Question: please answer with explanation: Consider the spin-1/2 atom in a rotating-B-field discussed in class and presented on pages 3 and 4 of the lecture notes
please answer with explanation:
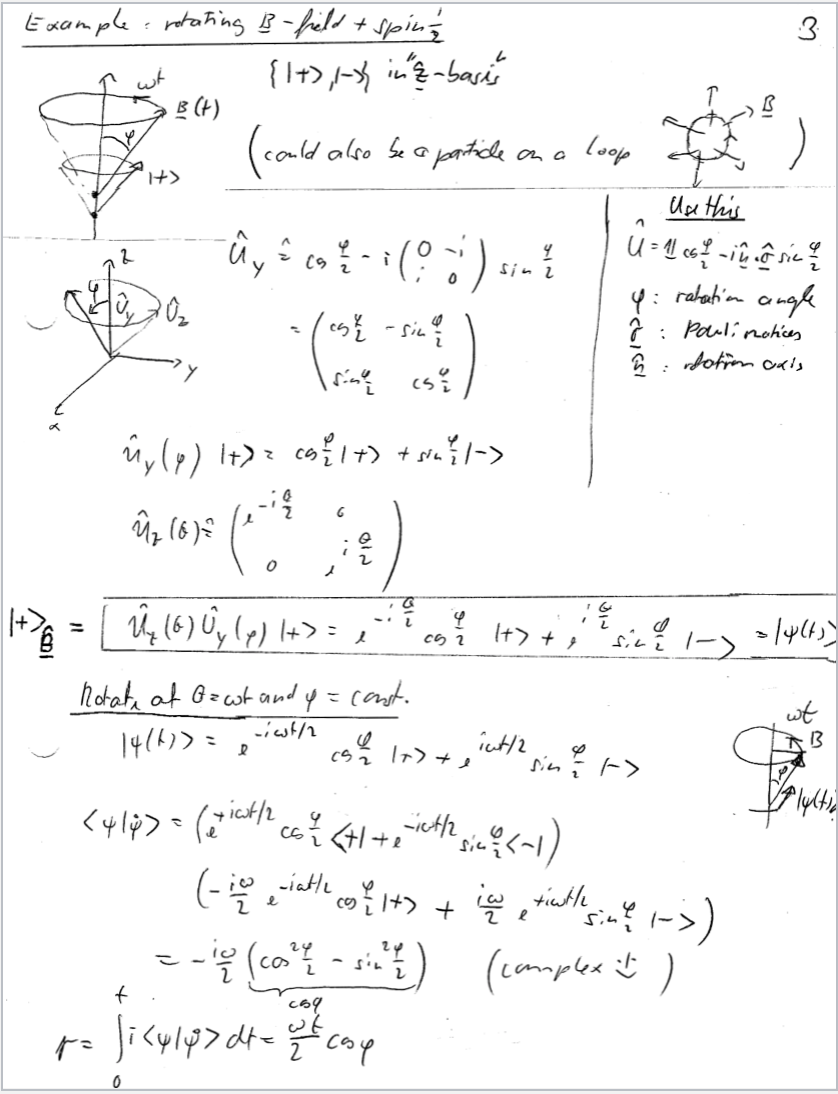
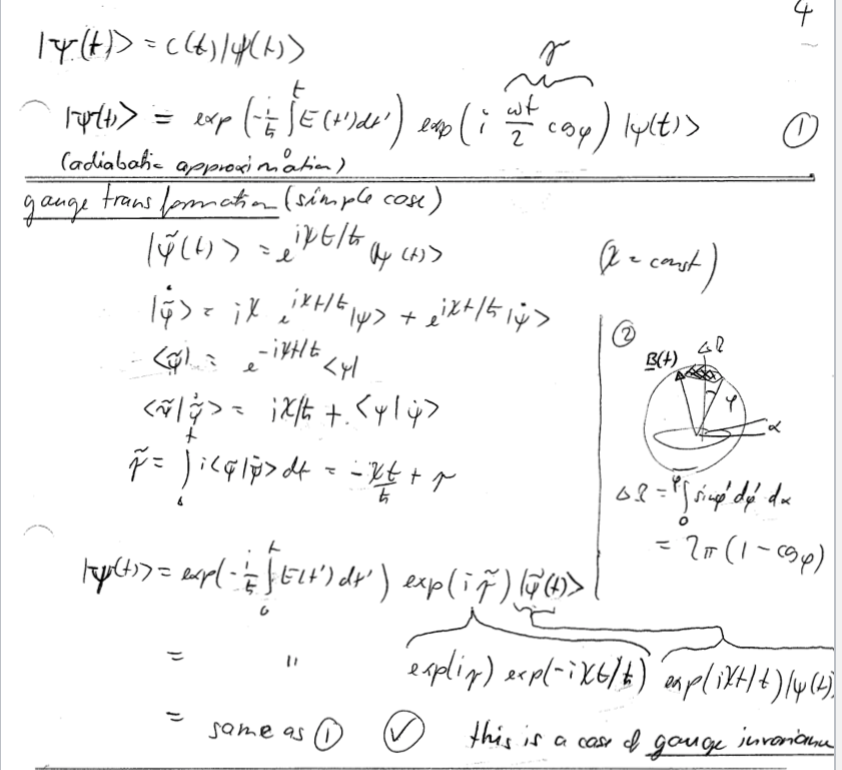
Consider the spin-1/2 atom in a rotating-B-field discussed in class and presented on pages 3 and 4 of the lecture notes from Feb. 9 (posted on Canvas). The field has a fixed magnitude B, a fixed angle o against the z-axis, and the projection into the xy-pane has an azimuthal angle 0 = wt from the x-axis (with fixed w). a) At time t = 0, the state is in the instantaneous spin-down eigenstate relative to B (which you may denote [-) , in the lecture note's notation). Find the instantaneous adiabatic eigen-state that connects with [-) , written in the (fixed) spin basis {|+), |-) } along z-direction. Use Dirac notation in your answer. To reduce work, you are encouraged to use the lecture notes for guidance for how to construct the adiabatic eigen-state by a sequence of two rotations. (Alternatively, you can find it by explicit solution of the instantaneous time-independent Schroedinger equation. This is a bit tedious; I am suggesting the rotation method). b) What are the dynamic and geometric phases of the final adiabatic state after a full rotation, wt = 27 ? (you may assume a g-factor of 2 and call the fixed field magnitude B). What is the phase angle of the final adiabatic solution of the full time-dependent Schroedinger equation relative to the initial state? (called a at the bottom of page 4 of the lecture notes). As was pointed out in class, and as is also explained in the notes, there is a difference between the uppercase I states, which are adiabatic solutions of the full time-dependent Schroedinger equation, and of the lowercase states, which are solutions of the instantaneous time-independent Schroedinger equation.Example : rotating B- field + spins 3. (1+ ) 1- in 2- basis B (+ ) ( could also be a particle on a loop use this 4 : rotation angle 7 : Paul: notices 8 : rootion cals sink ~IS 4 notate at Ozwot and y = cont. wit 14(4)) = -it/2 I B " sin - 1-> = exp ( = JE( + d' ) emp ( i z cap ) lylt's O ( adiabatic approximation ) grange transformation ( simple case ) (2 - const ) 2 B (A) 40 (4/ 4> = 1x / t + = 21 (1 - (9p) typhton = expl - = ] ELt 'S dy ) exp ( ing ) 19 ()> explin ) expl- ix6 / # ) explixtli ) ly ( 4 ) = same as O (V this is a case of gauge invorianul
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


