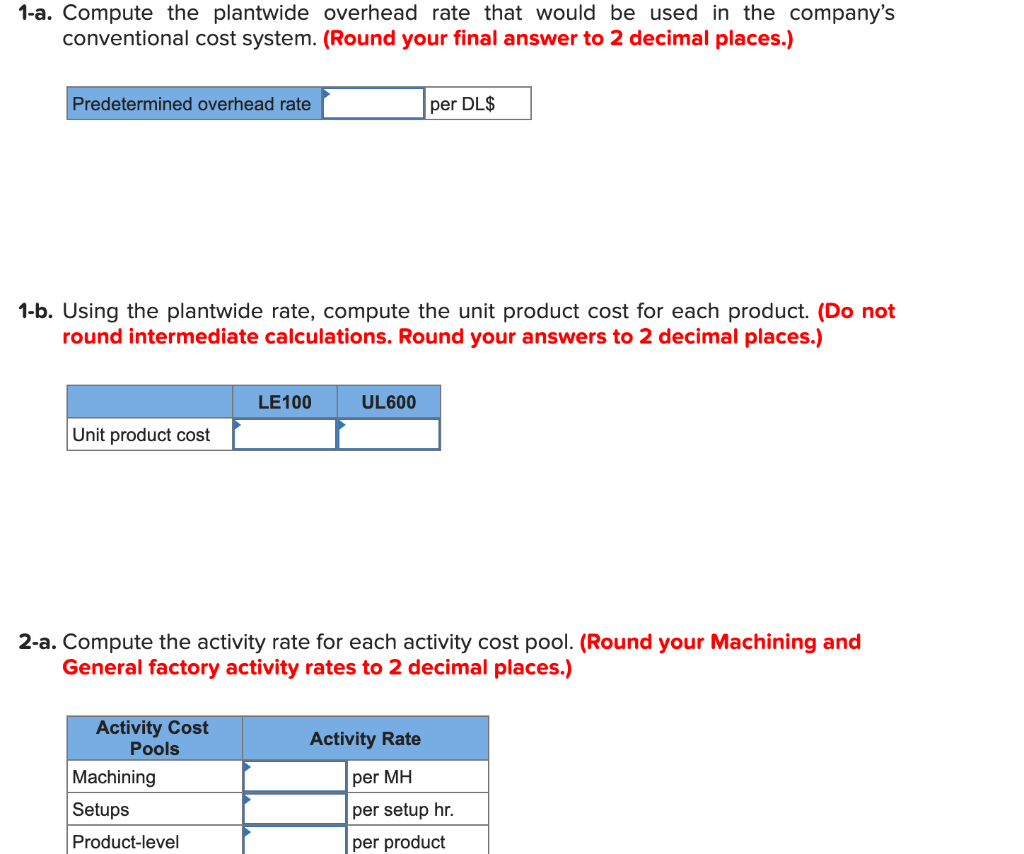
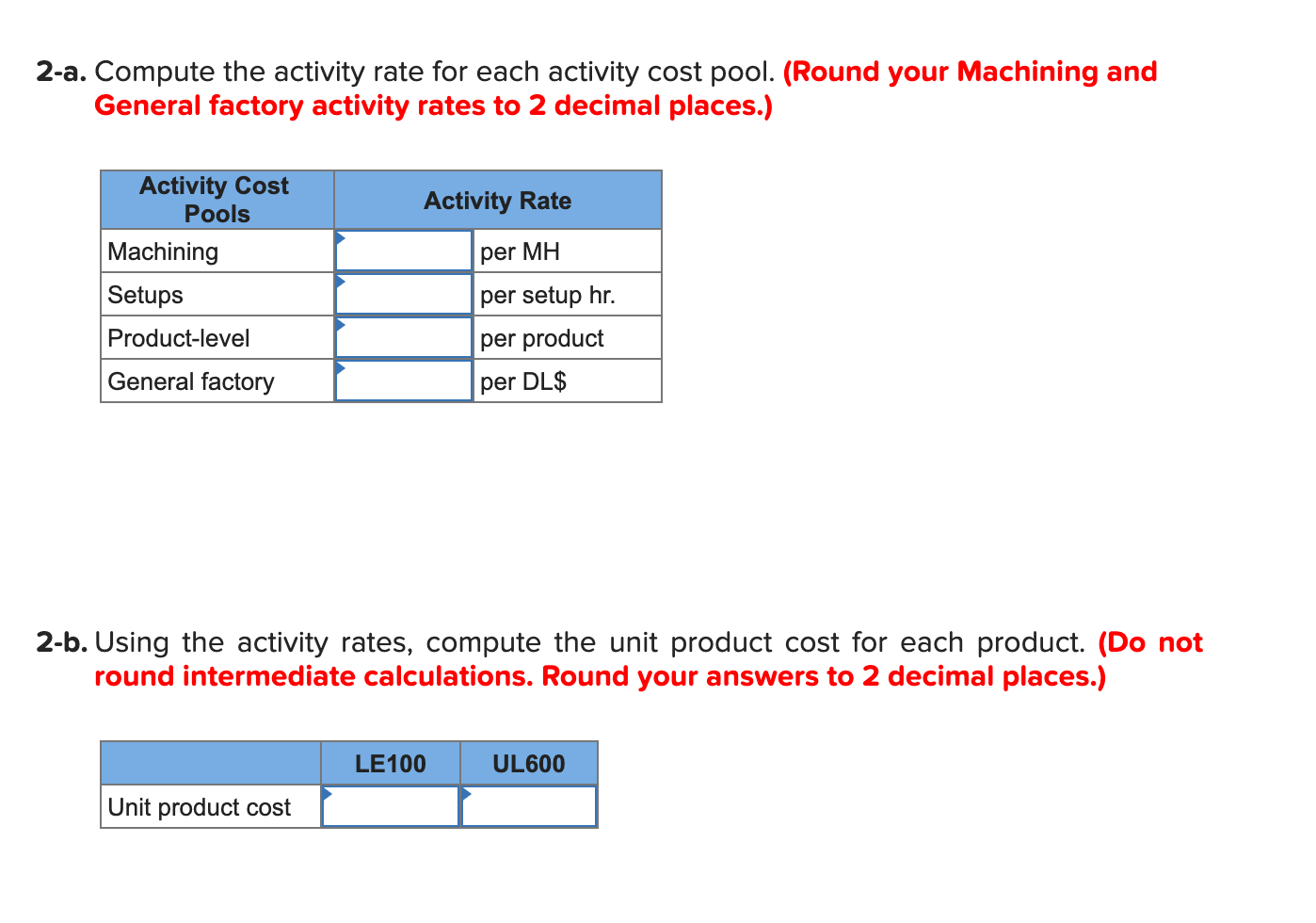
Madison Meats Inc. produces sausages in three production departments-Mixing, Casing and Curing, and Packaging. In the Mixing Department, meats are prepared and ground and then mixed with spices. The spiced meat mixture is then transferred to the Casing and Curing Department, where the mixture is force-fed into casings and then hung and cured in climate-controlled smoking chambers. In the Packaging Department, the cured sausages are sorted, packed, and labeled. The company uses the weighted- average method in its process costing system. Data for April for the Casing and Curing Department follow: Percent Completed Units Mixing Materials Conversion 2 100% 60% 50% Work in process inventory, April 1 Work in process inventory, April 30 2 100% 20% 10% Mixing Materials Conversion Work in process inventory, April 1 $ 5,104 $ 132 $ 1,086 382,096 33,449 Cost added during April $ $ $ 236,214 Mixing cost represents the costs of the spiced meat mixture transferred in from the Mixing Department. The spiced meat mixture is processed in the Casing and Curing Department in batches; each unit in the above table is a batch, and one batch of spiced meat mixture produces a set amount of sausages that are passed on to the Packaging Department. During April, 158 batches (i.e., units) were completed and transferred to the Packaging Department. Required: 1. Determine the equivalent units of production for April for mixing, materials, and conversion. (Round your answers to 1 decimal place.) Mixing Materials Conversion Equivalent units of production 2. Compute the costs per equivalent unit for April for mixing, materials, and conversion. (Round your intermediate calculation to 1 decimal place and final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Mixing Materials Conversion Cost per equivalent unit 3. Determine the total cost of ending work in process inventory and the total cost of units transferred to the Packaging Department in April. (Round your intermediate calculation to 1 decimal place and final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Mixing Materials Conversion Total Cost of ending work in process inventory Cost of units transferred out 4. Prepare a cost reconciliation report for the Casing and Curing Department for April. (Round your intermediate calculation to 1 decimal place and final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) MADISON MEATS INC. Cost Reconciliation Costs to be accounted for: Total cost to be accounted for Costs accounted for as follows: Total cost accounted for Sandstorm Manufacturing Inc. makes two types of industrial component partsthe LE100 and the UL600. It annually produces 66,000 units of LE100 and 13,100 units of UL600.The company's conventional cost system allocates manufacturing overhead to products using a plantwide overhead rate and direct labor dollars as the allocation base. Additional information relating to the company's two product lines is shown below: LE100 UL600 Total $372,325 $168,550 $540,875 Direct materials Direct labor $126,000 $ 45,500 $ 171,500 The company is considering implementing an activity-based costing system that distributes all of its manufacturing overhead to four activities as shown below: Activity Activity Cost Pool (and Activity Measure) Manufacturing Overhead UL600 Total LE100 96,000 65,500 $ 201,875 213,900 141,600 161,500 465 105 Machining (machine-hours) Setups (setup hours) Product-level (number of products) General factory (direct labor dollars) 360 1 1 2 126,000 77,175 $ $45,500 $171,500 Total manufacturing overhead cost $ 634,550 1-a. Compute the plantwide overhead rate that would be used in the company's conventional cost system. (Round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Predetermined overhead rate per DL$ 1-b. Using the plantwide rate, compute the unit product cost for each product. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) LE100 UL600 Unit product cost 2-a. Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool. (Round your Machining and General factory activity rates to 2 decimal places.) Activity Rate Activity Cost Pools Machining Setups Product-level per MH per setup hr. per product 2-a. Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool. (Round your Machining and General factory activity rates to 2 decimal places.) Activity Rate per MH Activity Cost Pools Machining Setups Product-level General factory per setup hr. per product per DL$ 2-b. Using the activity rates, compute the unit product cost for each product. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) LE100 UL600 Unit product cost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


