Question: Please, as soon as possible. Charge dilution has been found to be an effective method to reduce the nitric oxide emission. Dilution may be achieved

Please, as soon as possible.
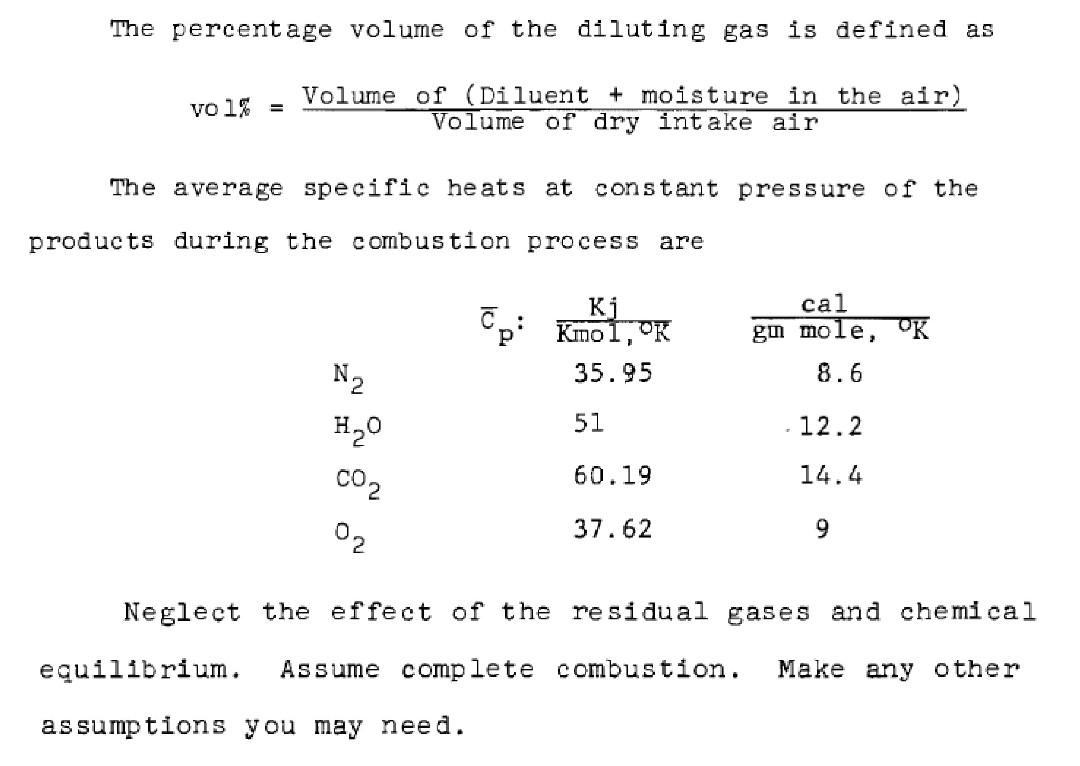
Charge dilution has been found to be an effective method to reduce the nitric oxide emission. Dilution may be achieved by exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), addition of water vapor, or excess air. You are required to compare between the effectiveness of each of the above three methods on increasing the heat capacity of the combustion products per kg of fuel. Assume the fuel 1s 07.3H13.2, the original combustible mixture (before dilution) is stoichiometric, the percentage volume of the diluting gas in each of the above three cases is 20%, the ambient air temperature is 26.67C (B0F) and its relative humidity is 70%. The percentage volume of the diluting gas is defined as vo 1% = Volume of (Diluent + moisture in the air) Volume of dry intake air The average specific heats at constant pressure of the products during the combustion process are Ki Kmo 1, "K 35.95 cal gu mole, OK 8.6 N2 HO 51 12.2 60.19 14.4 CO2 02 37.62 9 Neglect the effect of the residual gases and chemical equilibrium. Assume complete combustion. Make any other assumptions you may need. Charge dilution has been found to be an effective method to reduce the nitric oxide emission. Dilution may be achieved by exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), addition of water vapor, or excess air. You are required to compare between the effectiveness of each of the above three methods on increasing the heat capacity of the combustion products per kg of fuel. Assume the fuel 1s 07.3H13.2, the original combustible mixture (before dilution) is stoichiometric, the percentage volume of the diluting gas in each of the above three cases is 20%, the ambient air temperature is 26.67C (B0F) and its relative humidity is 70%. The percentage volume of the diluting gas is defined as vo 1% = Volume of (Diluent + moisture in the air) Volume of dry intake air The average specific heats at constant pressure of the products during the combustion process are Ki Kmo 1, "K 35.95 cal gu mole, OK 8.6 N2 HO 51 12.2 60.19 14.4 CO2 02 37.62 9 Neglect the effect of the residual gases and chemical equilibrium. Assume complete combustion. Make any other assumptions you may need
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


